The CBSE Class 10 Sample paper 2025-26 serves as a vital introductory tool for students preparing for their board examinations. Its primary function is to familiarize students with the revised format, new types of questions, and the overall difficulty level they can expect. By analyzing this paper, students can gain a clear understanding of the weightage of different topics and sections, enabling them to strategize their study plan effectively.

This introductory document is not just a collection of questions; it’s a window into the pedagogical approach of the CBSE. It emphasizes a shift towards conceptual understanding and critical thinking, moving away from rote memorization. The paper features application-based questions, case studies, and integrated questions that test a student’s ability to apply scientific principles to real-world scenarios. It also introduces new formats, such as assertion-reasoning questions and image-based problems, which require a different kind of analytical skill.
CBSE Class 10 Sample paper 2025-26 (Answers)
Section A: Biology
1. Select the group in which all organisms have the same mode of nutrition.
- A. Cuscuta, yeast, legumes, leeches and tapeworm
- B. Cactus, ticks, lice, leeches and cow
- C. Cuscuta, ticks, lice, leeches and tapeworm
- D. Cactus, grass, lice, lion and tapeworm
Answer and Reason: The correct option is C. All organisms in this group are parasites, which have a parasitic mode of nutrition. Cuscuta is a parasitic plant, while ticks, lice, leeches, and tapeworms are all parasitic animals. They depend on a host for their nutrition.
2. Which of the following options indicates the products formed after breakdown of the glucose in our muscle cells when there is lack of oxygen?
- A. Ethanol + carbon dioxide + Energy
- B. Lactic acid + Energy
- C. Lactic acid + carbon monoxide + Energy
- D. Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
Answer and Reason: The correct option is B. When there is a lack of oxygen in muscle cells, glucose breaks down into lactic acid and energy through anaerobic respiration.
3. Which of the following is a correct combination of function and part of the brain?
- A. Posture and balance: Cerebrum
- B. Salivation: Medulla in midbrain
- C. Hunger: Pons in hindbrain
- D. Blood pressure: Medulla in hindbrain
Answer and Reason: The correct option is D. The medulla, located in the hindbrain, is responsible for controlling involuntary actions, including blood pressure.
4. The blood glucose level in a patient was very high. It may be due to inadequate secretion of:
- A. growth hormone from pituitary gland
- B. oestrogen from ovary
- C. insulin from pituitary gland
- D. insulin from pancreas
Answer and Reason: The correct option is D. The hormone insulin, secreted by the pancreas, regulates blood glucose levels. Inadequate secretion of insulin leads to a high blood glucose level
5. In a cross between black furred rabbit (B) and white furred rabbit (b), all offspring were found to have black fur. What can be inferred about the genetic makeup of the parent rabbits?
- A. BB X bb
- B. Bb X Bb
- C. Bb X bb
- D. bb X bb
Answer and Reason: The correct option is A. The fact that all offspring have black fur indicates that the black fur allele (B) is completely dominant over the white fur allele (b). For all the offspring to exhibit the dominant trait (black fur), one parent must be homozygous dominant (BB) and the other must be homozygous recessive (bb). The cross BB x bb would produce all heterozygous Bb offspring, all of which would have black fur.
6. Which are the correct statements related to ozone?
- (i) Ozone layer helps in increasing the UV radiations reaching earth.
- (ii) Ozone is a deadly poison.
- (iii) Ozone layer shields the earth from UV radiations.
- (iv) Ozone layer prevents UV rays which cause skin cancer.
- (v) Ozone is formed with the help of Chloroflurocarbons.
- A. (i), (ii), (iii)
- B. (ii), (iii), (iv)
- C. (iii), (iv), (v)
- D. (i), (iv), (v)
Answer and Reason: The correct statements are (ii), (iii), and (iv). Ozone is a deadly poison. The ozone layer in the stratosphere acts as a shield, protecting the Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which is known to cause skin cancer. Statements (i) and (v) are incorrect. The ozone layer
7. Which of the following human activities has resulted in an increase of non-biodegradable substances?
- A. Organic farming
- B. Increase in tree plantation
- C. Use of plastic as packaging material
- D. Composting of kitchen waste
Answer and Reason: The correct option is C. Plastic is a non-biodegradable substance. The widespread use of plastics for packaging has led to an increase in non-biodegradable waste in the environment.
