The CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2023-24 is designed according to the latest competency-based exam pattern issued by the board. It includes a balanced mix of objective, short answer, long answer, and case-based questions to assess conceptual understanding and application skills.
CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2023-24 – Solved
Sample Question Paper 2023-24
Class X
Science (Subject Code – 086)
Max. Marks: 80 Time Allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
i. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
ii. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is
expected to attempt only one of these questions.
iii. Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
iv. Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions
should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
v. Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these
questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
vi. Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these
questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
vii. Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts
SECTION A (1 mark each)
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1 – 20. There is no negative mark for incorrect response
1.
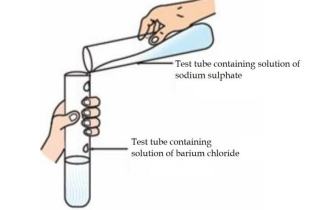
Identify the product which represents the solid state in the above reaction.
a) Barium chloride
b) Barium sulphate
c) Sodium chloride
d) Sodium sulphate
Answer: b) Barium sulphate
Explanation: The reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride is a double displacement reaction. It produces sodium chloride (aqueous) and barium sulphate, which forms as a white insoluble precipitate (solid).
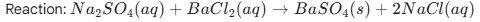
2. The colour of the solution observed after 30 minutes of placing zinc metal to copper
sulphate solution is
a) Blue
b) Colourless
c) Dirty green
d) Reddish Brown
Answer: b) Colourless
Explanation: Zinc is more reactive than copper and displaces it from the copper sulphate solution. The blue colour of copper sulphate fades as colourless zinc sulphate is formed.
3. Mild non-corrosive basic salt is
a) Ca (OH)2
b) NaCl
c) NaOH
d) NaHCO3
Answer: d) NaHCO3
Explanation: NaHCO3 (Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate or Baking Soda) is a mild, non-corrosive basic salt often used as an antacid. Ca(OH)2 and NaOH are bases (alkalis), not salts, and NaCl is a neutral salt.
4. On adding dilute sulphuric acid to a test tube containing a metal ‘X’, a colourless gas is
produced when a burning match stick is brought near it. Which of the following correctly
represents metal ‘X’?
a) Sodium
b) Sulphur
c) Copper
d) Silver
Answer: a) Sodium
Explanation: The gas produced is Hydrogen (H2), which burns with a “pop” sound when a match is brought near it. For this to occur with dilute acid, the metal must be more reactive than hydrogen. Copper and Silver are less reactive than hydrogen and will not react. Sulphur is a non-metal. Sodium is a reactive metal that displaces hydrogen from acids
5. Which one of the following correctly represents Sodium oxide?
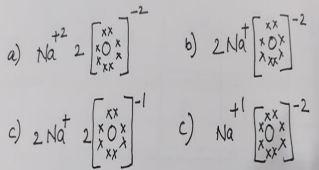
The correct representation of Sodium oxide is 2Na+ [O]2−. This ionic compound is formed when each of the two sodium atoms donates one electron to the oxygen atom.
6. An element with atomic number_____ will form a basic oxide.
a) 7 (2,5)
b) 17 (2,8,7)
c) 14 (2,8,4)
d) 11 (2,8,1)
Answer: d) 11 (2,8,1)
Explanation: Basic oxides are typically formed by metals. The element with atomic number 11 is Sodium (electronic configuration 2, 8, 1). As a metal, it readily loses an electron to form a basic oxide (Na2O). Elements with atomic numbers 7 (Nitrogen), 14 (Silicon), and 17 (Chlorine) are non-metals or metalloids which generally form acidic oxides.
7. An element ‘M’ has 50% of the electrons filled in the 3rd shell as in the 2nd shell. The
atomic number of ‘M’ is:
a) 10
b) 12
c) 14
d) 18
Answer: c) 14
Explanation: The 2nd shell can hold a maximum of 8 electrons. If the 3rd shell has 50% of that amount, it holds 4 electrons .
- The configuration is: K=2, L=8, M=4.
- Total atomic number = 2 + 8 + 4 = 14. (This element is Silicon).
8. Generally food is broken and absorbed within the body of organisms. In which of the
following organisms is it done outside the body?
a) Amoeba
b) Mushroom
c) Paramoecium
d) Lice
Answer: b) Mushroom
Explanation: Mushrooms (fungi) exhibit saprophytic nutrition. They break down complex organic matter outside their bodies using enzymes and then absorb the simpler nutrients. Amoeba and Paramecium digest food internally (holozoic nutrition), and Lice are parasites.
9 . Receptors are usually located in sense organs. Gustatory receptors are present in
a) tongue
b) nose
c) eye
d) ear
Answer: a) tongue
Explanation: Gustatory receptors are specialized for the sense of taste and are located on the tongue. (Olfactory receptors are found in the nose for smell).
