Reproduction is a vital process that ensures the continuity of life. In this chapter from Class 8 Science Ch Reproduction Oxford Book, students learn about the two main types of reproduction—sexual and asexual—as observed in animals. The chapter explains key concepts like fertilisation, embryo development, and different methods by which organisms give rise to their young. With clear explanations and diagrams, it lays the foundation for understanding how life is passed on from one generation to the next.
Class 8 Science Ch Reproduction Oxford Book Answers
1. Objective type questions
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
1. In asexual reproduction, a new individual is formed by both parents). (single parent/both parents)
2. In …..(budding/binary fission), a new organism grows out from a part the parent body.
3. Male and female individuals produce special reproductive cells called….. (Sperms/gametes).
4. The …….(penis/urethra) transfers the sperms along with semen into the female body.
5. The …….(ovary/uterus) is where the zygote matures and grows till it is ready to be born.
6. In ……..(internal/external) fertilization, fusion of male and female cells takes place inside the female body.
7. The male cells contain ……..(XX/XY) chromosomes.
Ans
B. Write T for the True and F for the False statements. Correct the false statements.
1. No animals can multiply asexually. They do so only by laying eggs.
2. Once a female reaches puberty, the ovary secretes hormones that stimulate it to release female cells called sperms.
3. Fertilization in a female body takes place inside the fallopian tubes.
4. The baby grows inside the mother’s womb for 40 days and is then pushed out of the mother’s body.
5. A newborn baby is very small and is unable to look after itself.
6. The larva of a butterfly looks like an adult and transforms due to drastic changes.
Ans:
- F – No animals can multiply asexually. They do so only by laying eggs.
Correction: Some animals can reproduce asexually, such as hydra and amoeba. - F – Once a female reaches puberty, the ovary secretes hormones that stimulate it to release female cells called sperms.
Correction: The ovary releases egg cells (ova), not sperms. Sperms are produced by males. - T – Fertilization in a female body takes place inside the fallopian tubes.
- F – The baby grows inside the mother’s womb for 40 days and is then pushed out of the mother’s body.
Correction: The baby grows inside the womb for about 40 weeks (approximately 9 months), not 40 days. - T – A newborn baby is very small and is unable to look after itself.
- F – The larva of a butterfly looks like an adult and transforms due to drastic changes.
Correction: The larva (caterpillar) of a butterfly does not look like the adult. It undergoes metamorphosis to become an adult butterfly.
C. Choose the correct option.
1. Which of these is a reproductive process shown in Hydra?
a. Budding
b. Binary fission
c. Through eggs
d. By giving birth to babies
2. Which of these is true about male gametes?
a. They are produced by ovaries.
b. They are produced by testes.
c. They are called sperms and have a tail.
d. Both b. and c.
3. Which of these is a narrow tube that helps to transport sperms produced in each testis?
a. Vas deferens
b. Fallopian tube
c. Urethra
outside the female body? 4
d. Penis
4. In which of these animals does the fusion of male and female gametes takes place
a. Cow and horse
b. Human beings
c. Cat and dog
d. Fish and frog
5. Which of these shows a male child?
a. XX
b. XY
c. YY
d. None of these
6. Which of these is true about asexual reproduction?
a. A new organism is formed from the cells of a single parent
b. Two parents are required to produce a new organism
c. Most plants and animals reproduce by this method
d. All of these
7. Which of these refers to reproductive cells produced by male and female individually?
a. Gametes
b. Zygotes
c. Embryo
d. None of these
8. In which of these reproductive organs does fertilization occur and a zygote gets
a. Ovary
b. Testes
c. Oviduct
d. Uterus
9. Which of these refers to the stage of growth of the human embryo when most body parts can be identified?
a. Zygote
b. Gametes
c. Foetus
d. Parturition
10. Which of these is true about the life cycle of a butterfly but not a frog?
a. It undergoes metamorphosis
b. The egg develops into a larva
c. The larva turns into a pupa before becoming an adult
d. The larva does not resemble the adult form
Which of these is a reproductive process shown in Hydra?
✅ a. Budding
Which of these is true about male gametes?
✅ d. Both b. and c.
(They are produced by testes and are called sperms, which have a tail.)