8. Assertion (A): Tallness of a pea plant is controlled by an enzyme. Reason (R): The gene for that enzyme makes proteins which help the plant to be tall.
- A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
- C. A is true but R is false.
- D. A is false but R is true.
Answer and Reason: The correct option is A. Both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason provides the correct explanation for the assertion. A gene contains the information to synthesize proteins, some of which function as enzymes. These enzymes control metabolic pathways that determine physical traits like the tallness of a plant
9. Assertion (A): Vulture will always have the least amount of pesticides in a food chain. Reason (R): Vulture occupies the last trophic level and it gets only 10% of energy of the previous trophic level.
- A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
- C. A is true but R is false.
- D. A is false but R is true.
Answer and Reason: The correct option is D. The assertion is false because of biomagnification; the concentration of pesticides increases at each successive trophic level. Therefore, a vulture, which is at the highest trophic level, will have the highest concentration of pesticides. The reason is a true statement, as only about 10% of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
10. Unlike animals, plants do not have any excretory products as they do not eat food. Comment upon the statement with justification.
Answer and Justification: The statement is incorrect. While plants do not eat food like animals do, they still perform metabolic activities, such as photosynthesis and respiration, which produce waste products
. They have several ways of getting rid of these waste products. Some waste products are stored in cellular vacuoles or in dead tissues like old xylem
. The plants can also excrete wastes through their leaves, which are later shed, or through their roots into the soil.
11. Students to attempt either option A or B.
A. How many chambers are there in the heart of the following organisms? How is mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood prevented in their body? (i) Fishes (ii) Humans
OR
B. Explain the mechanism by which the water is transported in plants?
Ans- A-
(i) The heart of a fish has two chambers. There is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood because the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the gills for oxygenation, and this blood then flows directly to the body.
(ii) The human heart has four chambers. The mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is prevented by the septum, a muscular wall that separates the left and right sides of the heart.
Ans- B
Answer: Water is transported in plants through the xylem tissue. This transport is primarily driven by transpiration pull, where water vapor lost from the leaves creates a suction force that pulls water up from the roots. This process is aided by the cohesive and adhesive properties of water molecules, which help to maintain a continuous column of water in the xylem vessels
12. About 100 acres of forest land was declared as Natural reserve park. The following organisms were predominant in the Natural reserve park: rabbit, frog, grass, fish, fox, water insects, zebra, peacock, snake, trees, bird, owl, insects, tiger, vulture, duck. Create a food web comprising two separate food chains with different producers by using the above data.
Ans: Here are two food chains from the data provided:
- Food chain 1: Grass → Zebra → Lion
- Food chain 2: Trees → Water insects → Frog → Snake → Vulture
13. Draw and explain how the nerve cells help in transmission of impulses?
Ans: Nerve cells, also known as neurons, are specialized cells that transmit electrical impulses throughout the body. They are the fundamental units of the nervous system. A neuron has three main parts:
Dendrites: These are tree-like extensions that receive nerve impulses from other neurons.
Cell Body (Soma): This part contains the nucleus and integrates the incoming signals.
Axon: This is a long, slender projection that transmits the nerve impulse away from the cell body to other neurons or target cells.
Transmission of Impulses– The transmission of a nerve impulse is an electrochemical process.
Signal Reception: An impulse is received by the dendrites of a neuron. Signal Integration: The impulse travels to the cell body, where the signals are processed. Signal Propagation: The impulse then moves down the axon as an electrical signal.
14. In a genetic experiment, plants with pure round green seeds (RRyy) were crossed with plants with wrinkled yellow seeds (rrYY).
(i) Show the gametes formed when F1 was self-pollinated.