10 A farmer wants to grow banana plants genetically similar enough to the plants already
available in his field. Which one of the following methods would you suggest for this
purpose?
a) Regeneration
b) Budding
c) Vegetative propagation
d) Sexual reproduction
Answer: c) Vegetative propagation
Explanation: Vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction that produces offspring genetically identical to the parent plant (clones). This is the standard method for maintaining specific traits in crops like bananas.
11.Height of a plant is regulated by:
a) DNA which is directly influenced by growth hormone.
b) Genes which regulate the proteins directly.
c) Growth hormones under the influence of the enzymes coded by a gene.
d) Growth hormones directly under the influence a gene.
Answer: c) Growth hormones under the influence of the enzymes coded by a gene.
Explanation: Genes code for specific enzymes (proteins). These enzymes catalyze the reactions that produce growth hormones (like auxin). The amount of hormone produced regulates the height of the plant. If the enzyme is efficient, more hormone is produced, resulting in a taller plant.
12. A sportsman, after a long break of his routine exercise, suffered muscular cramps during a
heavy exercise session. This happened due to:
a) lack of carbon dioxide and formation of pyruvate.
b) presence of oxygen and formation of ethanol.
c) lack of oxygen and formation of lactic acid.
d) lack of oxygen and formation of carbon dioxide.
Answer: c) lack of oxygen and formation of lactic acid.
Explanation: During heavy exercise, when the oxygen supply to muscle cells is insufficient to meet energy needs, glucose breaks down via an anaerobic pathway. This incomplete breakdown produces lactic acid, the accumulation of which causes muscle cramps
13. An object is placed in front of a convex mirror. Its image is formed :
a) at a distance equal to the object distance in front of the mirror.
b) at twice the distance of the object in front of the mirror.
c) half the distance of the object in front of the mirror.
d) behind the mirror and it’s position varies according to the object distance.
Answer: d) behind the mirror and its position varies according to the object distance.
Explanation: Convex mirrors always form virtual and erect images located behind the mirror (specifically between the pole and the principal focus). While the image is always diminished, its exact position changes as the object is moved closer to or further from the mirror.
14. When light enters the atmosphere it strikes on extremely fine particles, which deflect the
rays of light in all possible directions, This is due to –
a) reflection of light
b) atmospheric refraction
c) scattering of light
d) dispersion of light
Answer: c) scattering of light
Explanation: This phenomenon describes the scattering of light. Fine particles in the atmosphere (like air molecules and dust) interact with light and redirect it in different directions. This is why the sky appears blue
15. In 1987, an agreement was formulated by the United Nations Environment Programme
(UNEP) to freeze the production of “X” to prevent depletion of “Y”. “X” and “Y”
respectively referred here are:
a) Ozone; CFCs
b) CFCs; rays UV
c) CFCs; Ozone
d) UV rays; Diatomic oxygen
Answer: c) CFCs; Ozone
Explanation: The agreement mentioned is the Montreal Protocol. It mandated freezing the production of Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs – “X”) to prevent the depletion of the Ozone layer (“Y”), which protects the earth from harmful UV radiation.
16. Which of the following features relates to biodegradable substances?
a) Broken down by biological processes
b) Remain inert
c) Persist in environment for long time
d) May harm the ecosystem
Answer: a) Broken down by biological processes
Explanation: Biodegradable substances are materials that can be decomposed by the action of microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) into simpler substances, unlike non-biodegradable materials which persist in the environment
Question No. 17 to 20 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer
these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is true but R is false.
d) A is false but R is true.
17. Assertion (A): Rusting of Iron is endothermic in nature. Reason (R): As the reaction is slow, the release of heat is barely evident.
- Answer: d) A is false but R is true.
- Explanation: Rusting is an oxidation reaction, which is exothermic (releases heat), not endothermic. Therefore, the Assertion is false. The Reason is true; because rusting is a very slow process, the heat released dissipates over time and is not easily noticed.
18. Assertion (A): Probability of survival of an organism produced through sexual reproduction is more than that of organism produced through asexual mode. Reason (R): Variations provide advantages to individuals for survival.
- Answer: a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Explanation: Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes, leading to genetic variations. These variations allow organisms to adapt better to changing environmental conditions, thereby increasing their chances of survival compared to asexual clones.
19. Assertion (A): A compass needle is placed near a current carrying wire. The deflection of the compass needle decreases when the magnitude of the current in the wire is increased. Reason (R): The strength of a magnetic field at a point near the conductor increases on increasing the current.
- Answer: d) A is false but R is true.
- Explanation: The Assertion is false because increasing the current increases the strength of the magnetic field (as stated correctly in the Reason). A stronger magnetic field would cause a greater (or stronger) deflection of the compass needle, not a decrease.
20. Assertion (A): Biodegradable substances result in the formation of compost and natural replenishment. Reason (R): It is due to breakdown of complex inorganic substances into simple organic substances.
