Welcome to Class 8 Science Some Natural Phenomena-Oxford Book. This chapter explores fascinating natural events such as lightning and earthquakes. You’ll learn how these phenomena occur, the science behind them, and important safety tips to protect yourself. Our solutions are designed to help you understand key concepts clearly and score better in exams.
Class 8 Science Some Natural Phenomena-Oxford Book
I. Objective type questions
A. Choose the correct option.
1. When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk, the piece of silk gets.
a. positive charge b. charge depending on the way it was rubbed
c. no charge d. negative charge
Ans: d. negative charge
(Silk gains negative charge when rubbed with a glass rod.)
2. An electroscope is used for
a. creating lightning b. charging an object
c. detecting an electric charge d. protection against lightning
Ans: c. detecting an electric charge
(An electroscope is used to detect the presence of electric charge.)
3. Lightning is accompanied with
a. large amounts of electric current and very high temperature
b. earthquakes
c. volcanic eruptions
d. All of these
Ans: a. large amounts of electric current and very high temperature
(Lightning produces intense heat and electric current.)
4. The lithosphere consists of.
a. Earth’s mantle and core b. Earth’s crust and inner mantle
c. Earth’s core and crust d. Earth’s crust and upper mantle
Ans: d. Earth’s crust and upper mantle
(The lithosphere includes the crust and upper part of the mantle.)
5. Plate tectonics is a theory about
a. charges
b. lightning
c. structure of the surface of the Earth
d. structure of the inner core of the Earth
Ans: c. structure of the surface of the Earth
(Plate tectonics explains the movement of Earth’s surface plates.)
6. A sudden movement or a fracture in the Earth’s crust is called
a. earthquake b. lightning
c. thunder d. cyclonic storm
Ans: a. earthquake
(A sudden movement in Earth’s crust is called an earthquake.)
7. Seismology is the branch of science concerned with
a. floods b. earthquakes
c. lightning storms d. tides
Ans: b. earthquakes
(Seismology is the study of earthquakes.)
8. A lightning conductor provides an easy path for the charges (from the lightning strike) to
a. the building
b. the electrical fittings of the building
c. the water pipes of the building
d. deep underground
Ans: d. deep underground
(A lightning conductor directs the charge safely into the ground.)
9. The epicentre of an earthquake is
a. point vertically above the focus on the surface of the Earth
b. point at the Earth’s core
c. point below the focus in the mantle of the Earth
d. the graph of the earthquake
Ans: a. point vertically above the focus on the surface of the Earth
(The epicentre is the surface point above the earthquake’s origin.)
10. Lightning happens because of
a. earthquakes b. transfer of massive electric charges
c. electric poles d. volcanoes
Ans: b. transfer of massive electric charges
(Lightning is caused by the movement of electric charges in clouds.)
Class 8 Science Some Natural Phenomena-Oxford Book-1 Mark
B. Match the following.
Column A Column B
1. Natural phenomenon a. Electric discharge
2. Lightning b. Richter scale
3. Focus c. Lightning
4. Earthquake d. Sunrise
5. Thunder e. Earthquake
Ans:
| Column A | Column B |
|---|
| 1. Natural phenomenon | d. Sunrise |
| 2. Lightning | a. Electric discharge |
| 3. Focus | e. Earthquake |
| 4. Earthquake | b. Richter scale |
| 5. Thunder | c. Lightning |
Class 8 Science Some Natural Phenomena-Oxford Book-1Mark
II. Very short answer type questions
- What is charging by friction?
Ans: Charging by friction is the process of transferring electric charge between two objects by rubbing them together.
2.What is earthing?
Ans: Earthing is the process of transferring electric charge from a charged object to the ground to make it neutral.
3. What is the outer covering of Earth called?
Ans: The outer covering of Earth is called the crust.
4. Why is it unsafe to hold an umbrella during a thunderstorm?
Ans: It is unsafe because the metal parts of the umbrella can attract lightning, which may cause electric shock.
5. What is seismology?
Ans: Seismology is the branch of science that studies earthquakes and the movements of Earth’s crust.:
Class 8 Science Some Natural Phenomena-Oxford Book-3 marks
1. Explain with examples how an object can be charged by friction.
Ans: When we rub two objects together, they can become electrically charged. This happens because tiny particles called electrons move from one object to the other. The object that loses electrons becomes positively charged, and the one that gains electrons becomes negatively charged. This process is called charging by friction.
Examples:
- If you rub a glass rod with a silk cloth, the glass rod loses electrons and becomes positively charged. The silk gains electrons and becomes negatively charged.
- When you comb your dry hair with a plastic comb, the comb gets charged and can attract small paper bits.
So, charging by friction happens because of rubbing and transfer of charges between objects.
