Fun with Magnets Class 6 Science Oxford CBSE chapter helps students understand the amazing world of magnets. This lesson explains what magnets are, their poles, how they attract or repel, and their different shapes. It also teaches the uses of magnets in our daily life and simple experiments to identify magnetic properties. On this page, you will get all the important questions and answers from the Oxford CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12, explained in a clear and easy way to support learning and quick revision.

Fun with Magnets Class 6 Science Oxford CBSE Textbook Answers
I. Objective type questions
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words
- A magnet will attract a piece of iron.
- A ring magnet has two magnetic poles.
- The Earth has magnetic properties.
- Bar magnets should be stored in pairs with unlike poles alongside each other.
- Applying heat can destroy a magnet.
B. Choose the correct option
- The number of magnetic poles in a horseshoe magnet is — b. two
- If we run a magnet through iron filings, most of the iron filings will stick to the — d. both the north and the south poles
- A magnetic compass aligns in the — b. North–South direction
- When we bring two magnets together, they will — d. attract each other if the south pole of one magnet is facing the north pole of the other
- A magnet that can retain its magnetic properties for a very long time is called a — b. permanent magnet
- Which of these materials will a magnet stick to? — a. Iron
- A magnet attracts objects made of — d. all of these (iron, nickel, cobalt)
- Magnets can be made in which of the following shapes? — d. All of these (Ring, Bar, Horseshoe)
- If we break a magnet into two pieces, and both pieces retain their magnetic property, we will find that each piece has — b. two poles
- The South pole of a magnet repels — b. the South of another magnet
II. Very short answer type questions
A. Give one word for the following
- An object that attracts certain substances such as iron, nickel or cobalt — Magnet
- Parts of a magnet where the magnetic strength is the strongest — Poles
- A magnetic instrument used to find directions — Magnetic compass
B. Give two examples for the following
- Shapes of magnets — Bar, Horseshoe
- Materials that are not attracted to a magnet — Wood, Plastic
- Types of magnets — Permanent magnet, Electromagnet
III. Short answer type questions
1. What is a magnetic compass used for?
A magnetic compass is used to find direction; its needle aligns with Earth’s magnetic field showing North–South direction.
2. How do small pieces of iron behave when brought close to a magnet?
Small pieces of iron are attracted and move toward the magnet; they collect at the magnet’s poles.
3. How does a magnet behave when brought close to another magnet?
Two magnets either attract or repel each other depending on which poles face each other: opposite poles attract, like poles repel.
4. What are the materials used to make a permanent magnet?
Steel, cobalt, nickel, and special alloys like alnico and ferrite are used.
5. Give one property of a permanent magnet.
A permanent magnet retains its magnetic properties for a very long time.
6. Why does a freely suspended magnet always align itself in a certain direction?
Because Earth acts like a giant magnet; the suspended magnet aligns with Earth’s magnetic field so its north-seeking pole points toward geographic north.
