Air is an invisible yet essential mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth and supports life. In this chapter, Class 6 Science Chapter Air Around Us for Oxford, we learn about the composition of air, the presence of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and dust particles.

The chapter also explains how air supports burning, respiration, and plant growth, along with its role in weather and climate. These Oxford solutions for Class 6 Science provide clear explanations, solved exercises, and activities to help students understand concepts like air in soil, air pollution, and the importance of keeping our air clean.
Class 6 Science Chapter Air Around Us for Oxford Solution Textbook Answers
Objective type questions.
A. Match the following.
Column A Column B
1. Plants a. moist skin
2. Cockroach b. body surface
3. Earthworm c. stomata
4. Fish d. lungs
5. Dolphin e. spiracles
6. Hydrilla f. gills
Ans:
Column A Column B
1. Plants c. stomata
2. Cockroach e. spiracles
3. Earthworm b. body surface
4. Fish f. gills
5. Dolphin d. lungs
6. Hydrilla a. moist skin
B. Choose the correct option
- Which of the following gases is present in air in the highest percentage?
a. Oxygen
b. Carbon dioxide
c. Noble gases
d. Nitrogen ✅
Reason: Nitrogen makes up about 78% of Earth’s atmosphere. - Which of the following do frogs use for breathing in water?
a. Lungs
b. Moist skin ✅
c. Gills
d. Stomata
Reason: Frogs breathe through their moist skin when they are in water. - Which of the following animals have a pair of lungs with air sacs?
a. Birds ✅
b. Fish
c. Humans
d. Frogs
Reason: Birds have lungs connected to air sacs that help them with efficient breathing during flight. - Which of the following swim through water with part of their snout above the water surface to breathe through nostrils?
a. Amphibians
b. Dolphins
c. Alligators ✅
d. Fish
Reason: Alligators breathe through nostrils while keeping most of their body submerged. - Which of the following does not lead to air pollution?
a. Burning of fuels
c. Smoke from vehicles
b. Planting trees ✅
d. Harmful gases from industries
Reason: Planting trees improves air quality instead of polluting it. - Which of the following practices can reduce air pollution?
a. Recycling plastics
b. Planting more trees
c. Regular checking of vehicles for the emission of harmful gases
d. All of these ✅
Reason: All these measures help reduce air pollution. - Which of the following are present in air?
a. Water vapour
b. Smoke
c. Dust
d. All of these ✅
Reason: Air contains water vapour naturally, and may also contain dust and smoke particles. - Air pollution does not lead to
a. lung cancer
b. asthma
c. good health ✅
d. Difficulty in breathing
Reason: Air pollution causes many health problems, not good health. - Which of the following do not breathe through lungs?
a. Earthworm ✅
b. Mammals
c. Dolphins
d. Whales
Reason: Earthworms breathe through their moist skin, not lungs. - Which of the following processes produces carbon dioxide?
a. Photosynthesis
b. Burning
c. Breathing
d. Both (b) and (c) ✅
Reason: Burning and breathing both release carbon dioxide.
II. Very short answer type questions.
A. Give one word for the following.
- A thick blanket of air surrounding the Earth’s surface – Atmosphere
- Process by which plants use carbon dioxide present in the air to make their own food – Photosynthesis
- Tiny pores on the underside of a leaf – Stomata
- Tiny holes on the body of insects for respiration – Spiracles
- The addition of substances in the environment in quantities that are harmful to living beings – Pollution
III. Short answer type questions.
1. Write the composition of air.
Air is a mixture of gases. It contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases such as carbon dioxide, argon, water vapour, and traces of noble gases.
2. How do wet clothes dry?
Wet clothes dry because water present in them evaporates into water vapour due to heat from sunlight or air movement. The process of evaporation is faster in warm, dry, and windy conditions.
3. What are stomata? Discuss their function.
Stomata are tiny pores present on the surface of leaves. They are surrounded by guard cells that open and close the pores.
Functions:
- Allow exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) during respiration and photosynthesis.
- Help in the loss of water vapour during transpiration.
4. Why do earthworms come out on the surface during rainy season?
Earthworms breathe through their moist skin. During heavy rains, the soil gets filled with water and air spaces are reduced. To avoid suffocation, they come to the surface to get enough oxygen.
5. How is the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide maintained in nature?
The balance is maintained through photosynthesis and respiration.
- In photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
- In respiration, animals and humans take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
This continuous exchange keeps the proportion of these gases balanced in the atmosphere.
IV. Long Answer Type Questions
1. Describe an activity to demonstrate the following:
a. Presence of air in an empty bottle.
b. Presence of oxygen in air.
c. Presence of air in soil.
