Preparing for the CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2024-25? This page provides the official CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper for the 2023–24 session, along with the marking scheme.

Designed as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern, this sample paper helps students understand the type of questions to expect and how to manage time effectively in the exam. Solve the paper, review the solutions, and boost your confidence for the board exam!
CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2024-25 Step -by-Step Answers
1.Identify ‘p’, ‘q’ and ‘r’ in the following balanced reaction
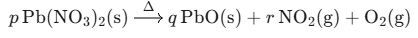
A. 2,2,4
B. 2,4,2
C. 2,4,4
D. 4,2,2
Ans: The balanced equation is:
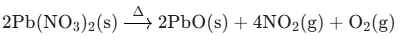
2.Match column I with column II and select the correct option using the given
codes.
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| a. A metal that forms amphoteric oxides | (iii) Al |
| b. A metal which melts when kept on our palm | (i) Ga |
| c. A metal that reacts with nitric acid | (iv) Mn |
| d. A metal which cannot displace hydrogen from acids | (ii) Au |
A. a – (ii), b – (i), c – (iii), d – (iv)
B. a – (iii), b – (i), c – (iv), d – (ii)
C. a – (iv), b – (ii), c – (iii), d – (i)
D. a – (iii), b – (ii), c – (i), d – (iv)
Ans: a. A metal that forms amphoteric oxides – (iii) Al
b. A metal which melts when kept on our palm – (i) Ga
c. A metal that reacts with nitric acid – (iv) Mn
d. A metal which cannot displace hydrogen from acids – (ii) Au
So, the correct option is:
B. a – (iii), b – (i), c – (iv), d – (ii)
4.An aqueous solution ‘A’ turns the phenolphthalein solution pink. On addition of
an aqueous solution ‘B’ to ‘A’, the pink colour disappears. Which of the following
statement is true for the solutions ‘A’ and ‘B’.
A. A is strongly basic and B is a weak base.
B. A is strongly acidic and B is a weak acid.
C. A has a pH greater than 7 and B has a pH less than 7.
D. A has a pH less than 7 and B has a pH greater than 7.
Ans: Phenolphthalein turns pink in basic solutions and remains colorless in acidic solutions.
- Solution A turns phenolphthalein pink ⇒ A is basic
- Adding solution B to A makes the pink color disappear ⇒ B is acidic, it neutralizes the base.
Correct answer: C. A has a pH greater than 7 and B has a pH less than 7.
5 .When 50g of lead powder is added to 300 ml of blue copper sulphate
solution, after a few hours, the solution becomes colourless. This is an
example of
A. Combination reaction
B. Decomposition reaction
C. Displacement reaction
D. Double displacement reaction
Ans: When lead (Pb) is added to blue copper sulphate (CuSO₄) solution, a chemical reaction takes place:
Pb (s) + CuSO₄ (aq) → PbSO₄ (aq) + Cu (s)
- Lead displaces copper from its salt solution because lead is more reactive than copper.
- The blue color of copper sulphate fades as copper is replaced by colorless lead sulphate.
- Copper metal is deposited.
Correct answer: C. Displacement reaction
6. The electronic configuration of three elements X, Y and Z are X- 2, 8, 7; Y- 2,
8, 2; and Z – 2, 8
A. Y and Z are metals
B. Y and X are non-metals
C. X is a non -metal and Y is a metal
D. Y is a non-metal and Z is a metal
Ans: Let’s analyze the electronic configurations:
- X – 2, 8, 7
→ 17 electrons → Atomic number 17 → Chlorine (Cl)
→ Needs 1 electron to complete octet → Non-metal - Y – 2, 8, 2
→ 12 electrons → Atomic number 12 → Magnesium (Mg)
→ Has 2 valence electrons → Metal - Z – 2, 8
→ 10 electrons → Atomic number 10 → Neon (Ne)
→ Full outer shell → Noble gas (non-metal)
Correct answer: C. X is a non-metal and Y is a metal
7 .Which of the following is an endothermic reaction?