(ii) A total of 144 seeds were produced which developed into saplings.
Show the ratio in which these traits are independently inherited in these 144 sapling.
Answer:
(i) A cross between a pure round green seed plant (RRyy) and a wrinkled yellow seed plant (rrYY) will result in a F₁ generation with the genotype RrYy (round and yellow). When this F₁ plant is self-pollinated, the gametes formed will be RY, Ry, rY, and ry.
(ii) For a dihybrid cross, the phenotypic ratio for the traits that are independently inherited is 9:3:3:1.
- Round Yellow: (9/16) * 144 = 81
- Round Green: (3/16) * 144 = 27
- Wrinkled Yellow: (3/16) * 144 = 27
- Wrinkled Green: (1/16) * 144 = 9
15. Neha consumed boiled sweet potatoes and boiled eggs for breakfast…
A. Neha consumed boiled sweet potatoes and boiled eggs for breakfast. Help her to understand some steps in the process of digestion of the food taken by her by answering the questions given below.
(Attempt either subpart A or B.)
A. Which of these food items is rich in proteins? In which part of the alimentary canal is the digestion of this component initiated?
Name the enzymes, conditions required and the glands associated with the digestion here.
OR
B. Which of these food items contains fats? How is it digested?
C. Which of these food items is rich in starch? How is its digestion initiated?
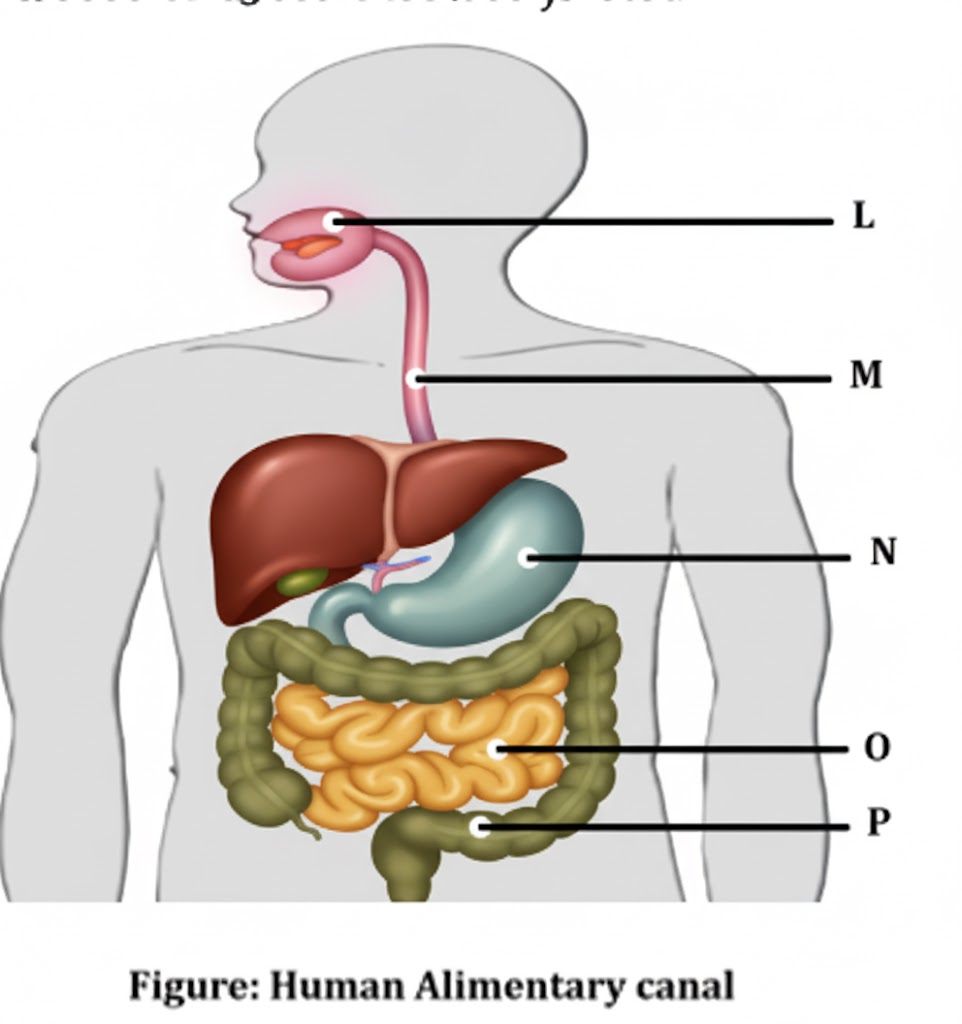
D. The figure given below represents parts of the human alimentary canal.
Which of these parts will have the maximum amount of digested food as soon as the process of digestion is completed?
(For visually impaired students)
D. How will the digested food be taken up by the alimentary canal?
Ans: Boiled egg is rich in proteins. The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach where the gastric glands secrete gastric juice containing pepsin enzyme and hydrochloric acid (HCl). Pepsin breaks down proteins into simpler peptides, while HCl provides the acidic medium necessary for enzyme activity. Further digestion of proteins takes place in the small intestine by trypsin and peptidase enzymes secreted from the pancreas and intestinal glands, finally converting proteins into amino acids.
Ans: Boiled egg yolk contains fats. The digestion of fats occurs in the small intestine. Bile juice from the liver, stored in the gall bladder, emulsifies large fat globules into tiny droplets to increase the surface area for enzyme action. Then, the enzyme lipase from the pancreas breaks down these fat droplets into fatty acids and glycerol. This process takes place in an alkaline medium provided by bile.