IV. Long answer type questions
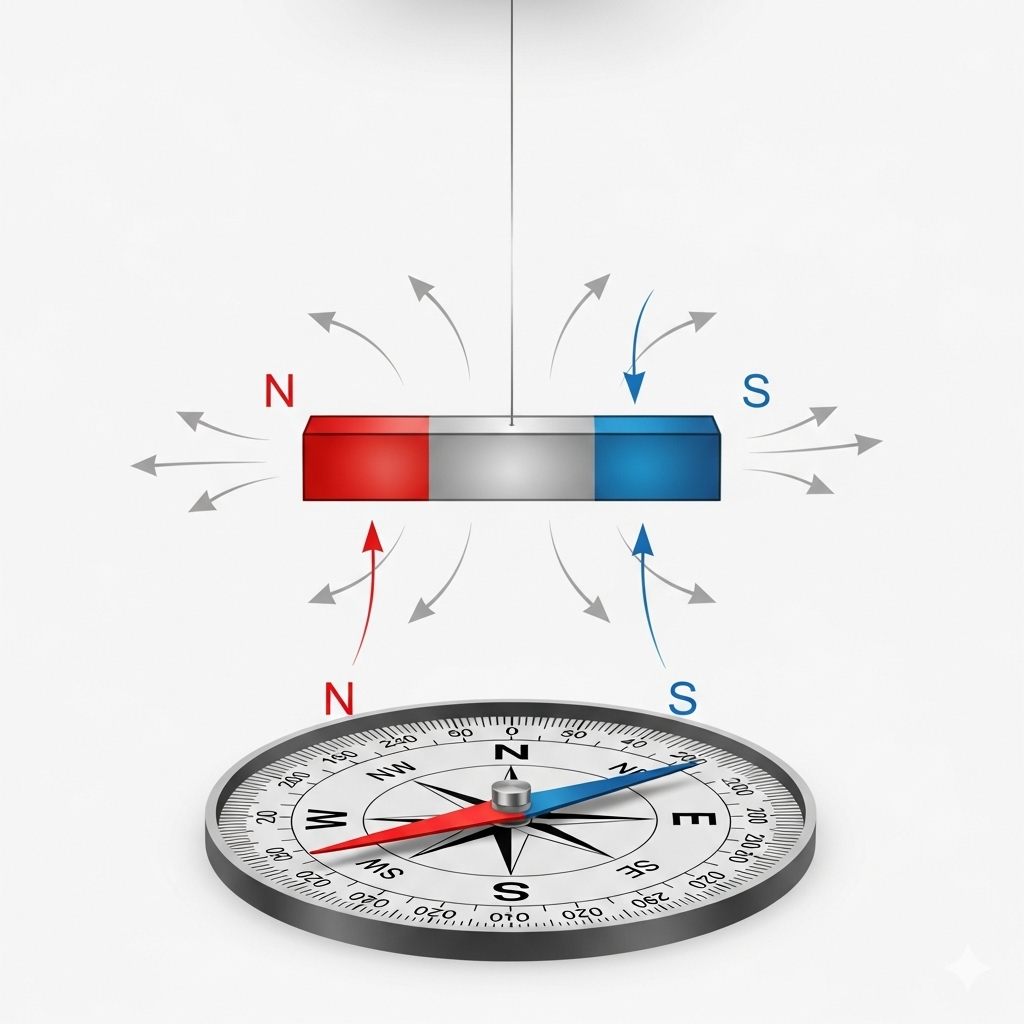
1. Give a short description of any activity to find the poles of a given magnet.
Ans: Activity Description
- To find the poles of a magnet, you can perform a simple activity by freely suspending it.
- The end of the magnet pointing towards the geographic north is its North pole, and the end pointing towards the geographic south is its South pole. This principle is what makes a compass work.
- Take a bar magnet and tie a thread around its center.
- Hold the thread and suspend the magnet so it can swing freely.
- Wait for the magnet to come to rest. The ends of the magnet will align themselves in the north-south direction of the Earth.
