Class 7 Electric Current and its effects Oxford
Master every concept and question type with detailed NCERT-based MCQs and topic-wise explanations for NEET & CBSE exams.
📥 Download Free PDFAbout This Chapter
This chapter provides a clear understanding of the key concepts of Class 7 Electric Current and its effects Oxford, including definitions, applications, and solved MCQs from NCERT Class 11 & 12 Biology. Designed for both board and NEET aspirants, it helps build strong conceptual foundations.
🧠 Concept Clarity
Focus on key NCERT concepts with short, easy-to-understand notes.
📘 Chapter-wise Practice
Attempt carefully curated MCQs from previous and expected exams.
💡 Detailed Solutions
Each question includes an explanation to strengthen your conceptual understanding.
🔥 High-Scoring Topics
Highlights important topics most frequently asked in NEET & CBSE papers.
Sample MCQs from Class 7 Electric Current and its effects Oxford
a) Mitochondria
b) Chloroplast
c) Nucleus
d) Golgi apparatus
✅ Correct Answer: b) Chloroplast
a) Carotene
b) Xanthophyll
c) Chlorophyll
d) Anthocyanin
✅ Correct Answer: c) Chlorophyll
Download Complete Class 7 Electric Current and its effects Oxford PDF Now
Get all questions with detailed solutions in one free downloadable PDF.
📥 Download NowClass 7 Electric Current and its effects Oxford Textbook Answers
In this chapter, students learn about electric current and its effects, including heating and magnetic effects. The Class 7 Electric Current and its Effects Oxford solutions provide clear, step-by-step answers to all questions, helping students understand concepts easily and prepare effectively for exams.
Fill in the Blanks with the Correct Words
- When we connect two cells to form a battery, we should connect the positive terminal of one cell to the negative terminal of the other cell.
- In an electric circuit, the connecting wire should be made of a conductor.
- A device that is used to open or close an electrical circuit is called a switch.
- A fuse works on the heating effect of electric current.
- In an electric bell, the electromagnet is magnetised when the soft iron strip touches the interrupter.
Choose the Correct Option
- What is a drawing of an electrical circuit with standard symbols called?
a. An electrical circuit
b. A battery
c. An electrical drawing
d. A circuit diagram
Answer: d. A circuit diagram - What happens when the switch is ‘on’ in an electric circuit?
a. The circuit is open and current flows through it.
b. The circuit is closed and current does not flow through it.
c. The circuit is closed and current flows through it.
d. The circuit is open and current does not flow through it.
Answer: c. The circuit is closed and current flows through it. - Why does the filament of an incandescent bulb glow?
a. It is the heating effect of electric current.
b. It is the magnetic effect of electric current.
c. An electric fuse is connected to it.
d. An electromagnet is connected to it.
Answer: a. It is the heating effect of electric current. - What is the part of a heating appliance containing a tightly wound coil, that heats up, called?
a. Electric iron
b. Element
c. Electromagnet
d. Fuse
Answer: b. Element - What is an electric fuse?
a. An electromagnetic device
b. A safety device
c. A source of current
d. An element
Answer: b. A safety device - What is the role of an electric switch?
a. To open or close an electric circuit
b. To produce heat
c. To make a magnet
d. To provide a path for the flow of current
Answer: a. To open or close an electric circuit - How many electric cell(s) does an electric battery consist of?
a. Only one
b. Only two
c. Only five
d. Two or more
Answer: d. Two or more - What effect of current do an electric toaster and a filament light bulb use?
a. The heating effect of electric current
b. The magnetic effect of electric current
c. Both a and b
d. Neither a nor b
Answer: a. The heating effect of electric current - What happens when an electric current is passed through a coil wrapped around an iron piece?
a. The iron piece becomes rubbery.
b. The iron piece becomes hard.
c. The iron piece becomes magnetic.
d. The iron piece becomes soft.
Answer: c. The iron piece becomes magnetic. - What happens to the magnetic effect on an electromagnet when the electric current is switched off?
a. It becomes stronger.
b. It changes the direction.
c. It does not change.
d. It becomes zero.