A. Burning of candle.
B. Cooking of food.
C. Decomposition of Vegetable matter.
D. Reaction of Sodium with air
Ans: A. Burning of candle – This releases heat → Exothermic
B. Cooking of food – Requires heat to be absorbed → Endothermic
C. Decomposition of vegetable matter (like composting) – Usually gives off heat → Exothermic
D. Reaction of sodium with air – Releases heat → Exothermic
Correct answer: B. Cooking of food
Because it absorbs heat, making it an endothermic reaction.
8. During cellular oxidation of Glucose, ATP is produced along with formation of
other products in this reaction. Which of the following events is associated with
production of maximum ATP molecules per molecule of Glucose during this
process? Synthesis of
A. ethanol in yeast
B. lactic acid in muscle cells
C. carbon dioxide in yeast cells
D. carbon dioxide in human cells
Ans: Ethanol in yeast
- This is anaerobic respiration (fermentation).
- Produces only 2 ATP per glucose. ❌
B. Lactic acid in muscle cells
- Also anaerobic respiration, happens in humans during heavy exercise.
- Produces only 2 ATP per glucose. ❌
C. Carbon dioxide in yeast cells
- Again, refers to anaerobic fermentation, producing ethanol and CO₂.
- Yields 2 ATP. ❌
D. Carbon dioxide in human cells
- Refers to aerobic respiration, which occurs in mitochondria.
- Complete oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and H₂O produces ~36–38 ATP. ✅
Correct answer: D. Carbon dioxide in human cells
Because it represents aerobic respiration, which produces the maximum ATP per molecule of glucose.
9. During which of the following stages of the circulation of blood in a normal
human being, the oxygenated blood is pumped to all parts of the body?
A. contraction of the left atrium
B. contraction of left ventricle
C. relaxation of the right atrium
D. relaxation of the right ventricle
Ans:
- Left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium.
- When the left ventricle contracts, it pumps the oxygen-rich blood into the aorta, which then distributes it to all parts of the body.
- This is the main pumping action for systemic circulation.
Other options explained:
- A. contraction of the left atrium: pushes blood into the left ventricle, not to the whole body.
- C. relaxation of the right atrium: allows it to receive deoxygenated blood, no pumping involved.
- D. relaxation of the right ventricle: allows it to fill with blood, not related to oxygenated blood circulation.
So, only option B involves the pumping of oxygenated blood to the body.
10. Which of the following adaptations in herbivores helps in digestions of
cellulose?
A. Longer large intestine
B. Smaller large intestine
C. Smaller small intestine
D. Longer small intestine
Ans: Herbivores consume a plant-based diet rich in cellulose, which is difficult to digest. To help break down cellulose:
- They have a longer small intestine, which provides more time and surface area for digestion and absorption.
- Some herbivores (like cows) also have special bacteria in their digestive tract that help break down cellulose.
Other options:
- A. Longer large intestine – Helpful in water absorption, not cellulose digestion specifically.
- B. Smaller large intestine – Would reduce digestion efficiency. ❌
- C. Smaller small intestine – Less time for digestion. ❌
Therefore, a longer small intestine is the key adaptation in herbivores for digesting cellulose.
11 .There was a cerebellar dysfunction in a patient. Which of the following activities
will get disturbed in this patient as a result of this?
A. Salivation
B. Hunger control
C. Posture and balance
D. Regulation of blood pressure
Ans: The cerebellum is the part of the brain that primarily controls:
- Posture
- Balance
- Coordination of voluntary movements
- Motor learning
So, cerebellar dysfunction leads to issues like:
- Loss of balance
- Poor coordination
- Difficulty in walking or standing
Other options:
- A. Salivation – Controlled by autonomic nervous system, not cerebellum. ❌
- B. Hunger control – Regulated by the hypothalamus, not cerebellum. ❌
- D. Regulation of blood pressure – Handled by medulla oblongata and autonomic system. ❌
Cerebellum = balance and posture, so option C is correct.
12. In snails individuals can begin life as male and depending on environmental
conditions they can become female as they grow. This is because
A. male snails have dominant genetic makeup.
B. female snails have dominant genetic makeup.
C. expression of sex chromosomes can change in a snail’s life time.
D. sex is not genetically determined in snails.
Ans: In snails and some other organisms:
- Sex is not always fixed by genetics at the time of birth.
