In our daily life, we notice many changes happening around us. Some changes are fast, like melting of ice, while others are slow, like rusting of iron. In Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Changes around us Oxford, we learn about different kinds of changes such as reversible and irreversible, physical and chemical, and natural and man-made changes.

This chapter helps us understand how and why these changes occur, and their importance in our daily life. By studying this, students will be able to classify changes with examples and relate them to real-life situations.
Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Changes around us Oxford Solution Full Concept
🔬 Changes Around Us
Class 6 Science Chapter 6 – Comprehensive Concept Explanation
1. Classification of Changes: Reversible vs. Irreversible
Every change can be classified based on whether the original material can be retrieved after the change has occurred.
These two classifications are strongly related to the scientific terms for changes: Reversible Changes are usually **Physical Changes**, while Irreversible Changes are often **Chemical Changes**.
🔄 Reversible Changes ⇆
A change that can be undone or reversed by simply changing the conditions (like heating, cooling, stretching, or folding). The material’s fundamental nature does not change.
- Core Principle: No new substance is formed.
- Nature: Temporary.
- Examples:
- Melting of Ice: Ice ↔ Water ↔ Ice (Changing state).
- Stretching a Spring: Returns to original shape when force is removed.
- Blowing a Balloon: The size change is undone by releasing the air.
❌ Irreversible Changes →
A change that cannot be undone to get the original material back. These changes are permanent and involve a fundamental alteration of the substance.
- Core Principle: A **new substance** with different properties is formed.
- Nature: Permanent.
- Examples:
- Burning of Paper: Paper is converted to ash and smoke.
- Cooking an Egg: The proteins are permanently changed by heat.
- Souring of Milk: Bacteria convert lactose into lactic acid (curd).
2. Ways to Bring About Changes
Changes are caused by external factors, primarily the application of heat or the mixing of different substances.
Changes Caused by Heating
-
Expansion and Contraction: Most objects expand (increase in size) when heated and contract (decrease in size) when cooled. This is a reversible physical change.
Application: Metal Rim on a Cart Wheel: The smaller metal rim is heated to expand, fitted onto the wooden wheel, and then cooled with water to contract, creating a tight, permanent fit.
- Permanent Alteration: Heating can cause chemical changes, such as **baking** (dough to bread) or the **drying of Plaster of Paris (POP)**. Once POP is mixed with water and hardens, the change is irreversible.
Changes Caused by Mixing
- Dissolving: Mixing sugar and water is reversible because the water can be evaporated to recover the sugar crystals.
- Chemical Reaction: Mixing cement powder with water leads to a hard, solid mass that cannot be easily reversed, signifying a permanent chemical change.
3. Physical Changes vs. Chemical Changes
The concepts of reversibility often align with physical and chemical changes, which define the scientific nature of the transformation.
| Feature | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
|---|---|---|
| **Definition** | Change in physical properties (size, shape, state) only. | Change in chemical composition leading to **new substance(s)**. |
| **New Substance?** | **NO** new substance is formed (e.g., water remains H₂O). | **YES**, one or more new substances are formed. |
| **Reversibility** | Generally **Reversible**. | Generally **Irreversible**. |
| **Examples** | Melting, Boiling, Tearing, Cutting, Dissolving. | Burning, Rusting, Cooking, Ripening, Digestion. |
| **Clues** | No change in core identity. | Color change, Gas production, Heat/Light given off, New smell. |
- Feature: Definition**Physical:** Change in **form/state** only.**Chemical:** Change in **composition** (new substance).
- Feature: New Substance?**Physical:** **NO** new substance formed.**Chemical:** **YES**, new substance formed.
- Feature: Reversibility**Physical:** Generally Reversible.**Chemical:** Generally Irreversible.
- Feature: Examples**Physical:** Melting ice, Tearing paper.**Chemical:** Burning wood, Cooking food.
- Feature: Clues**Physical:** Identity unchanged.**Chemical:** Color/gas change, Heat/light given off.
Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Changes around us Oxford Book Answers
II. Very Short Answer Type Questions
A. Give two examples for the following:
- Physical changes – Melting of ice, Tearing of paper
- Chemical changes – Burning of wood, Rusting of iron
- Reversible changes – Freezing of water, Stretching of rubber band
- Irreversible changes – Burning of paper, Cooking of food
- Application of expansion – Fixing metal rims on wooden wheels, Railway tracks laid with gaps
B. Identify the type of changes that occur when the following happens:
- Breaking of a glass jar – Physical and irreversible change
- Making cottage cheese from milk – Chemical and irreversible change
- Powdering of sugar – Physical and reversible change
- Melting of ice – Physical and reversible change
III. Short Answer Type Questions
1. Compare reversible and irreversible changes by citing two examples of each.
Answer:
i) Reversible changes can be reversed to get the original substance. Example: Melting of ice, Dissolving salt in water. ii) Irreversible changes cannot be reversed. Example: Burning of paper, Rusting of iron.