Ans:
a. Presence of Air in an Empty Bottle
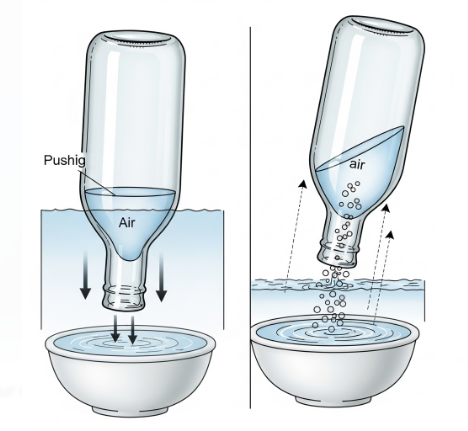
- Aim: To show that an “empty” bottle contains air.
- Materials Required: A glass tumbler, water, an empty glass bottle.
- Procedure:
- Take the empty bottle and hold it upside down.
- Dip the mouth of the bottle straight into a container of water without tilting.
- Observe what happens.
- Observation: The water does not enter the bottle because air inside the bottle prevents it from doing so. When you tilt the bottle, bubbles escape and water enters.
- Conclusion: An empty bottle is not truly empty — it contains air that occupies space.
b. Presence of Oxygen in Air
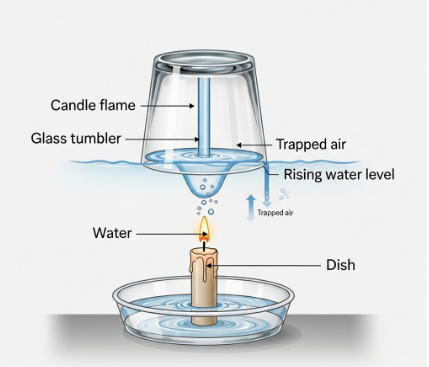
- Aim: To show that oxygen is present in air and is used up during burning.
- Materials Required: A candle, a shallow dish, water, a glass jar, matchbox.
- Procedure:
- Fix a candle in the middle of a shallow dish and fill the dish with some water.
- Light the candle.
- Cover the burning candle with an inverted glass jar.
- Observe the flame and the water level inside the jar.
- Observation: The candle burns for a short time and then goes out. The water level rises inside the jar after the flame goes out.
- Conclusion: Oxygen in the air inside the jar is used for burning. When it is used up, the flame goes out and the water rises to occupy the space left by the used oxygen.
c. Presence of Air in Soil
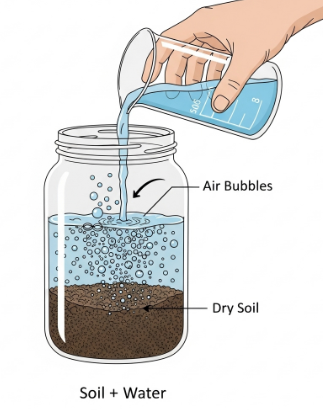
- Aim: To show that soil contains air.
- Materials Required: A beaker, dry soil, water, stirring rod.
- Procedure:
- Take some dry soil in a beaker.
- Pour water slowly into the beaker containing soil.
- Stir lightly and observe bubbles coming out.
- Observation: Bubbles of air escape from the soil when water is poured in.
- Conclusion: The spaces between soil particles contain air.
2. Discuss the mechanisms for respiration in insects, earthworm, aquatic animals, and birds.
- Insects: They breathe through tiny holes on their body surface called spiracles. Spiracles connect to a network of tubes called tracheae which carry oxygen directly to body cells.
- Earthworm: They breathe through their moist skin. Oxygen from the air dissolves in the moisture on their skin and diffuses into their bloodstream.
- Aquatic Animals: Many aquatic animals, like fish, have gills. Gills extract dissolved oxygen from water and expel carbon dioxide.
- Birds: Birds have lungs and also air sacs. Air sacs store extra air and provide continuous oxygen supply even when exhaling, enabling them to fly efficiently.
3. Discuss the causes, effects, and measures to reduce air pollution.
- Causes of Air Pollution:
- Emissions from vehicles and factories.
- Burning of fossil fuels.
- Agricultural activities like stubble burning.
- Release of harmful gases from industries.
- Effects of Air Pollution:
- Respiratory problems like asthma and bronchitis.
- Global warming due to greenhouse gases.
- Acid rain damaging soil, water, and buildings.
- Harm to animals and plants.
- Measures to Reduce Air Pollution:
- Use public transport, cycle, or walk instead of private vehicles.
- Adopt renewable sources of energy like solar and wind.
- Plant more trees to absorb carbon dioxide.
- Enforce strict emission norms for industries and vehicles.
Class 10
Class 9
Class 8
Class 7
Class 6
Class 12
Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