Which of these is a narrow tube that helps to transport sperms produced in each testis?
✅ a. Vas deferens
In which of these animals does the fusion of male and female gametes take place outside the female body?
✅ d. Fish and frog
(This is called external fertilization.)
Which of these shows a male child?
✅ b. XY
Which of these is true about asexual reproduction?
✅ a. A new organism is formed from the cells of a single parent
Which of these refers to reproductive cells produced by male and female individually?
✅ a. Gametes
In which of these reproductive organs does fertilization occur and a zygote gets formed?
✅ c. Oviduct
(Also called the fallopian tube.)
Which of these refers to the stage of growth of the human embryo when most body parts can be identified?
✅ c. Foetus
Which of these is true about the life cycle of a butterfly but not a frog?
✅ c. The larva turns into a pupa before becoming an adult
(This pupa stage is unique to butterflies in metamorphosis.)
II. Very short answer type questions
A Give one word for the following.
1. The process by which living things produce offspring of their own kind
2. Special reproductive cells
3. The process by which male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote
4. Male sex hormone
5. The process by which an ovum is released from the ovary
6. The period in which the baby stays and grows inside the mother’s womb.
7. The part of the female body that is called the womb
8. Animals that give birth to live offspring
9. Animals that lay eggs that hatch into offspring
10. The transformation of a larva into an adult through a series of drastic changes
Ans:
- The process by which living things produce offspring of their own kind
Reproduction - Special reproductive cells
Gametes - The process by which male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote
Fertilisation - Male sex hormone
Testosterone - The process by which an ovum is released from the ovary
Ovulation - The period in which the baby stays and grows inside the mother’s womb
Gestation - The part of the female body that is called the womb
Uterus - Animals that give birth to live offspring
Viviparous animals - Animals that lay eggs that hatch into offspring
Oviparous animals - The transformation of a larva into an adult through a series of drastic changes
Metamorphosis
III. Short answer type questions
1. What is reproduction? Name two types of reproduction in an organism.
Answer:
Reproduction is the biological process by which living organisms produce offspring of their own kind to ensure the continuity of life.
Two types of reproduction are:
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
2. What is asexual reproduction? Give two examples of animals that reproduce asexually.
Answer:
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction in which a single parent produces offspring without the involvement of gametes.
Examples: Hydra (budding) and Amoeba (binary fission).
3. What are gametes? Name the male and female gametes.
Answer:
Gametes are special reproductive cells involved in sexual reproduction.
- Male gamete: Sperm
- Female gamete: Ovum (egg)
4. Differentiate between internal and external fertilization.
Answer:
| Internal Fertilization | External Fertilization |
| Fertilization occurs inside the female body. | Fertilization occurs outside the female body, usually in water. |
| Example: Humans, cats | Example: Frogs, fish |
5. What are chromosomes? Name the two types of sex chromosomes.
Answer:
Chromosomes are thread-like structures found in the nucleus of cells that carry genetic information.
Two types of sex chromosomes are:
- X chromosome
- Y chromosome
6. What is parturition?
Answer:
Parturition is the process of giving birth to a fully developed baby after the gestation period.
7. What are viviparous animals? Give two examples.
Answer:
Viviparous animals are those that give birth to live young ones instead of laying eggs.
Examples: Humans, Dogs
8. Define metamorphosis. Name two animals that undergo metamorphosis.
Answer:
Metamorphosis is a biological process in which an organism undergoes a drastic transformation in body form from the larval stage to the adult stage.
Examples: Butterfly, Frog
9. Write a short note on gender issues and myths associated with female infanticide.
Answer:
Gender issues arise from the belief that males are superior to females. This often leads to discrimination against girls, including the harmful practice of female infanticide—the killing of newborn girls due to a preference for sons. Myths include the belief that only sons can carry on the family name or support parents in old age. These beliefs are unjust and illegal and need to be challenged through awareness and education.
10. What are some of the problems associated with adolescent pregnancy?
Answer:
Adolescent pregnancy can lead to several health and social problems including:
- Increased risk of maternal and infant health complications
- Interrupted education and limited career opportunities
- Social stigma and emotional stress
- Higher chances of poverty and dependency
IV. Long answer type questions
1.With the help of a labelled diagram, explain how an animal reproduces asexually.