Ands: Boiled sweet potato is rich in starch, which is a complex carbohydrate. The digestion of starch begins in the mouth, where the salivary glands secrete saliva containing the enzyme salivary amylase (ptyalin). This enzyme breaks down starch into maltose, a simpler sugar. The slightly alkaline medium in the mouth helps salivary amylase to act effectively. The digestion of starch continues in the small intestine, where pancreatic amylase further converts it into glucose, which can then be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Ans: The maximum amount of digested food is found in the small intestine once the process of digestion is completed. The walls of the small intestine have numerous finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption. These villi are richly supplied with blood capillaries that absorb the end products of digestion — glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, and glycerol — and transport them to different parts of the body through the bloodstream.
Answer: (D) After digestion, the small intestine absorbs the digested food through its inner wall, which is lined with tiny finger-like projections called villi.
These villi increase the surface area for absorption. The blood capillaries present inside the villi absorb glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, and glycerol and transport them to all parts of the body through the bloodstream. Thus, the digested food is taken up by the alimentary canal and distributed for energy, growth, and repair.
16. Attempt either option A or B.
A. Puneet wanted to grow banana plants.
(i) Based on your knowledge on plant reproduction, should he opt for seeds or any alternate method of reproduction? Justify your answer.
(ii) Offsprings of a banana plant usually show very little variation. What causes variation and are variations good or bad? Justify.
OR
B. Annie was conducting research on the number of fruits produced by watermelon under different conditions. She grew 25 watermelon plants each in both glass house A and B. She introduced pollinators in glass house A only.
(i) What difference will she observe in the number of fruits produced in the two glass houses? Explain with reason.
(ii) List three changes that will occur in a flower once it gets fertilized.
Ans-A
Ans: He should use an alternate method of reproduction, such as vegetative propagation by suckers or rhizomes. This method produces new banana plants identical to the parent plant and is faster and more reliable than growing from seeds.
Ans: (ii) Offsprings of a banana plant show very little variation because they are produced asexually. In asexual reproduction, only one parent is involved, and the offspring receive identical genetic material, resulting in no or very few variations.
However, variations are useful in the long term, as they help species adapt to changing environments and survive better
Ans-B
Ans: (i) In glass house A, where pollinators were introduced, Annie will observe more fruits compared to glass house B, where pollinators were absent.