- Instead, it can be influenced by environmental conditions, such as temperature, population density, or availability of resources.
- This phenomenon is called environmental sex determination or sequential hermaphroditism.
- For example, a snail may start life as a male and later become female as it grows.
Why other options are incorrect:
- A & B: Dominant genetic makeup doesn’t cause sex change. ❌
- C: The expression of sex chromosomes doesn’t change during a snail’s life in this context. ❌
Therefore, D is correct: Sex is not genetically determined in snails.
13. In the following cases, a ray is incident on a concave mirror. In which case
is the angle of incidence equal to zero?
A. A ray parallel to the principal axis.
B. A ray passing through the centre of curvature and incident obliquely.
C. A ray passing through the principal focus and incident obliquely.
D. A ray incident obliquely to the principal axis, at the pole of the mirror.
Ans:
- When a ray passes through the centre of curvature (C) of a concave mirror, it strikes the mirror perpendicularly (i.e., normal to the surface).
- At the point of incidence, the reflected ray retraces its path because the angle of incidence = angle of reflection = 0°.
So, even if the ray is oblique to the principal axis, it is normal to the mirror surface at the point of contact.
Why the others are incorrect:
- A. Ray parallel to the principal axis
→ It strikes the mirror at an angle, not normal, so angle of incidence ≠ 0. ❌ - C. Ray through the principal focus and incident obliquely
→ Also strikes at an angle, not perpendicularly. ❌ - D. Ray incident obliquely at the pole
→ Definitely not normal to the surface; angle is significant. ❌
Therefore, option B is correct: Angle of incidence is zero when the ray passes through the centre of curvature.
15. Identify the incorrect statement
‘The energy available to the producers is maximum’ because:
A. It is the first trophic level which absorbs1% of light energy directly from
the source.
B. It utilizes the most of the chemical energy for its own respiration, growth,
reproduction, movement etc.
C. It utilizes 10% of light energy and transfers the rest to the next trophic
level.
D. It transfers only 10% of light energy to the next trophic level.
Ans:
- Producers (like plants) absorb about 1% of the light energy from the sun (Option A is correct).
- They use most of the absorbed energy for respiration, growth, reproduction, and other life processes (Option B is correct).
- Only about 10% of the energy stored as biomass is transferred to the next trophic level (Option D is correct).
- Option C is incorrect because producers do not utilize just 10% of light energy and transfer the rest; they actually utilize most of the absorbed energy, and only about 10% of that energy is transferred to the next level.
So, C is the incorrect statement.
16. Which of the following is not a role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
A. Natural replenishment of soil.
B. Enrichment of oxygen in atmosphere.
C. Waste decomposition.
D. Break-down of dead remains.
Ans:
- Decomposers (like bacteria and fungi) play important roles such as:
- Natural replenishment of soil by recycling nutrients (A)
- Decomposing waste (C)
- Breaking down dead remains (D)
- However, enrichment of oxygen in the atmosphere is not a role of decomposers; this is mainly done by plants and photosynthetic organisms through photosynthesis.
So, option B is not a role of decomposers.
Question No. 17 to 20 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer
these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
17 .Assertion (A): On adding dil. HCl to a test tube containing a substance ‘X’, a
colourless gas is produced which gives a pop sound when a burning match
stick is brought near it.
Reason (R): In this reaction metal ‘X’ is displaced by Hydrogen.
Ans: C. A is true but R is false
When a metal (say zinc, magnesium, or iron) reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl), the metal displaces hydrogen from the acid — not the other way around.
The reaction looks like this: Metal + Dilute HCl → Metal chloride + Hydrogen gas
For example: Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂ (gas)
- The metal loses electrons (oxidized) and hydrogen ions (H⁺) from the acid gain electrons to form hydrogen gas (H₂).
- The hydrogen gas produced is colourless and makes a pop sound when a burning matchstick is brought near it.
- So, hydrogen is displaced by the metal, not metal displaced by hydrogen.