2. Describe how baking a cake is an example of an irreversible reaction.
Answer:
When a cake is baked, heat causes chemical reactions between the ingredients. A new substance (cake) is formed which cannot be changed back into the original ingredients. Hence, it is an irreversible change.
3. Compare physical and chemical changes by giving two examples of each.
Answer:
Physical changes are changes in which no new substance is formed, and the change can often be reversed.
Examples: Melting of ice , Tearing of paper
Chemical changes are changes in which new substances are formed, and the change cannot be reversed. Examples: Burning of wood , Rusting of iron
4. Describe how breaking of glass is an irreversible and physical change.
Answer:
When glass breaks, its shape and size change, but no new substance is formed — this makes it a physical change. However, the broken glass cannot be joined back into its original form, which means the change cannot be reversed, so it is irreversible. Hence, breaking of glass is a physical but irreversible change.
5. What will happen if an inflated balloon is kept in the sun for some time?
Answer:
When an inflated balloon is kept in the sun, the air inside it gets heated and expands. As a result, the size of the balloon increases. If the heat is too much, the balloon may even burst due to the increased air pressure inside.
IV. Long Answer Type Questions
1. Describe how the three physical states of water can be changed from one state to another.
Answer: Water can exist as solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (steam).
On heating, ice melts to form water (melting).
On further heating, water becomes steam (evaporation).
On cooling, steam condenses to water (condensation), and water freezes to ice (freezing).
2. Which type of change—reversible or irreversible—takes place in each of the following cases? Give reasons.
a. Ripening of fruit – Irreversible change (cannot become unripe again)
b. Tearing of paper – Irreversible change (cannot be joined exactly as before)
c. Melting of ice cream – Reversible change (can be frozen again)
d. Curdling of milk – Irreversible change (curd cannot be turned back into milk)
3. Which type of change, physical or chemical ,takes place in each of the following cases? Give reasons for each
i) Baking a cake
ii) Burning of paper
iii) Tearing of paper
iv) Breaking of glass
Ans:
| Case | Type of Change | Reason |
| i) Baking a cake | Chemical Change | New substances with different properties are formed due to chemical reactions involving ingredients like flour, eggs, and leavening agents (e.g., baking soda or powder). The change is generally irreversible. |
| ii) Burning of paper | Chemical Change | The paper reacts with oxygen (combustion) to form completely new substances like ash, carbon dioxide, and water vapor (and releasing heat and light). This change is irreversible. |
| iii) Tearing of paper | Physical Change | Only the size and shape of the paper are altered. The chemical composition of the paper remains the same; it’s still cellulose. No new substance is formed. |
| iv) Breaking of glass | Physical Change | The glass is simply broken into smaller pieces. Its chemical composition (silica and other components) remains unchanged. It’s the same material, just in a different shape/size. No new substance is formed. |
4.Describe one example each of expansion in solids, liquid and gases
Ans:
| State of Matter | Example of Expansion | Description |
| Solid | Expansion Joints in Bridges and Railroad Tracks | Metal expands when heated. Gaps are deliberately left between sections of steel tracks or bridge spans. On a hot day, the metal expands and the gaps close up. This prevents the structure from buckling or cracking. |
| Liquid | Liquid-in-Glass Thermometer | The liquid (like mercury or colored alcohol) inside the thermometer bulb absorbs heat. The liquid expands significantly more than the glass tube, causing it to rise up the narrow, calibrated scale. This expansion allows for accurate temperature measurement. |
| Gas | Hot Air Balloon Lifting | Air (a gas mixture) inside the balloon’s envelope is heated by a burner. The air expands, causing its volume to increase and its density to decrease (as the same mass now occupies a larger space). The less dense hot air provides lift by floating upward in the denser, cooler surrounding air. |
5.Describe one example each of Contraction in solids, liquid and gases
Ans:
| State of Matter | Example of Contraction | Description |
| Solid | Overhead Power Lines/Cables in Winter | Metal wires, like electrical cables strung between poles, are deliberately left with some slack (sag) during warm weather. In the cold of winter, the metal contracts (gets shorter) significantly. The slack prevents the wires from becoming too taut and snapping or pulling down the poles. |
| Liquid | Falling Level in a Thermometer | When a thermometer is removed from a warm object and cools to room temperature, the liquid (mercury or alcohol) inside contracts (its volume decreases). This contraction causes the liquid column to fall back down the calibrated tube, indicating the drop in temperature. |
| Gas | Deflated Tires/Balloons in Cold Weather | When a car tire or an inflated balloon is exposed to very cold weather (e.g., overnight in winter), the gas (air) inside cools down. According to the gas laws, as the temperature decreases, the volume and/or pressure of the gas decreases, causing the tire or balloon to appear partially deflated or softer. |