This is because pollination (transfer of pollen from anther to stigma) is necessary for fertilization and fruit formation. Without pollinators, flowers will not get fertilized, leading to fewer or no fruits.
Ans: (II) Once a flower is fertilized, the following three changes occur: The petals, sepals, and stamens wither and fall off, while the ovary wall may develop into the fruit wall (pericarp). The ovary develops into a fruit. The ovules change into seeds.
Section B: Chemistry
17. Which of the following equations represent redox reactions and what are the values for ‘p’ and ‘q’ in these equations?
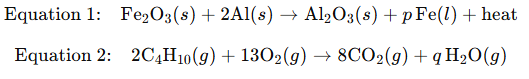
Options:
A. Only equation 1 is a redox reaction, p = 1 and q = 3
B. Both equations 1 and 2 are redox reactions, p = 2 and q = 4
C. Only equation 2 is a redox reaction, p = 2 and q = 10
D. Both equations 1 and 2 are redox reactions, p = 2 and q = 10
Ans: The correct answer is D. Both equations 1 and 2 are redox reactions, p=2 and q=10 . Both are redox reactions because oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously. In equation 1, aluminum is oxidized and iron is reduced. In equation 2, the hydrocarbon is oxidized and oxygen is reduced. By balancing the equations, we find p=2 and q=10.
18. Four statements about the reactions of oxides with dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide are listed.
I. Aluminium oxide reacts with both dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
II. Calcium oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
III. Zinc oxide reacts with both dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
IV. Sulphur dioxide does not react with either dilute hydrochloric acid or aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Which statements are correct?
Options:
A. I and II
B. I and III
C. II and IV
D. III and IV
Ans: The correct answer is B. I and III .
Statement I is correct as aluminum oxide is amphoteric and reacts with both acids and bases. Statement III is also correct as zinc oxide is amphoteric and reacts with both acids and bases. Calcium oxide is a basic oxide and only reacts with acids, and sulfur dioxide is an acidic oxide and only reacts with bases.
19 : An iron nail is added to each of the two test tubes ‘P’ and ‘Q’ containing aqueous copper(II) sulphate and aqueous silver nitrate respectively. Which of the following observation is correct?
A. In test tube ‘P’ iron nail is coated with a blue coating and in test tube ‘Q’ there is no reaction.
B. Iron nail is coated with a brown coating in test tube ‘P’ and silver coating in test tube ‘Q’.
C. There is no reaction in either of the test tubes ‘P’ or ‘Q’.
D. There is no reaction in test tube ‘P’ but a silver coating on iron nail is seen in test tube ‘Q’.
Ans: The correct answer is B. Iron nail is coated with a brown coating in test tube ‘P’ and silver coating in test tube ‘Q’ .
Iron is more reactive than both copper and silver. In test tube P, iron displaces copper, leading to a brown coating of copper on the nail. In test tube Q, iron displaces silver, resulting in a silver coating on the nail.
20 : Methyl orange is added to dilute hydrochloric acid and to aqueous sodium hydroxide.
What is the colour of the methyl orange in each solution?
| Sample | Colour in dilute HCl | Colour in aqueous NaOH |
|---|---|---|
| A | Orange | Red |
| B | Red | Yellow |
| C | Red | Orange |
| D | Yellow | Red |
Ans: Methyl orange is an acid–base indicator: In acidic solution (HCl) → it turns red. In basic solution (NaOH) → it turns yellow. Thus, the correct observation is Red in dilute HCl and Yellow in NaOH solution.
21. Which of the following substances when dissolved in equal volume of water, will have the highest pH value?
A. Sulphuric acid
B. Acetic acid
C. Magnesium hydroxide
D. Sodium hydroxide
Ans: The correct answer is D. Sodium hydroxide. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a strong base, which dissociates completely in water to produce a high concentration of hydroxide ions, resulting in a high pH value.