Therefore, the reason statement “metal X is displaced by hydrogen” is false, because it’s actually the metal displacing hydrogen from the acid.
18. Assertion (A): Generally, the number of chromosomes in a cell and in a germ
cell is not the same in species.
Reason (R): When two germ cells combine, they restore the normal number of
chromosomes in a species.
Ans:
Assertion (A): Generally, the number of chromosomes in a cell and in a germ cell is not the same in species.
Reason (R): When two germ cells combine, they restore the normal number of chromosomes in a species.
Correct option:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
19. Assertion (A): A convex mirror always forms an image behind it and the image
formed is virtual.
Reason (R): According to the sign convention, the focal length of a convex
mirror is positive.
Ans: Assertion (A): A convex mirror always forms an image behind it and the image formed is virtual.
Reason (R): According to the sign convention, the focal length of a convex mirror is positive.
Correct option:
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
20. Assertion (A): If the lions are removed from a food chain it will not affect the
food chain, however if the plants are removed from a food chain it will disturb
the ecosystem.
Reason (R): Plants are producers who can make food using sunlight, while
lions are consumers.
Ans: Assertion (A): If the lions are removed from a food chain it will not affect the food chain, however if the plants are removed from a food chain it will disturb the ecosystem.
Reason (R): Plants are producers who can make food using sunlight, while lions are consumers.
Correct option:
D. A is false but R is true
20.
Assertion (A): If the lions are removed from a food chain it will not affect the food chain, however if the plants are removed from a food chain it will disturb the ecosystem.
Reason (R): Plants are producers who can make food using sunlight, while lions are consumers.
Answer: A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
- Plants are producers and form the base of the food chain by making their own food through photosynthesis.
- Removing plants affects the entire food chain because all consumers depend directly or indirectly on producers.
- Lions are top consumers and their removal affects the food chain, but the primary energy source (plants) is more crucial to ecosystem stability.
- Therefore, the reason correctly explains the assertion.
21. Identify the type of each of the following reactions stating the reason for your
answers.
A. Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe + heat
B. Pb (NO3)2 + 2KI → PbI2( )+ 2KNO3
Ans:
A. Exothermic Displacement reaction/Redox reaction.
Heat is evolved or a More reactive element displaces a less reactive
element or aluminium reduces iron (II) oxide to iron
B. Double displacement / Precipitation reaction
As there is an exchange of ions between reactants and products
(Yellow) precipitate (of Lead iodide) is formed
23. Attempt either option A or B.
A. List the steps for the synthesis of glucose by the plants. What special
feature is found in desert plants related to this process?
OR
B. Explain the role of the following enzymes in the process of digestion of food
in humans:
(i) Salivary amylase
(ii) Pepsin
(iii) Trypsin
(iv) Lipase
Ans:
Steps for Synthesis of Glucose (Photosynthesis):
- Plants take in carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air through tiny openings called stomata.
- Water (H₂O) is absorbed by the roots from the soil.
- Chlorophyll in the chloroplasts captures sunlight energy.
- Using sunlight energy, plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and oxygen (O₂) through a series of chemical reactions.
- The overall simplified equation:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Special Feature in Desert Plants (CAM Photosynthesis):
This adaptation helps desert plants conserve water while still synthesizing glucose.
Desert plants use a special adaptation called CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) photosynthesis.
They open their stomata at night to take in CO₂, minimizing water loss during the hot daytime.
CO₂ is stored as an acid overnight and used for photosynthesis during the day when stomata are closed.
OR
B.
(i) Salivary amylase
- Present in saliva, it begins the digestion of starch (a carbohydrate) into simpler sugars like maltose in the mouth.
(ii) Pepsin
- Secreted by the stomach, pepsin breaks down proteins into smaller peptides in the acidic environment of the stomach.
(iii) Trypsin
- Produced by the pancreas and active in the small intestine, trypsin further breaks down peptides into even smaller peptide chains or amino acids.
(iv) Lipase
Secreted by the pancreas and active in the small intestine, lipase breaks down fats (lipids) into glycerol and fatty acids.
27. Give reasons for the following
i. Certain metals are used for making cooking utensils.
ii. Hydrogen gas does not evolve when certain metals except Mg & Mn
react with nitric acid.