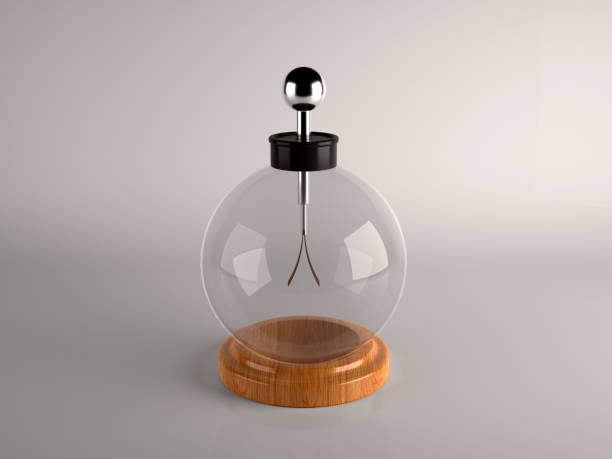
2. What is an electroscope? Draw a neat labelled diagram and explain how it works.
Ans: An electroscope is a device used to detect electric charge on an object.
It has a metal rod with a metal disc or knob at the top and two thin metal leaves (usually gold or aluminium) at the bottom, kept inside a glass container.
How it works:
- When a charged object touches the metal knob, the electric charge travels down to the metal leaves.
- Since both leaves get the same charge, they repel each other and move apart.
- If there is no charge, the leaves remain together.

3. With the help of a simple diagram, explain how a lightning conductor can protect a building from a lightning strike.
Ans: A lightning conductor is a metal rod placed at the highest point of a building. It is connected to a thick wire that runs down the building and goes deep into the ground.
How it works:
- When lightning strikes, the conductor gives the electric charge a safe path to travel from the top of the building into the ground.
- This prevents the lightning from damaging the building or causing a fire.
It’s like giving lightning a shortcut to the Earth so that it doesn’t harm anything.
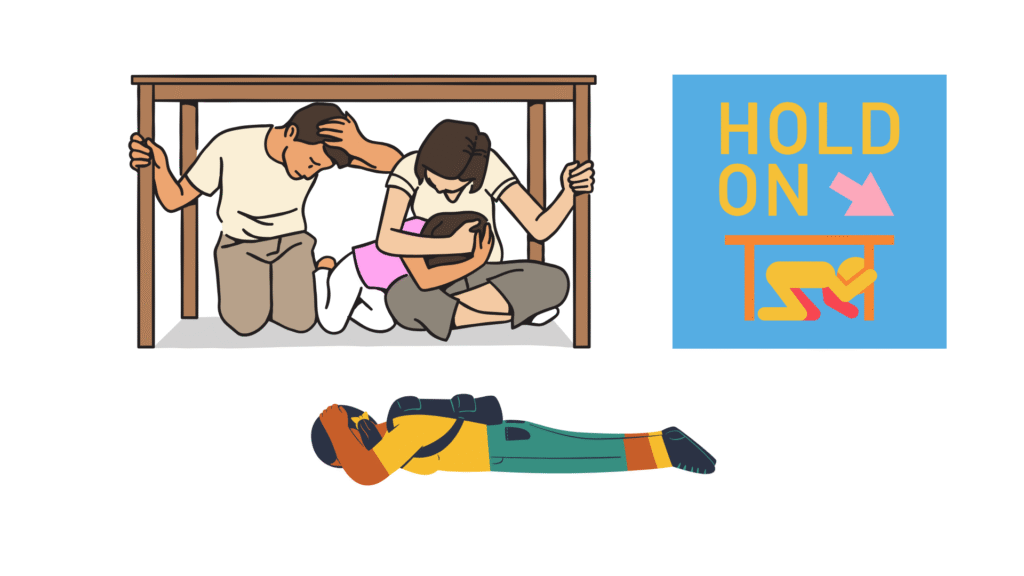
4. List three steps that we can take to protect ourselves from being struck by lightning during a thunderstorm.
Ans: Here are three easy and important safety steps:
- Stay indoors – Don’t go outside when you hear thunder or see lightning.
- Stay away from metal – Don’t touch anything made of metal, like bicycles or wires.
- Avoid water and electrical devices – Don’t take a bath or use mobile phones or TVs during a storm, because lightning can travel through wires and water.
These simple steps can keep you safe during a thunderstorm.
For Visualization:
5. Draw a diagram and explain the internal structure of the Earth.
Ans: The Earth is made of three main layers:
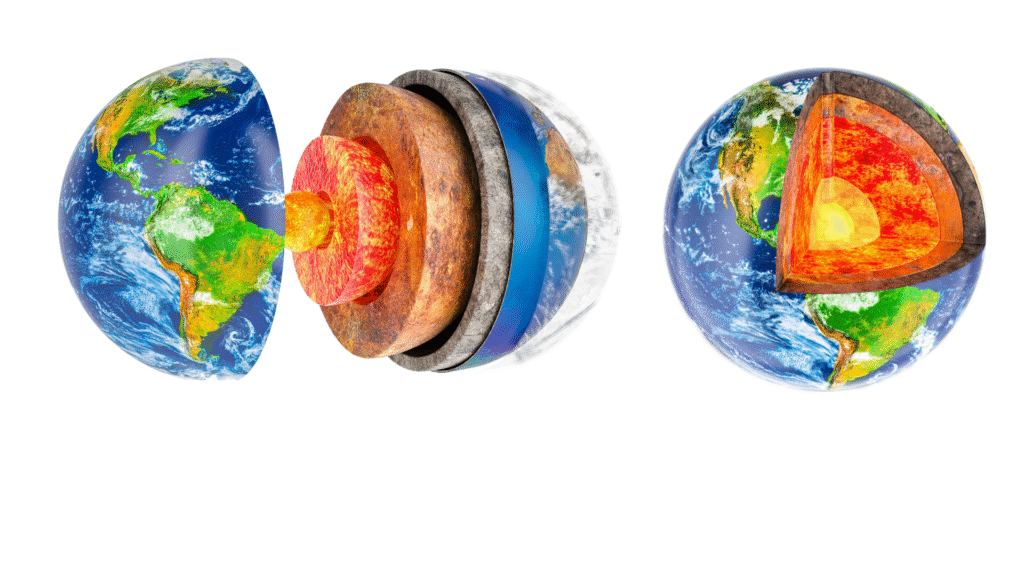
- Crust – The thin outer layer where we live. It is made of solid rocks.