22. When excess of carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, the milkiness disappears because
A. Water soluble calcium carbonate converts to water soluble calcium bicarbonate.
B. Insoluble calcium carbonate converts to water soluble calcium bicarbonate.
C. Water soluble calcium carbonate converts to insoluble calcium bicarbonate.
D. Insoluble calcium carbonate converts to insoluble calcium bicarbonate.
Ans: The correct answer is B. insoluble calcium carbonate converts to water soluble calcium bicarbonate. The initial milkiness is caused by the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate. When excess carbon dioxide is added, it reacts with the calcium carbonate and water to form soluble calcium bicarbonate, which makes the solution clear again.
23. In the reaction of aqueous solution of barium chloride with aqueous solution of sodium sulphate, the aqueous solution formed will be:
A. BaCl₂
B. BaSO₄
C. Na₂SO₄
D. NaCl
Ans: The correct answer is D. Sodium chloride (NaCl) . This is a double displacement reaction that produces an insoluble precipitate of barium sulfate (BaSO4) and a soluble aqueous solution of sodium chloride (NaCl).
24. Assertion (A): C4H8, C4H6 and C4H10 are members of the same homologous series. Reason (R): C4H8, C4H6, C3H4, C3H6, C2H4, C2H2 are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true.
Ans:
Assertion (A): C₄H₈, C₄H₆ and C₄H₁₀ are members of the same homologous series.
Reason (R): C₄H₈, C₄H₆, C₃H₄, C₃H₆, C₂H₄, C₂H₂ are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Correct Option: C — Assertion is true but Reason is false.
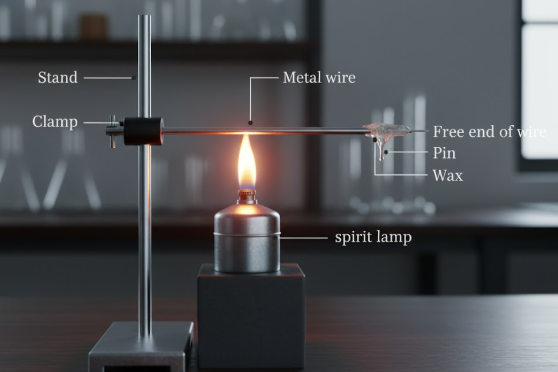
25. The following activity is set-up in the science lab by the teacher. He clamped an aluminium wire on a stand and fixed a pin to the free end of the wire using wax. Then he heated the wire with a burner from the end where the wire is clamped. Students observed the pin fall off.
A. If the teacher replaces aluminium wire by silver wire, will the students’ observation change? Justify your answer.
B. Will the aluminium wire melt? Give reason for your answer.
Ans:
A. No — the observation (pin falling off) will not change.
The pin falls because heat from the burner travels along the wire and melts the wax holding the pin. Both aluminium and silver will conduct heat to the wax, so the wax will melt and the pin will fall. (Silver conducts heat faster than aluminium, so the pin may fall slightly sooner with silver, but the outcome — pin falling — remains the same.)
B. No — the aluminium wire will not melt under this demonstration.
Aluminium has a high melting point (~660°C) and in this setup the wax melts long before the wire reaches its melting temperature; heat is also dissipated along the wire and into the clamp. Thus the wax melts and the pin falls while the aluminium wire remains solid.
26. Attempt either option A or B.
A. An element ‘X’ is stored in kerosene and cannot be extracted from its ore using a reducing agent. ‘X’ forms an ionic compound on reaction with chlorine.
(i) Can we store ‘X’ in water? Give reason to support your answer.
(ii) Identify element ‘X’. Name the process used and write the equation for extraction of ‘X’ from its ore.
OR
B. The domes of many buildings in Europe are made of copper. These domes now appear greenish in colour.
(i) Why do the domes appear greenish though copper is orange-red in colour?
(ii) In your opinion, should the copper domes be replaced by iron domes to overcome the problem of change of colour of copper domes?
(iii) Domes used to be made from thin sheets of metals. Why did the ancient architects use copper to make domes?
Answer: A.
(i) No, we cannot store ‘X’ in water because it reacts vigorously with water, producing hydrogen gas and heat, which may cause an explosion.