Answer:
One common method of asexual reproduction in animals is budding, seen in Hydra.
Explanation:
- A small outgrowth or bud forms on the parent’s body.
- The bud grows using the nutrients from the parent.
- Once fully developed, it detaches and becomes a new individual.
Labelled Diagram Description:
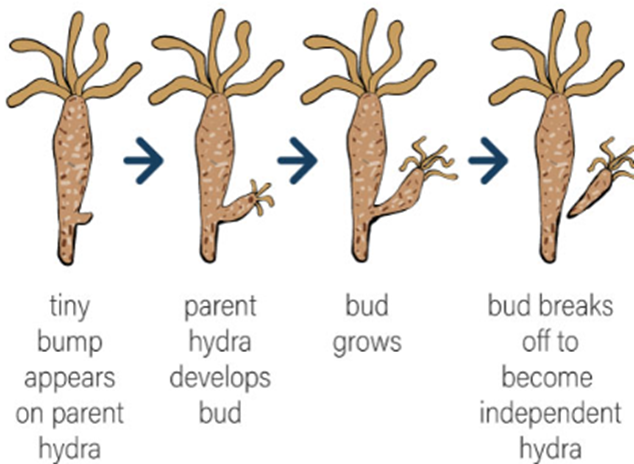
- Parent Hydra
- Developing bud
- Tentacles on the bud
- Bud detaches
2. Explain the structure of human male and female gametes with the help of diagrams.
Ans: Structure of Human Male and Female Gametes
Human Male Gamete (Sperm Cell)
The male gamete is called the sperm cell. It is small, motile, and specially designed to carry the male genetic material to the female gamete (egg) during fertilization.
Structure of Human Sperm Cell:
- Head:
- The head contains the nucleus, which carries the haploid set of chromosomes (23 chromosomes in humans).
- It is covered by a cap-like structure called the acrosome, which contains enzymes that help in penetrating the egg during fertilization.
- Middle Piece:
- The middle piece contains mitochondria that provide energy (ATP) required for the movement of the sperm.
- Tail (Flagellum):
- The tail is a long, whip-like structure that propels the sperm forward, allowing it to swim towards the egg.
Human Female Gamete (Egg Cell or Ovum)
The female gamete is called the egg cell (ovum). It is larger than the sperm cell and non-motile. The egg contains the female genetic material and, upon fertilization, provides the nutrients required for the early development of the zygote.
Structure of Human Egg Cell:
- Cytoplasm:
- The cytoplasm of the egg contains yolk, which provides nourishment for the early stages of development.
- Nucleus:
- The nucleus of the egg contains the female haploid set of chromosomes (23 chromosomes in humans).
- Plasma Membrane:
- The egg is surrounded by a plasma membrane, which prevents more than one sperm from fertilizing it.
Conclusion:
- Male gamete (sperm): Small, motile, with a tail for movement and acrosome for penetrating the egg.
- Female gamete (egg): Larger, non-motile, contains cytoplasm for nourishment and a nucleus with chromosomes.
These gametes fuse during fertilization to form a zygote, which develops into an embryo.
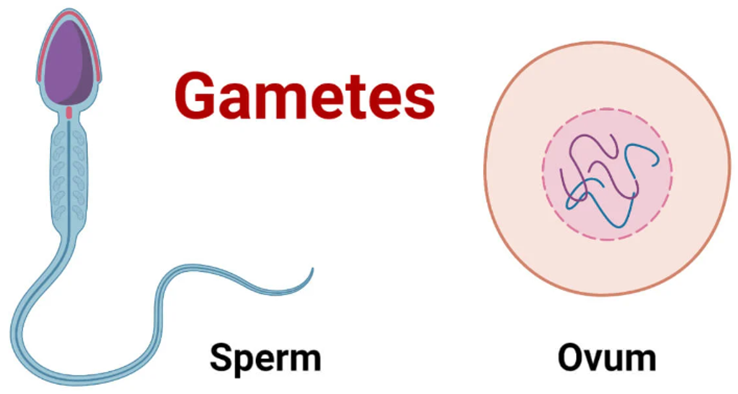
- Sperm: Head → Nucleus, Middle piece → Mitochondria, Tail → Flagellum
- Ovum: Circular cell → Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Cell membrane
3. With the help of a labelled diagram, explain how reproduction takes place in human beings.
Ans: Explanation (Sexual Reproduction in Humans):
- Male reproductive organ produces sperms in testes.