Explanation: The Assertion is true; biodegradable waste forms compost. However, the Reason is false because decomposition involves the breakdown of complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances (like nutrients, water, and gases), not the other way around.
Answer: c) A is true but R is false.
Section-B
Question No. 21 to 26 are very short answer questions
21 Dil. HCl is added to Zn granules.” How will you prove that chemical change has taken place
here? Support your response with two arguments.
22 State the post-fertilisation changes that lead to fruit formation in plants. 2
23 What is the purpose of making urine in the human body? Name the organs that stores and
releases the urine.
OR
Why do arteries have thick and elastic walls whereas veins have valves?
24. The refractive indices of three media are given below:
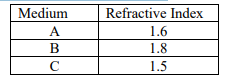
A ray of light is travelling from A to B and another ray is travelling from B to C.
(a) In which of the two cases the refracted ray bends towards the normal?
(b) In which case does the speed of light increase in the second medium?
Give reasons for your answer.
25. A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into three equal parts. These parts are then connected
in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this parallel combination is R1, what is the value
of the ratio R1 : R?
OR
Refer to the image below and state how the magnetic field pattern indicates regions where
the magnetic field is stronger outside the magnet? What happens to the magnetic field
when the current in the circuit is reversed?
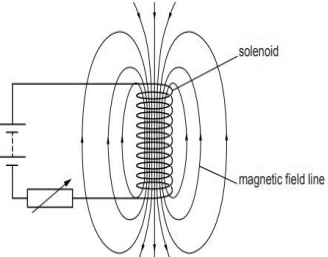
26. Study the food chain given below and answer the questions that follow:
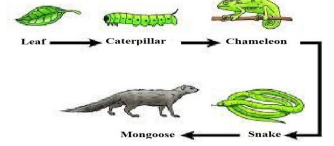
a) If the amount of energy available at the third trophic level is 100 joules, then how
much energy will be available at the producer level? Justify your answer.
b) Is it possible to have 2 more trophic levels in this food chain just before the fourth
trophic level? Justify your answer.
27. The given reaction shows one of the processes to extract the metals like Iron and
Manganese.
MnO₂ (s) + Al(s) → Mn(l) + Al₂O₃(s) + Heat
a) Give reason why the above reaction is known as a thermite reaction.
b) Identify the substance oxidised and reduced in the above reaction.
c) Give a reason why Aluminium is preferably used in thermite reactions.
28. An element ‘M’ with electronic configuration 2 8 3 combines separately with Cl-, SO4-2 anions. Write the chemical formulae of the compounds formed. Predict with the suitable reason the nature of the bond formed by element ‘M’ in general. How will the electrical
conductivity of the compounds formed vary with respect to ‘M’?
OR
A reddish-brown metal ‘X’, when heated in air, gives a black compound ‘Y’, which when
heated in presence of H₂ gas gives ‘X’ back. ‘X’ is refined by the process of electrolysis;
this refined form of ‘X’ is used in electrical wiring.
Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’. Draw a well-labeled diagram to represent the process of refining ‘X’.
29. We are advised to take iodised salt in our diet by doctors. Justify it’s importance in our body.
30 What is the probability of a girl or a boy being born in a family? Justify your answer.
31 (i) Explain why the refractive index of any material with respect to air is always greater
(ii) In the figure below a light ray travels from air into the semi-circular plastic block. Give
a reason why the ray does not deviate at the semi-circular boundary of the plastic
block.
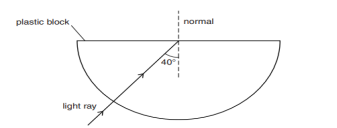
(iii)Complete the ray diagram of the above scenario when the light ray comes out of the
plastic block from the top flat end.
32 (i) State the law that explains the heating effect of current with respect to the measurable
properties in an electrical circuit.
(ii) List the factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends.
33. Anannya responded to the question: Why do electrical appliances with metallic bodies are
connected to the mains through a three pin plug, whereas an electric bulb can be connected
with a two pin plug?
She wrote: Three pin connections reduce heating of connecting wires.
(i) Is her answer correct or incorrect? Justify.
(ii) What is the function of a fuse in a domestic circuit?
Section-D
Question No. 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
34 a) Rehmat classified the reaction between Methane and Chlorine in presence of sunlight as a substitution reaction. Support Rehmat’s view with suitable justification and illustrate the reaction with the help of a balanced chemical equation.
b) Chlorine gas was prepared using electrolysis of brine solution. Write the chemical
equation to represent the change. Identify the other products formed in the process and
give one application of each.