(ii) The element ‘X’ is sodium (Na).
It is stored in kerosene to prevent reaction with moisture and air.
It cannot be extracted by a reducing agent because it is highly reactive and found in the form of compounds.
It is extracted by electrolysis of molten sodium chloride (NaCl).
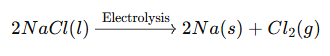
Ans- B
(i) The domes appear greenish because copper reacts slowly with carbon dioxide, oxygen, and moisture in the air to form a green coating of basic copper carbonate [CuCO₃·Cu(OH)₂].
(ii) No, copper domes should not be replaced by iron domes. Iron corrodes easily and forms rust (Fe₂O₃·xH₂O), which weakens the metal. The green coating on copper actually protects it from further corrosion.
(iii) Copper was used because it is malleable, durable, and resistant to corrosion. It can be easily shaped into thin sheets and lasts long even when exposed to air and rain.
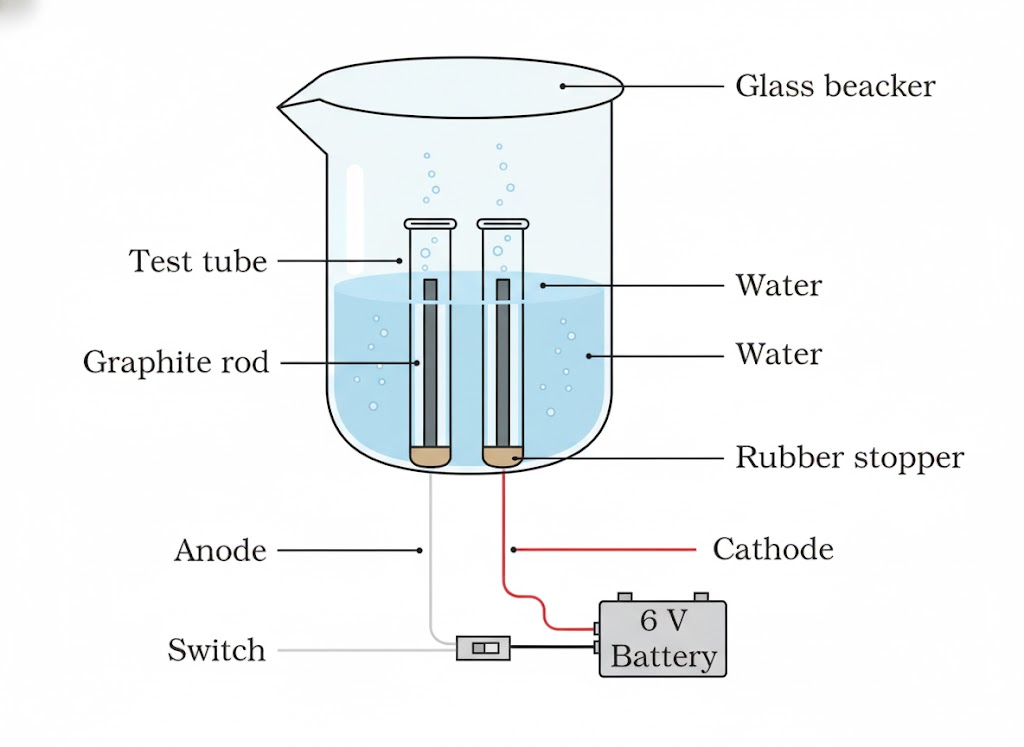
27. Amrita electrolysed distilled water using the set-up shown in Figure 1. She was expecting two gases to be evolved at the anode and cathode respectively.