ANS: A. Certain metals (like aluminium/ copper) are used for making cooking
utensils as they are good conductors of heat and have high melting
points.
B. Hydrogen gas is not evolved when a metal reacts with nitric acid. This is
because HNO3 is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises the H2 produced to
water and itself gets reduced to any of the nitrogen oxides (N2O, NO,
NO2). But magnesium (Mg) and manganese (Mn) react with very dilute
HNO3 to evolve H2 gas.
29.Water is used by the leaves of the plants for photosynthesis but rather than
watering the leaves, we water the plant through the soil. How does this water
reach the leaves of the plant?
Ans:
Water reaches the leaves of the plant through the following process:
- Water is absorbed by the root hairs from the soil.
- It then moves upward through the plant via specialized tubes called xylem vessels.
- The water travels through the stem and reaches the leaves.
- In the leaves, water is used in photosynthesis and also helps keep the cells turgid.
- This upward movement of water from roots to leaves is driven by capillary action, root pressure, and transpiration pull (loss of water vapor from the leaves).
So, watering the soil allows the roots to absorb water, which is then transported to the leaves where it is needed for photosynthesis.
30. A. In a family of four individuals, the father possessed long ears and the mother
possessed short ears. If the parents had pure dominant and recessive traits
respectively and F1 individual is married to an unrelated individual of the
same genotype, then calculate the ratio of genetic makeup of F2 generation.
Show a suitable cross.
B. If father had short ears and the mother had long ears, and both the parents
are homozygous for the allelic pair of genes, explain what effect it will have
on the ratio of genetic makeup in F2 generation, if F1 individual is married
to an unrelated individual of the same genotype.
Ans:
A. Father has long ears (pure dominant), mother has short ears (pure recessive)
- Let L = long ears (dominant)
- Let l = short ears (recessive)
Parents’ genotypes:
Father = LL (homozygous dominant)
Mother = ll (homozygous recessive)
F1 generation:
All offspring get L from father and l from mother → Genotype = Ll (heterozygous, long ears)
F1 individual (Ll) marries an unrelated individual of the same genotype (Ll)
Cross: Ll × Ll
| Parent 1 | L | l |
|---|---|---|
| Parent 2 | L | LL |
| l | Ll |
F2 Genotypes:
- LL = 1
- Ll = 2
- ll = 1
Ratio of genotypes in F2: 1 : 2 : 1
Phenotypic ratio:
- Long ears (LL + Ll) = 3
- Short ears (ll) = 1
B. Father has short ears (pure recessive), mother has long ears (pure dominant)
- Father = ll
- Mother = LL
F1 generation:
All offspring get L from mother and l from father → Genotype = Ll (heterozygous, long ears)
Again, if F1 (Ll) marries an unrelated Ll individual, the cross and genetic ratio in F2 remains the same as in part A:
Genotypic ratio = 1 (LL) : 2 (Ll) : 1 (ll)
Phenotypic ratio = 3 (long ears) : 1 (short ears)
Effect on ratio:
The order of parents (which one has the dominant or recessive homozygous genotype) does not affect the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation in this case. The ratios remain the same because the F1 genotype is heterozygous (Ll) regardless
B. No change in ratio/the ratio of F2 generation will still be 1LL:2Ll:1ll/ ratio
will be the same.
As the cross is still between a pure dominant and recessive allele/ genes/
traits/characters /as shown in the cross above.
Question No. 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
34 Attempt either option A or B.
A.
(i) “Keerthi thinks that Substitution reaction occurs in saturated
Hydrocarbons, on the contrary Krishi thinks, it occurs in unsaturated
Hydrocarbons.” Justify with valid reasoning whose thinking is correct.
(ii) “Methane and Propane and their Isomers are used as fuels” Comment.
Draw the electron dot structure of the immediate lower homologue of
Propane. Give any two characteristics of homologues of a given
homologous series. (iii) A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you predict
why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Ans:
(i) Substitution reactions in hydrocarbons – Keerthi vs Krishi
- Keerthi’s view: Substitution reactions occur in saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes).