- Mantle – The thick layer below the crust. It is made of hot, flowing rock.
- Core – The deepest part of the Earth. It has two parts:
- Outer core – Made of liquid metal.
- Inner core – Made of solid metal, mostly iron and nickel.
6. Give a simple diagrammatic representation of how an earthquake occurs.
Ans: An earthquake happens when there is a sudden movement in the Earth’s crust. This usually happens at fault lines where two plates of the Earth move against each other.
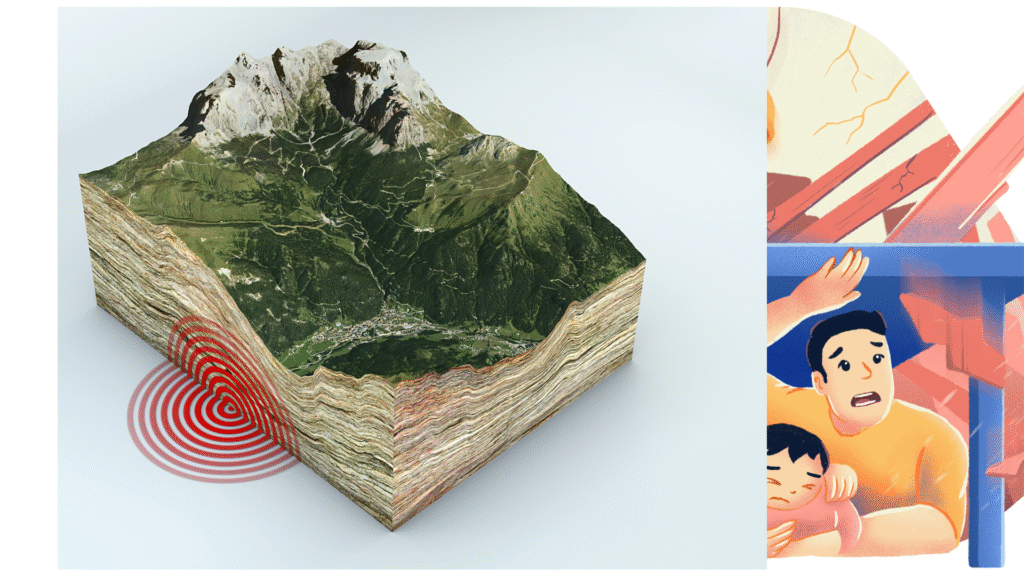
- The place inside the Earth where it starts is called the focus.
- The point directly above the focus on the Earth’s surface is called the epicentre.
- The shock waves that come out from the focus are called seismic waves.
These waves shake the ground and cause the earthquake.
7. In what way can we design buildings to minimize the loss of life and property in the event of an earthquake? Give two examples. Also, mention the importance of the location of the building in reference to earthquake safety.
Ans: To make buildings safer during earthquakes, we should:
- Use earthquake-resistant designs like strong foundations and flexible structures that can absorb shaking.
- Install shock absorbers and use light materials that reduce damage if something falls.
Examples:
- Buildings in Japan often have base isolators that help the building move without breaking.
- In some places, wooden homes are used because wood bends and doesn’t easily crack during shaking.
Location is also important:
- Buildings should be made on strong ground, not on loose soil or near steep slopes.
- Avoid constructing buildings close to fault lines, where earthquakes are more likely to happen.
Choosing the right design and location helps save lives and reduces damage during an earthquake.
Conclusion:
In Class 8 Science–Natural Phenomena-Oxford Solutions, we explored the fascinating world of natural events that shape our environment. From understanding the science behind electric charges and lightning to learning about earthquakes and the internal structure of the Earth, this chapter deepens our understanding of the forces that affect our planet.
By studying the effects of these phenomena and the safety measures we can take, such as using lightning conductors or earthquake-resistant buildings, we not only gain knowledge but also develop the ability to protect ourselves and our surroundings.
The chapter also helped us understand the importance of tectonic plate movements and how seismic waves play a role in earthquakes, shaping the land beneath our feet.
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
NEET BIOLOGY
- Evolution
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Human Health and Disease
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
For the official Class 6 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 6):
