NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials introduces the concept of zeroes of a polynomial through graphical representation. This exercise helps students understand how the graph of a polynomial function intersects the x-axis and how these intersection points relate to the zeroes (or roots) of the polynomial.
The number of zeroes of a polynomial is determined by counting the points where its graph cuts or touches the x-axis. For example:
- If a graph cuts the x-axis at two points, the polynomial has two zeroes.
- If it touches the x-axis at one point, it has one zero.
- If it doesn’t touch or cut the x-axis, it has no real zeroes.
This graphical approach builds a visual understanding of polynomials and sets the foundation for algebraic methods that follow in later exercises.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1
Question 1:
The graphs of y = p(x) are given below for some polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x) in each case.
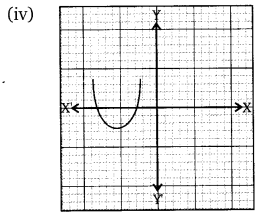
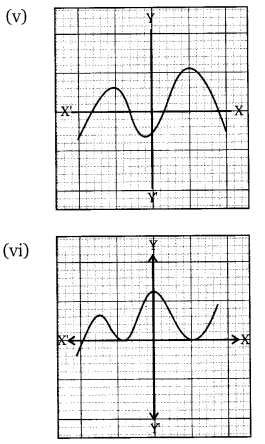
Solution: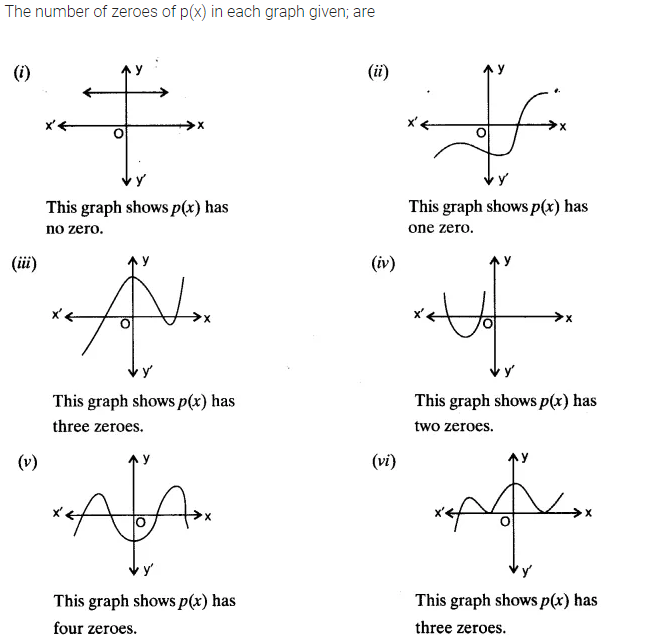
New Syllabus – NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Q1. The graphs of y = p(x) are given. Find the number of zeroes in each case.
👉 (In the NCERT textbook or your PDF, 6 different graphs are shown labeled (i) to (vi). For each graph, count how many times the curve cuts or touches the x-axis.)
Graph (i):
- The graph does not intersect or touch the x-axis.
- Number of zeroes = 0
Graph (ii):
- The graph touches the x-axis at one point (does not cross).
- Number of zeroes = 1
Graph (iii):
- The graph intersects the x-axis at two distinct points.
- Number of zeroes = 2
Graph (iv):
- The graph cuts the x-axis at three distinct points.
- Number of zeroes = 3
Graph (v):
- The graph intersects the x-axis at four points.
- Number of zeroes = 4
Graph (vi):
- The graph touches the x-axis at one point (tangent).
- Number of zeroes = 1
Summary Table (Answer Key):
| Graph | Number of Zeroes |
|---|---|
| (i) | 0 |
| (ii) | 1 |
| (iii) | 2 |
| (iv) | 3 |
| (v) | 4 |
| (vi) | 1 |
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
NEET BIOLOGY
- Evolution
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Human Health and Disease
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
In conclusion, NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials helps students understand the graphical meaning of zeroes of a polynomial. By observing how the graph intersects the x-axis, students learn how to determine the number of zeroes a polynomial has. This visual approach strengthens their conceptual understanding and prepares them for solving polynomials algebraically in later exercises.