- Krishi’s view: Substitution reactions occur in unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes/alkynes).
Correct answer: Keerthi is correct.
Reason:
- Saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) mainly undergo substitution reactions, where an atom (usually hydrogen) is replaced by another atom (like chlorine or bromine). For example, in methane (CH₄), hydrogen atoms can be substituted by halogens in the presence of UV light.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes and alkynes) primarily undergo addition reactions because of the presence of double or triple bonds. These bonds are sites for atoms or groups to add across the multiple bonds.
(ii) Methane and Propane and their isomers used as fuels
- Methane and propane, along with their isomers, are used as fuels because they are hydrocarbons that combust easily, releasing energy.
- Methane (CH₄) is the simplest alkane and is a major component of natural gas.
- Propane (C₃H₈) is widely used as LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) for heating and cooking.
Electron dot structure of the immediate lower homologue of propane (which is ethane, C₂H₆):
H H
| |
H-C-C-H
| |
H H
- Each dash represents a pair of shared electrons (covalent bonds).
Two characteristics of homologues in a homologous series:
- They have the same general formula but differ by a CH₂ group.
- They show gradual change in physical properties (like boiling point, melting point) but have similar chemical properties.
(iii) Why a mixture of ethyne and oxygen is used for welding, but not ethyne and air?
Ans: A mixture of ethyne and oxygen produces a very high temperature flame (about 3000°C or more). This extremely hot flame is strong enough to melt and weld metals.
But ethyne and air produce a flame of much lower temperature because air contains only 21% oxygen. This flame is not hot enough to melt most metals and cannot be used for welding.
OR
B.
(i) ‘A’ & ‘B’ are sodium salts of long-chain carboxylic acid and long chain
Sulphonic acid respectively. Which one of A or B will you prefer as a
cleansing agent while using underground water (hand pump water)?
Give the reason for your answer.
(ii) Elaborate on the process of cleansing action. Illustrate micelle with the
help of labelled diagram.
(iii) Write the chemical equation of the preparation of soap from an ester
CH3COOCH3. What is the name of this process?
Ans:
(i) Between soap (A) and synthetic detergent (B), I would prefer synthetic detergent (B) as a cleansing agent when using underground (hand pump) water.
Reason:
- Underground water usually contains hardness causing ions like Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺.
- Soaps (A) form insoluble salts (scum) with these ions, reducing their cleansing efficiency.
- Synthetic detergents (B), especially those with sulphonic acid groups, do not form scum with hard water ions and remain effective as cleansing agents.
(ii) Process of cleansing action:
- Cleansing action happens because soap/detergent molecules have two ends:
- Hydrophilic (water-attracting) head (polar, ionic group)
- Hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail (non-polar hydrocarbon chain)
- When soap is added to water and dirt/oil is present, the hydrophobic tails of soap molecules attach to the grease/oil/dirt particles.
- The hydrophilic heads remain in water.
- The soap molecules surround the dirt particles with their tails inward and heads outward, forming micelles.
- These micelles trap the dirt/oil inside and make it soluble in water, so it can be rinsed away.
Micelle Diagram:

(iii) Preparation of soap from an ester (CH₃COOCH₃):
- The process is called Saponification.
- When an ester reacts with a strong base like NaOH, it breaks down into an alcohol and the sodium salt of a carboxylic acid (soap).
Chemical equation:
CH₃COOCH₃ + NaOH → CH₃COONa + CH₃OH
- Here, CH₃COONa is sodium acetate (soap-like salt, but this is a simple example; soaps are usually sodium salts of fatty acids).
- CH₃OH is methanol (alcohol).
35. The image below shows a developing fetus in the mother’s womb. The
developing fetus is connected to the placenta by means of umbilical cord.
The Umbilical vein and artery run inside the umbilical cord.
(i) Name two substance that moves through the blood vessels. (1)
(ii) If the placenta has less villi how will it affect the baby’s growth? (1)
(iii) Name the region where the embryo develops inside the female body.