- Female reproductive organ produces ova in ovaries.
- During reproduction, sperm is deposited into the vagina and travels through the uterus to meet the ovum in the oviduct (fallopian tube).
- Fertilization occurs here, forming a zygote.
- The zygote travels to the uterus, implants in the wall, and develops into a baby.
Labelled Diagram Description:
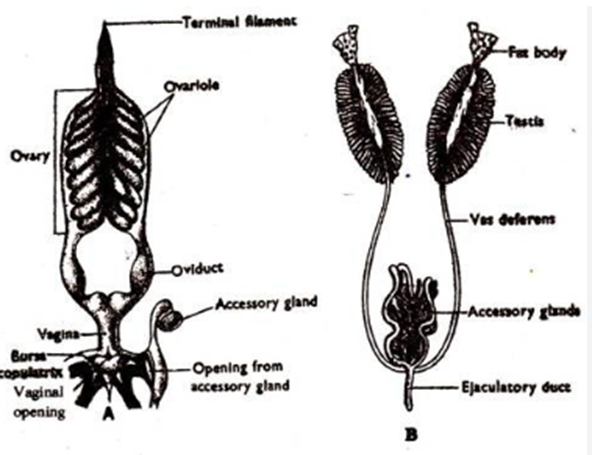
- Male: Testes, Vas deferens, Urethra, Penis
- Female: Ovary, Oviduct, Uterus, Vagina
4. Describe the stepwise process of fertilization in human beings.
Answer: Stepwise Process of Fertilization in Human Beings
Fertilization in human beings is the process by which a male sperm and a female egg (ovum) combine to form a zygote. This process takes place in the fallopian tube of the female reproductive system. Here’s a detailed stepwise explanation:
Step 1: Ovulation (Release of Egg)
- Every month, during the menstrual cycle, one mature egg is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube. This process is called ovulation.
- The egg is now ready to be fertilized by the sperm.
Step 2: Sperm Entry (Through the Female Reproductive Tract)
- During sexual intercourse, millions of sperm are ejaculated into the vagina.
- The sperm swim through the cervix and into the uterus, and from there, they travel up to the fallopian tube where the egg is located.
Step 3: Capacitation of Sperm
- Before fertilization, the sperm undergo a process called capacitation.
- Capacitation involves biochemical changes in the sperm’s membrane, allowing it to penetrate the egg’s outer layers.
Step 4: Sperm Penetration
- The sperm reach the egg and bind to its outer membrane. The outer layer of the egg is called the zona pellucida.
- The sperm’s acrosome (cap-like structure at the head of the sperm) releases enzymes that break down the zona pellucida, allowing the sperm to penetrate the egg.
- Only one sperm successfully enters the egg.
Step 5: Fusion of Nuclei
- Once the sperm enters the egg, its nucleus combines with the egg’s nucleus, each contributing half of the 23 chromosomes (haploid sets).
- This fusion results in the formation of a diploid zygote (with a total of 46 chromosomes), which contains the genetic material from both the mother and father.
Step 6: Formation of Zygote
- The fertilized egg (zygote) now contains a complete set of 46 chromosomes (23 from the mother and 23 from the father).
- The zygote begins to divide through mitosis and forms multiple cells, eventually becoming a blastocyst.
Step 7: Implantation
- The zygote continues dividing as it travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus.
- After a few days, the blastocyst reaches the uterus and attaches itself to the thickened endometrial lining of the uterus, where it will continue to develop.
- This process is known as implantation, marking the beginning of pregnancy.
5. With the help of an example, illustrate how a pair of chromosomes determine the sex of a child in human beings.
Answer:
Sex Determination in Humans
- Humans have two types of sex chromosomes: X and Y.
- Females have XX chromosomes, and males have XY chromosomes.
Process of Determining Sex:
- Mother’s Egg: Always carries an X chromosome (since females are XX).
- Father’s Sperm: Can carry either an X or a Y chromosome.