OR
Raina while doing certain reactions observed that heating of substance ‘X’ with vinegar like smell with a substance ‘Y’ (which is used as an industrial solvent) in presence of conc. Sulphuric acid on a water bath gives a sweet-smelling liquid ‘Z’ having molecular formula C4H8O2. When heated with caustic soda (NaOH), ‘Z’ gives back the sodium salt of and the compound ‘Y’.
Identify ‘X’, ‘Y’, and ‘Z’. Illustrate the changes with the help of suitable chemical
equations.
35 Given below are certain situations. Analyze and describe its possible impact on a person:
a) Testes of a male boy are not able to descend into scrotum during his embryonic
development.
b) Vas deferens of a man is plugged.
c) Prostate and seminal vesicles are not functional.
d) Egg is not fertilised in a human female.
e) Placenta does not attach to the uterus optimally.
OR
a) A doctor has advised Sameer to reduce sugar intake in his diet and do regular exercise
after checking his blood test reports. Which disease do you think Sameer is suffering
from? Name the hormone responsible for this disease and the organ producing the
hormone.
b) Which hormone is present in the areas of rapid cell division in a plant and which
hormone inhibits the growth?
36.
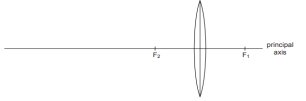
The above image shows a thin lens of focal length 5m.
(i) What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
(ii) If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical
centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed?
(iii) Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii)
OR
A 10 cm long pencil is placed 5 cm in front of a concave mirror having a radius of curvature
of 40 cm
(i) Determine the position of the image formed by this mirror.
(ii) What is the size of the image?
(iii)Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image as mentioned in the part (i).
SECTION – E
Question No. 37 to 39 are case-based/data -based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts.
Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
37 The table given below shows the hints given by the quiz master in a quiz

Based on the above hints answer the following questions
a) Give the IUPAC names of A and F
b) Illustrate with the help of chemical equations the changes taking place. (A -C and A F)
OR
Name the chemical reactions which occur in steps 2 and 5. Identify the compounds
formed in these steps if ‘A’ is replaced with its next homologue.
38. Figures (a) to (d) given below represent the type of ear lobes present in a family consisting
of 2 children – Rahul, Nisha and their parents.
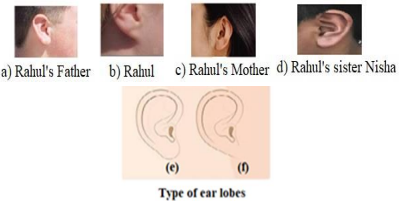
Excited by his observation of different types of ear lobes present in his family, Rahul
conducted a survey of the type of ear lobes found {Figure (e) and (f)} in his classmates. He
found two types of ear lobes in his classmates as per the frequency given below:
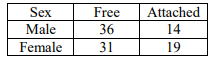
a) Which of the two characteristics – ‘free ear lobe’ or ‘attached ear lobe’ appears to be
dominant in this case? Why?
b) Is the inheritance of the free ear lobe linked with sex of the individual? Give reason for
your answer.
c) What type of ear lobe is present in father, mother, Rahul and his sister Nisha? Write the
genetic constitution of each of these family members which explains the inheritance of
this character in this family?
(Gene for Free ear lobe is represented by F and gene for attached ear lobe is represented
by f for writing the genetic constitution).
OR
Suresh’s parents have attached earl obes. What type of ear lobe can be seen in Suresh
and his sister Siya? Explain by giving the genetic composition of all.
39.
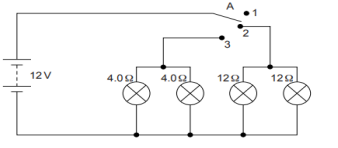
Vinita and Ahmed demonstrated a circuit that operates the two headlights and the two
sidelights of a car, in their school exhibition. Based on their demonstrated circuit, answer
the following questions.
(i) State what happens when switch A is connected to
a) Position 2
b) Position 3
(ii) Find the potential difference across each lamp when lit.
(iii) Calculate the current
a) in each 12 Ω lamp when lit.
b) In each 4 Ω lamp when lit.
OR
(iv) Show, with calculations, which type of lamp, 4.0 Ω or 12 Ω, has the higher power.
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 10):
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
The CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2023-24 is a valuable tool for students preparing for their board exams. It not only familiarizes students with the new question pattern but also sharpens their problem-solving and analytical thinking skills. By solving all sections — including objective, case-based, and competency-based questions — students can strengthen their grasp on Physics, Chemistry, and Biology topics in a structured manner.
Moreover, the solutions provided for the CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2023-24 are explained in simple language, following the NCERT-based approach, which ensures clarity and accuracy. It is highly recommended that students review the marking scheme and answer structure through these solved examples to maximize their performance in the actual exam.
In conclusion, the CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2023-24 is more than just a practice resource—it is a complete guide for effective revision and exam strategy. Students who solve it thoroughly and learn from the solutions are more likely to perform well and score higher in their final board examination.