Explain how this region is adapted for nourishing the baby. (1)
(iv) Some of the fetal cells fall off into the amniotic fluid and can be
collected by careful procedure. The cells were screened and found to
contain XY chromosome. (2)
Ans:
(i) Two substances that move through blood vessels are oxygen and nutrients.
(ii) If the placenta has fewer villi, the exchange of nutrients and oxygen between mother and baby will reduce, leading to poor growth of the baby.
(iii) The embryo develops inside the uterus (womb).
The uterus is adapted for nourishing the baby because it has a thick muscular wall and a rich supply of blood vessels that provide nutrients and oxygen to the growing embryo through the placenta.
(iv) The fetal cells falling into the amniotic fluid can be collected by amniocentesis.
If the cells contain XY chromosomes, it indicates that the fetus is genetically male.
OR
a) What is the sex of the foetus?
b) How is this prenatal sex determination misused?
For visually impaired students
B. A developing fetus is connected to the placenta by means of umbilical cord.
The Umbilical vein and artery run inside the umbilical cord.
(i) Name two substance that moves through the blood vessels.
(ii) If the placenta has less villi how will it affect the baby’s growth?
(iii) Name the region where the embryo develops inside the female body.
Explain how this region is adapted for nourishing the baby. (1)
(iv) Some of the fetal cells fall off into the amniotic fluid and can be
collected by careful procedure. The cells were screened and found to
contain XY chromosome.
a) What is the sex of the foetus?
b) How is this prenatal sex determination misused?
Ans:
a) The sex of the foetus is male because the cells contain XY chromosomes.
b) Prenatal sex determination is misused for sex-selective abortion or female foeticide, where female fetuses are aborted due to societal preference for male children. This practice is illegal and unethical.
(i) Two substances that move through the blood vessels in the umbilical cord are oxygen and nutrients.
(ii) If the placenta has fewer villi, the exchange of oxygen and nutrients between mother and fetus decreases, which can lead to poor growth and development of the baby.
(iii) The embryo develops inside the uterus.
The uterus is adapted for nourishing the baby because it has a thick muscular wall and rich blood supply, and the placenta provides nutrients and oxygen to the fetus through the umbilical cord.
37.A. Distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid experimentally.
Attempt either subpart B or C.
B. Give the IUPAC name of the first member of Alkene which is formed by
addition of conc. sulphuric acid to it. Illustrate the change with the help
of a chemical equation.
OR
C. “All combustion reactions are oxidation but all oxidation reactions are
not combustion.” Justify.
Ans:
A. Experimental distinction between ethanol and ethanoic acid:
- Take two test tubes, one with ethanol and one with ethanoic acid.
- Add sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) to each.
- Observation:
- Ethanol: No reaction, no gas evolved.
- Ethanoic acid: Effervescence occurs due to the release of carbon dioxide gas (CO₂).
- Conclusion: Effervescence with sodium bicarbonate indicates presence of acid (ethanoic acid).
B.
- The first member of alkene is ethene (IUPAC name).
- When concentrated sulfuric acid adds to ethene, it forms ethyl hydrogen sulfate.
- Chemical equation:
C₂H₄ + H₂SO₄ → C₂H₅OSO₃H
OR
C.
- All combustion reactions are oxidation reactions because they involve the combination of a substance with oxygen, producing heat and light.
- But all oxidation reactions are not combustion because oxidation can happen without burning, such as rusting of iron or reaction of glucose in cells.
- Therefore, combustion is a specific type of oxidation that involves flame and heat.
38. Mohan and Rohit observed that shoots of a plant growing in shade bend
towards the sunlight. Whereas, leaves of ‘Touch me not’ plant fold and droop
soon after touching. They were curious to know how these movements occur in plantsIn order to help them understand the movements in the plants, answer the
following questions:
Attempt either subpart A or B.
A. What causes the bending of shoots in the plants as shown in figure A?
Ans:
A. The bending of shoots towards sunlight is caused by the unequal distribution of a plant hormone called auxin.
- When light falls on one side of the shoot, auxin accumulates more on the shaded side.
- This causes cells on the shaded side to elongate more than those on the lighted side.
- As a result, the shoot bends towards the light source.