Fertilization:
- If the father’s sperm carries an X chromosome, the fertilized egg will be XX, resulting in a female child.
- If the father’s sperm carries a Y chromosome, the fertilized egg will be XY, resulting in a male child.
Example:
- Female Child (XX):
Mother (X) + Father (X) = XX → Female - Male Child (XY):
Mother (X) + Father (Y) = XY → Male
Conclusion:
- The father determines the sex of the child by contributing either an X (female) or Y (male) chromosome.
Diagram Description:
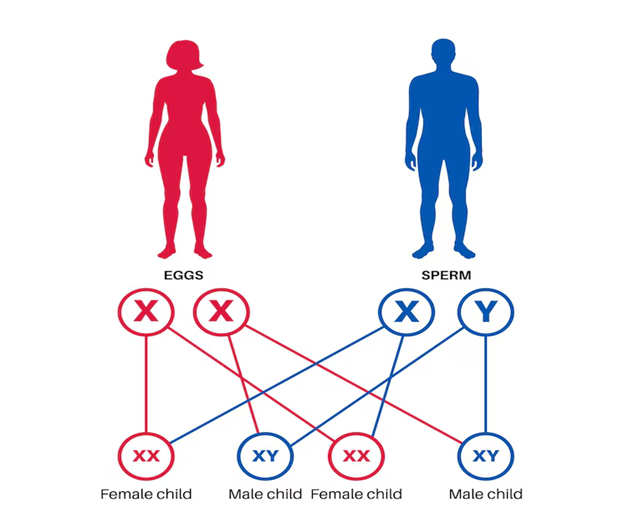
6. With the help of a labelled diagram, explain the life cycle of a frog.
Answer:
Life Cycle of a Frog
The life cycle of a frog is an example of complete metamorphosis. It involves four distinct stages: egg, tadpole, juvenile frog (tadpole with legs), and adult frog.
Stages in the Life Cycle of a Frog:
- Egg Stage:
- Female frogs lay eggs in water. The eggs are surrounded by a jelly-like substance that protects them.
- The eggs hatch into larvae known as tadpoles.
- Tadpole Stage:
- Tadpoles hatch from the eggs and are aquatic.
- They have a tail for swimming and gills for breathing underwater.
- Tadpoles feed on algae and other small organisms in the water.
- Juvenile Frog (Tadpole with Legs):
- As the tadpole matures, it begins to grow hind legs, followed by front legs.
- The tail starts to shrink, and the lungs develop, allowing the frog to breathe air.
- The tadpole is now transforming into a juvenile frog.
- Adult Frog:
- The tail disappears completely, and the frog becomes fully adapted to life on land and water.
- The adult frog can now breathe through lungs and skin and is capable of reproducing to start the cycle again.
Diagram Labels:
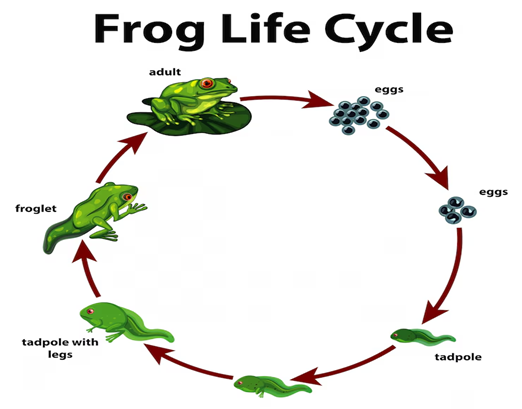
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
For the official Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for all Classes):
Understanding the process of reproduction is essential to grasp how life continues on Earth. The Class 8 Science Ch Reproduction Oxford Book Solutions help clarify important concepts such as sexual and asexual reproduction, fertilisation, and embryo development. With the Class 8 Science Ch Reproduction Oxford Book Solutions, students can easily revise key topics and strengthen their understanding of complex biological processes. Whether it’s preparing for exams or completing homework, the Class 8 Science Ch Reproduction Oxford Book Solutions provide step-by-step guidance for all textbook questions. By consistently referring to the Class 8 Science Ch Reproduction Oxford Book Solutions, students build a solid foundation in biology, ensuring long-term academic success.