2. Explain a simple method by which an iron needle can be magnetized.
Ans:
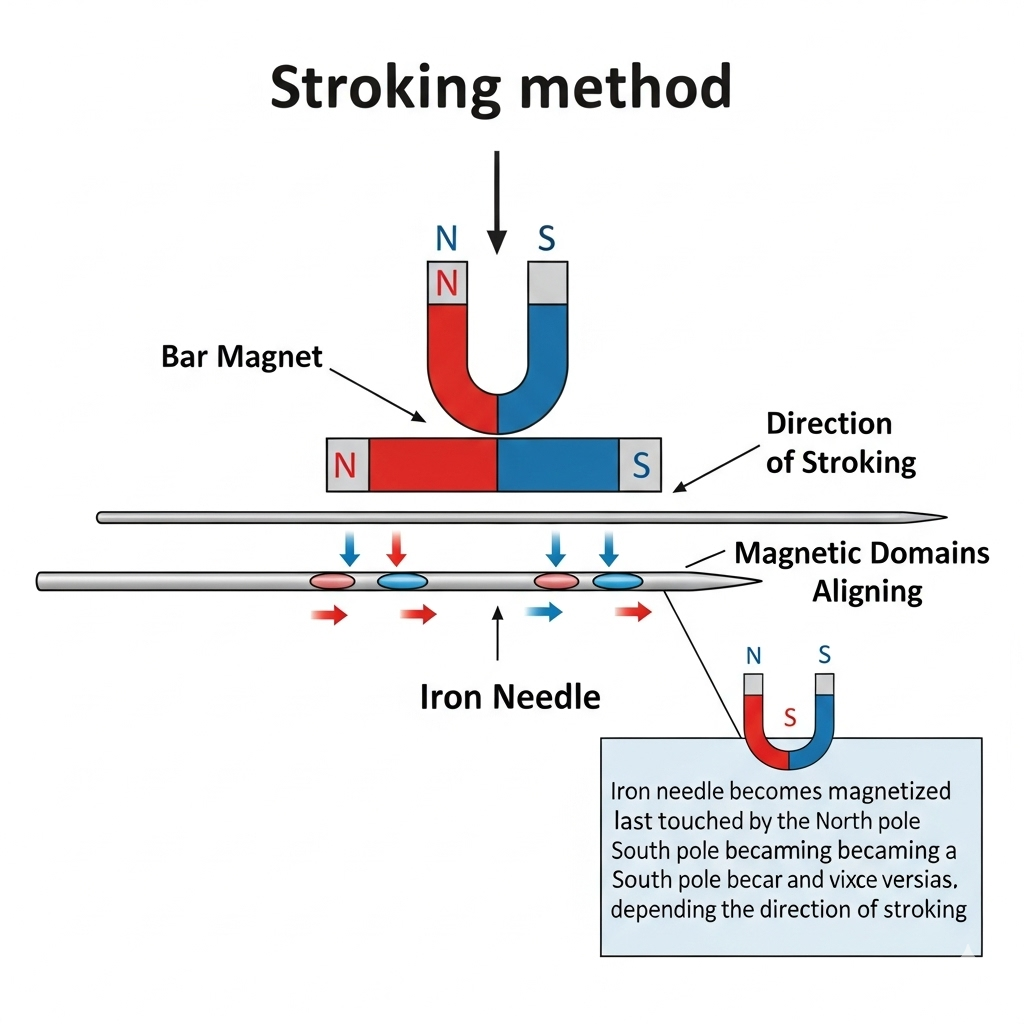
A simple and effective method to magnetize an iron needle is the single-touch stroking method. This process aligns the magnetic domains within the iron needle, turning it into a temporary magnet.
Steps:
- Take a powerful magnet (like a bar magnet).
- Place the iron needle on a flat surface.
- Hold one pole of the bar magnet (e.g., the North pole) and stroke the iron needle from one end to the other, lifting the magnet completely off the needle after each stroke.
- Repeat this process for about 20-30 times, always stroking in the same direction and using the same pole of the magnet.
Explanation:
Inside unmagnetized iron, the tiny magnetic regions called magnetic domains are randomly arranged. When you stroke the iron needle with a magnet, the strong magnetic field of the magnet forces these domains to align in the same direction. The end of the needle where you start the stroke will acquire the same polarity as the stroking magnet’s pole, while the other end will acquire the opposite polarity. The more you stroke, the more aligned the domains become, and the stronger the resulting magnetism of the needle.
3. Write a short note on ‘Care of Magnets’.
- Do not drop, hammer, or heat magnets as they lose magnetism.
- Store bar magnets in pairs with opposite poles together and keepers across the ends.
- Keep away from moisture and corrosive substances.
- Avoid placing magnets near sensitive electronic devices.
4. What are magnets used for?
Magnets are used in compasses for navigation, in electric motors and generators, in loudspeakers, in magnetic storage devices, in medical imaging (MRI), in lifting heavy scrap iron, in maglev trains, and in many household items like fridge magnets and magnetic clasps.
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
NEET BIOLOGY
- Evolution
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Human Health and Disease
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
You can access the official NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics on the NCERT website at the following link:
NCERT Class 10 Mathematics Solutions
This page will guide you to the textbook and solutions, as provided by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT).