More…Important Questions from Oxford Book
I. Objective type questions
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
1. Glass sheets and flower petals are examples of (smooth/rough) surfaces.
Answer: Smooth
2. (Hard/Soft) materials can be compressed easily.
Answer: Hard
3. Materials that allow some light to pass through them are called (transparent/translucent) materials.
Answer: Translucent
4. (Solids/Gases) are highly compressible.
Answer: Gases
5. Liquids that do not dissolve in water are called (immiscible/soluble) in water.
Answer: Immiscible
B. Choose the correct option.
1. Which of the following has a rough surface?
a) Sandpaper
b) Petals of a flower
c) Surface of an apple
d) Glass sheet
Answer: a) Sandpaper
2. Which of the following can be compressed to a small extent?
a) Gases
b) Liquids
c) Solids
d) None of these
Answer: b) Liquids
3. Which of the following is translucent?
a) Cellophane paper
b) Oiled paper
c) Water
d) Wood
Answer: a) Cellophane paper
4. Which of the following is a characteristic feature of a solid?
a) It has no definite shape.
b) It is highly compressible.
c) It has no definite volume.
d) Its particles are closely packed.
Answer: d) Its particles are closely packed.
5. Which of the following is insoluble in water?
a) Common salt
b) Sugar
c) Wax
d) Carbon dioxide
Answer: c) Wax
6. Which of the following is a conductor of heat?
a) Metals
b) Plastic
c) Bamboo
d) Glass
Answer: a) Metals
7. Which of the following states of matter has close packing of particles?
a) Solid state
b) Liquid state
c) Gaseous state
d) All of these
Answer: a) Solid state
8. Which of the following materials will sink in water?
a) Wood
b) Feather
c) Rock
d) Leaf
Answer: c) Rock
9. Which of the following gases is soluble in water?
a) Hydrogen
b) Nitrogen
c) Helium
d) Carbon dioxide
Answer: d) Carbon dioxide
10. Which of the following is a conductor of electricity?
a) Air
b) Copper wire
c) Plastic
d) Wood
Answer: b) Copper wire
II. Very short answer type questions
1. Give two examples of soft materials.
Answer: Cotton, Rubber
2. Give two examples of transparent materials.
Answer: Glass, Water
3. Give two examples of opaque materials.
Answer: Wood, Metal
4. Give two examples of gases insoluble in water.
Answer: Oxygen, Nitrogen
5. Give two examples of magnetic materials.
Answer: Iron, Nickel
6. Give two examples of insulators of heat.
Answer: Wood, Plastic
B. Give one word for the following:
1. Materials that have uneven or bumpy surface.
Answer: Rough materials
2. Materials that do not allow light to pass through them.
Answer: Opaque materials
3. Liquids that are soluble in water.
Answer: Miscible liquids
4. Materials that are attracted to a magnet.
Answer: Magnetic materials
5. Materials that do not have a definite shape and volume.
Answer: Gases
III. Short answer type questions
1. Which property of metals makes them suitable for making jewellery?
Answer: Metals are malleable and ductile, so they can be drawn into wires and sheets to make jewellery.
2. Compare hard and soft materials with one example of each.
Answer: Hard materials cannot be easily compressed (e.g., Iron). Soft materials can be easily compressed (e.g., Rubber).
3. What is floatation?
Answer: The tendency of lighter objects to float and heavier objects to sink in water is called floatation.
4. Why are cooking utensils made of metals while their handles are made of wood or hard plastic?
Answer: Metals are good conductors of heat, so they help in cooking. Wood and hard plastic are insulators, so they are used for handles to protect from heat.
5. Why are electric cables made of metal wires?
Answer: Because metals are good conductors of electricity.
6. What are conductors and insulators of electricity? Give one example of each.
Answer: (i) Conductors: Materials that allow electricity to pass (e.g., Copper). (ii) Insulators: Materials that do not allow electricity to pass (e.g., Plastic).