Answer: d. It becomes zero.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
- Two or more cells joined together: Battery
- Thin wire that glows in an incandescent light bulb: Filament
- A device that limits the amount of current flowing in a circuit: Fuse
- A long wire that has been wound many times into a tightly packed coil: Solenoid or Coil
- The part of an electric bell that is attracted to the electromagnet, when switched on: Armature or Soft iron strip
Short Answer Type Questions
1. Name any four components of an electric circuit with their symbols:
- Cell: −∣∣+
- Wire: –
- Switch (open): −∘/∘−
- Bulb: ⊙
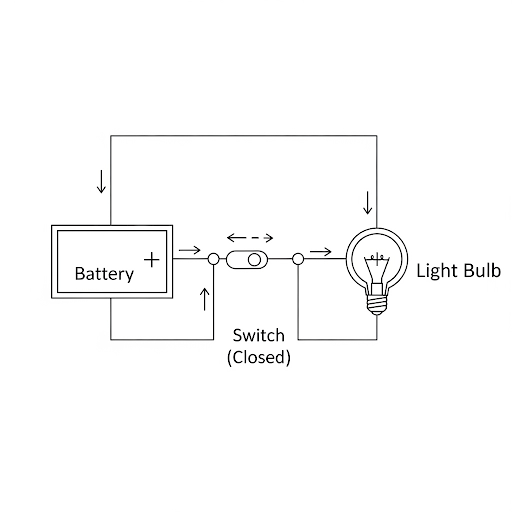
2. Draw a circuit diagram where an electric current will flow. Add a component that will help open and close the circuit and label it.
Ans : An electric circuit where current flows requires a closed loop. The diagram below shows a simple circuit with a power source (battery), a consuming device (bulb), and a switch to open and close the circuit.
To ensure the current flows, the switch must be in the closed or ON position. When the switch is open, the flow of electricity is interrupted.
Diagram of a Closed Circuit
3. Explain ‘heating effect of electric current’:
Ans : The Heating Effect of Electric Current
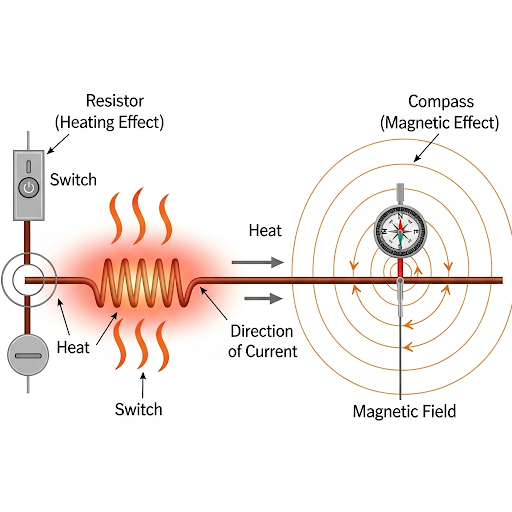
The heating effect of electric current is when a wire or any conductor gets hot as electricity passes through it. This happens because the tiny particles that carry electricity (electrons) bump into the atoms of the wire. These collisions make the atoms vibrate faster, which produces heat.
This effect is used in many things you use every day, like:
Electric Fuses: A fuse contains a wire that melts and breaks the circuit if too much electricity flows through it. This protects your appliances from damage.
Electric Heaters and Toasters: These have a special wire inside that gets very hot when electricity flows through it, which is used to heat air or toast bread.
Electric Bulbs: The very thin wire inside a light bulb, called the filament, gets so hot that it glows and produces light.
4. What is ‘magnetic effect of electric current’?
Ans: The magnetic effect of electric current is the phenomenon where a magnetic field is produced around a wire or a conductor when an electric current flows through it.
This effect was discovered in 1820 by a Danish scientist named Hans Christian Oersted. He observed that a compass needle would deflect (move) when it was placed near a wire carrying an electric current. This showed a direct connection between electricity and magnetism.
eg, Loudspeakers: They use electromagnets to create sound vibrations.
5. Purpose of an electromagnet in an electric bell:
Ans: It attracts and releases a soft iron strip (armature) repeatedly. When the circuit is closed, it magnetizes and pulls the hammer to strike the gong, then demagnetizes when the circuit opens. This cycle produces continuous ringing.
Long Answer Type Questions
1. Draw two electric circuits showing two situations when current will not flow. Explain.
- Situation 1: Open Circuit
- Drawing: Cell, bulb, switch in ‘off’ position.
- Explanation: Switch is open, creating a break. Current cannot flow; bulb does not glow.
- Situation 2: Broken Component
- Drawing: Cell, bulb with broken filament or cut wire.
- Explanation: Broken component creates discontinuity. No current flows; bulb does not glow.