This movement is called phototropism and it helps the plant maximize light absorption for photosynthesis.
OR
B. What causes the folding of the leaves in ‘Touch me not’ plant as shown
in figure B? (2)
C. Compare the movement of growth of the pollen tube towards ovule with
the movements shown in part A of the above figure. (1)
D. Compare the movement shown in figure B with the movement of body
parts in the animals. (1)
Ans:
B. The folding of leaves in the ‘Touch me not’ plant (Mimosa pudica) is caused by a rapid loss of water from specialized cells called pulvini at the base of the leaflets. When these cells lose water, they become flaccid, causing the leaflets to fold and droop as a defense mechanism against touch or injury.
C. The growth movement of the pollen tube towards the ovule is a growth movement driven by chemical signals, whereas the bending of shoots towards light (phototropism) is a curvature movement caused by differential cell elongation due to auxin distribution.
D. The folding movement of the ‘Touch me not’ leaves is a rapid, reversible movement similar to the quick reflex actions in animals, where body parts respond swiftly to stimuli for protection.
39. During a field trip, Mohan and Rohit observed that shoots of sunflower plants
bend towards the sunlight. Whereas, leaves of ‘Touch me not’ plant begin to
fold and droop soon after touching even during the day. They were curious to
know how these movements occur in plants.
Attempt either subpart A or B.
A. What causes the bending of shoots in the sunflower plants towards
sunlight?
OR
B. What causes the folding of the leaves in ‘Touch me not’ plants when
touched by hand? (2)
C. Compare the movement of growth of the pollen tube towards ovule with
the bending of shoots of sunflower plant towards sunlight. (1)
D. Compare the movement in folding of leaves of ‘Touch me not’ plants with
the movement of body parts in the animals. (1)
Ans:
A. The bending of shoots in sunflower plants towards sunlight is caused by phototropism. This happens because the plant hormone auxin redistributes to the shaded side of the shoot, causing cells there to elongate more than on the sunny side. This uneven growth causes the shoot to bend towards the light.
B. The folding of leaves in the ‘Touch me not’ plant (Mimosa pudica) when touched is due to a rapid loss of water (turgor pressure) from specialized cells called pulvini at the base of the leaflets. This causes these cells to become flaccid and the leaves to fold and droop as a protective response.
C. The growth of the pollen tube towards the ovule is a growth movement directed by chemical signals (chemotropism), whereas the bending of shoots towards sunlight is a curvature movement caused by differential cell elongation due to hormone (auxin) distribution.
D. The folding of leaves in ‘Touch me not’ plants is a rapid, reversible movement similar to reflex actions in animals, where body parts quickly respond to stimuli for protection or survival.
39. Azim Taraporewala was a traveller and science enthusiast. During one of his
travels he found himself on the edge of an island without any mode of
communication. As he had read in many stories, he thought he would light a
fire on the beach and travelling boats or ships could see that fire and come to
give him a ride. He had run out of lighters and match-sticks but had a reading
glass. Being a science enthusiast he knew some tricks and used that lens and
a scrap of paper to light a fire, with the help of scorching rays from the sun.
A. Which lens can be used by Azim to create the fire?
B. What property of the lens helps Azim to create the fire?
Attempt either subpart C or D.
C. List two more uses of this kind of lens.
OR
D. Explain with reason the condition under which the lens can form both
real as well as virtual images.
Ans:
A. Azim can use a convex lens (also called a converging lens) to create the fire.
B. The property of the lens that helps Azim create the fire is its ability to converge (focus) parallel rays of sunlight to a single point called the focal point, where the energy is concentrated enough to ignite the paper.
C. Two more uses of a convex lens are:
- Used in magnifying glasses to produce a magnified virtual image of small objects.
- Used in cameras, microscopes, and the human eye to focus light and form clear images.
OR
D. A convex lens can form both real and virtual images depending on the position of the object relative to the lens’s focal length:
- When the object is beyond the focal length, the lens forms a real and inverted image on the other side.
- When the object is within the focal length, the lens forms a virtual, erect, and magnified image on the same side as the object.
This happens because the bending of light rays changes with object distance from the lens.
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 10):
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