IV. Long answer type questions
1. Differentiate between transparent, translucent and opaque. Give two examples for each.
Answer: Materials can be classified based on how they allow light to pass through them: Examples: Wood, cardboard.
Transparent materials –(i) These materials allow light to pass through them completely. (ii)Objects can be seen clearly through them. Examples: Clear glass, clean water.
Translucent materials –(I) These materials allow light to pass through them only partially. (ii) Objects cannot be seen clearly, they appear blurred or unclear. Examples: Oiled paper, frosted glass.
Opaque materials –(i) These materials do not allow light to pass through them at all. (ii) Objects cannot be seen through them.
2. What is magnetism? Describe an activity to differentiate between magnetic and non-magnetic substances.
Magnetism is a force of attraction or repulsion that acts between certain materials, mainly those made of iron, nickel, cobalt, and some alloys. It arises due to the motion of electric charges, especially the movement of electrons inside atoms.
Activity to Differentiate Between Magnetic and Non-magnetic Substances – This simple activity helps you to classify objects based on their magnetic properties.
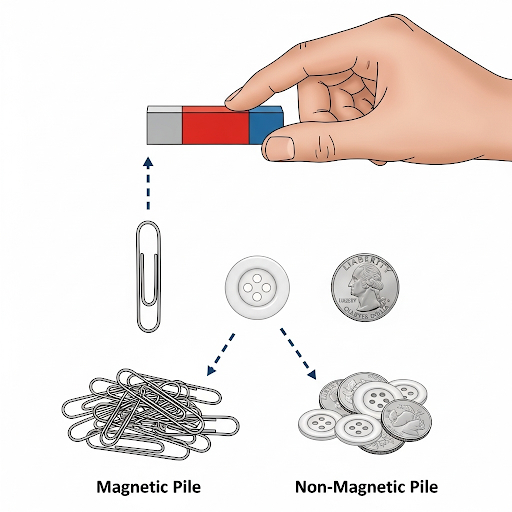
Materials:
A magnet (bar magnet or horseshoe magnet) Various small objects: Magnetic: Paperclip, iron nail, steel key, pin Non-magnetic: Plastic ruler, rubber band, wooden stick, glass marble, aluminum foil, paper
Procedure:
1. Gather the objects and place them on a table or a flat surface. 2. Take the magnet and slowly bring it close to each object, one at a time. 3. Observe what happens. If an object is pulled toward the magnet, it is a magnetic substance. 4. If an object does not react to the magnet, it is a non-magnetic substance. 5. Record your observations in a two-column chart to organize your findings. This will help you see which materials are magnetic and which are not.
This activity demonstrates that magnetism is a property of specific materials and not all objects, even those made of metal, are attracted to a magnet.
3. Describe grouping of materials depending upon their solubility in water.
Answer: Materials can be grouped into two main types based on their solubility in water: (i) Soluble materials – These are substances that completely dissolve in water. Example: sugar, salt, lemon juice. (ii) Insoluble materials – These are substances that do not dissolve in water. They remain separate and settle down or float. Example: sand, chalk powder, oil.
Thus, depending on whether a material dissolves in water or not, we can classify it as soluble or insoluble.
Changes Around Us: Review Worksheet
Class 6 Science | Chapter 6
1. A change that results in the formation of one or more new substances is called a(n) change.
2. Most substances tend to when heated and contract when cooled.
3. The process of turning milk into curd is an example of a(n) change.
4. Changes affecting only the size, shape, or state of a substance are called changes.
5. The symbol **⇆** represents a change.
Classify the following changes as **Reversible** (R) or **Irreversible** (I) by writing the correct letter in the box.
1. Melting of wax.
2. Burning of a candle.
3. Tearing a piece of paper.
4. Dissolving salt in water.
5. Rusting of iron.
Complete the table to distinguish between Physical and Chemical Changes based on the features given.
| Feature | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
|---|---|---|
| **New Substance Formed?** | ||
| **Example of Reversibility** | ||
| **Change in Composition** |
1. Explain how the principle of expansion and contraction is used to fix a metal rim tightly onto a wooden wheel.
2. Give two visible clues that indicate a chemical change has occurred.
Math & Science Solutions by Class
Class 10
Class 9
Class 8
Class 7
Class 6
Class 12
- Class 12 Math Solutions
- Class 12 Physics Solutions Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
In this lesson, we explored different types of changes happening around us, such as reversible and irreversible changes, and how they affect our daily life. Understanding these ideas in Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Changes around us Oxford helps students relate science to real-world situations. By studying Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Changes around us Oxford, learners become more observant and aware of the changes in nature and the environment.