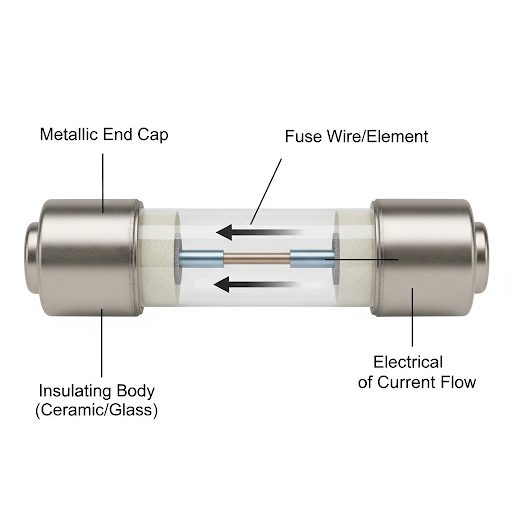
2. Explain the working of an electric fuse:
Ans: An electric fuse is a safety device used in electrical circuits to protect appliances and wiring from damage caused by too much electric current. It works based on the heating effect of electric current.
How an Electric Fuse Works
A fuse contains a short, thin wire made of a special material, usually an alloy of tin and lead. This material has two important properties:
- High Resistance: This means it heats up quickly when a current flows through it.
- Low Melting Point: This allows it to melt easily when it gets too hot.
If there is a sudden overload (too many devices running at once) or a short circuit (a fault that allows a very large current to flow), the current increases dramatically. This causes the fuse wire to heat up very rapidly due to its high resistance.
Because of its low melting point, the wire quickly melts and breaks the circuit. This stops the flow of electricity to the device, preventing it from being damaged or causing an electrical fire.
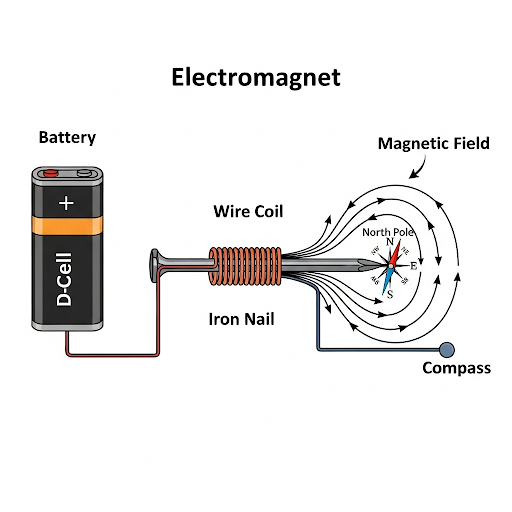
3. Draw a rough figure of a simple electromagnet. How to check if it is magnetic?
Ans: A simple electromagnet consists of a soft iron core with an insulated copper wire wrapped around it, and the ends of the wire are connected to a power source, like a cell.
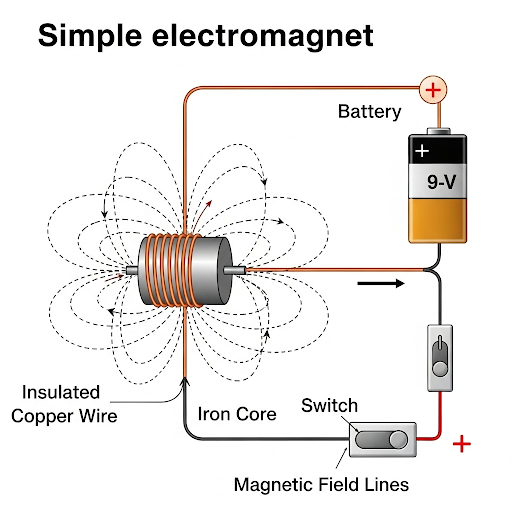
To check if the electromagnet is magnetic, you can do the following:
- Connect the circuit: Ensure the wire is connected to the cell to allow current to flow.
- Bring a magnetic object near it: Place a small object made of a magnetic material, such as a paper clip or a pin, near the soft iron core.
- Observe: If the iron core has become magnetic, it will attract and pick up the paper clip. You can also use a compass; the needle will deflect when brought near the electromagnet.
When the power is switched off, the electromagnet will lose its magnetism, and the paper clip will fall off, proving that its magnetism is dependent on the flow of electric current.
Class 7 Science Oxford Book Solutions-All Chapters – Complete Chapter Links
Click on each chapter to access the detailed, step-by-step solutions:
- Chapter 1: Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 2: Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3: Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4: Chemicals and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 5: Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Chapter 6: Heat
- Chapter 7: Climate and Adaptations
- Chapter 8: Soil
- Chapter 9: Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 10: Transportation of Substances in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 11: Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 12: Motion and Time
- Chapter 13: Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 14: Winds, Storms, and Cyclones
- Chapter 15: Light
- Chapter 16: Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17: Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18: Wastewater Story
For the official Class 7 Science Solutions, you can visit:
In conclusion, the Class 7 Electric Current and its effects Oxford helps students understand how electric current flows and its heating and magnetic effects. By studying the Class 7 Electric Current and its effects Oxford, students can grasp concepts clearly and apply them in practical situations.