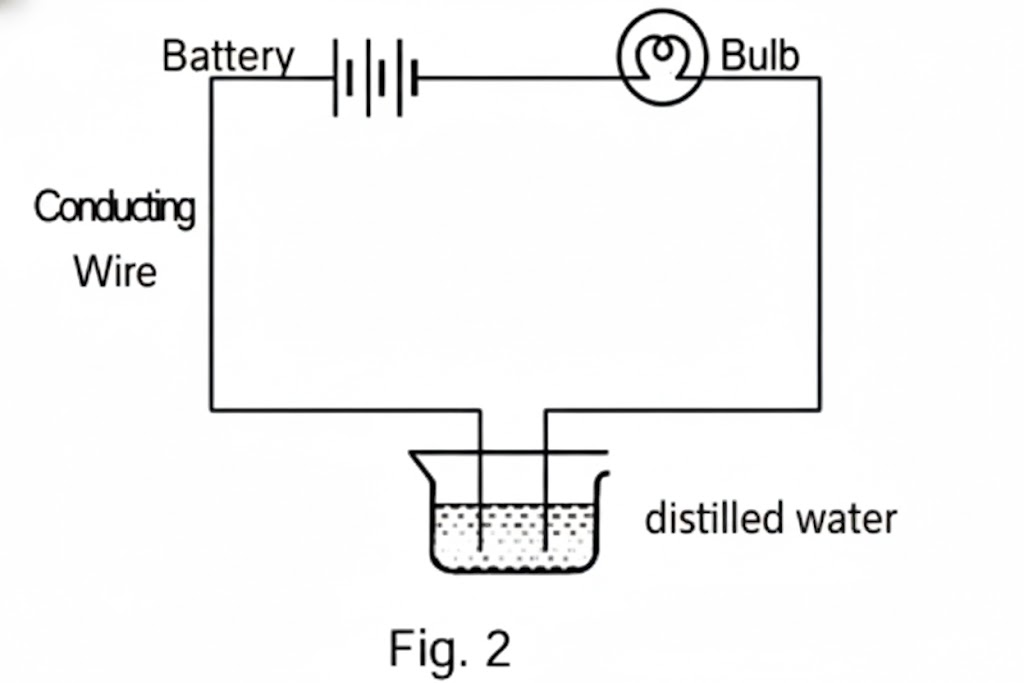
Suddenly, she realised that the bulb in the circuit did not glow when she used distilled water (Figure 2).
After this realisation, she added a substance to the distilled water for electrolysis to take place.
Answer the following questions:
A. Which gas was she expecting to be formed at the anode and which one at the cathode respectively?
B. Why did the bulb not glow when Amrita passed electricity through distilled water?
C. Which substance was added by Amrita to distilled water to get the expected result?
Ans:
A. Amrita was expecting to get oxygen gas at the anode and hydrogen gas at the cathode.
B. The bulb did not glow because distilled water is a poor conductor of electricity. It does not contain enough free ions to carry the electric current.
C. Amrita likely added a substance such as a small amount of an acid (like sulphuric acid) or a base (like sodium hydroxide) to the water to make it a good conductor.
For visually impaired students Identify the type of reaction:
A. ZnO+C→Zn+CO This is a reduction reaction.
B. ZnCO3→ZnO+CO2 This is a decomposition reaction.
C. 2Mg+O2→2MgO+heat This is a combination and redox reaction.
28. Sara took 2 mL of dilute NaOH solution in a test tube and added two drops of phenolphthalein solution to it. The solution turned pink in colour. She added dilute H₂SO₄ to the above solution drop by drop until the solution in the test tube became colourless.
40 drops of dilute H₂SO₄ were used for the change in colour from pink to colourless.
When Sara added a drop of NaOH to the solution, the colour changed back to pink again.
Sara now tried the activity with different volumes of NaOH and recorded her observations:
| S. No. | Volume of dil. NaOH (mL) | Drops of dil. H₂SO₄ used |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 20 |
| 2 | 3 | 30 |
| 3 | 4 | 40 |
Answer the following questions based on the above information:
A. If Sara used concentrated H₂SO₄ in place of dilute H₂SO₄, how many drops will be required for the colour change to be observed?
(a) 40 (b) < 40 (c) > 40
Justify your answer.
B. Sara measured 20 drops of dilute H₂SO₄ and found its volume to be 1 mL. If she observed a change in colour by using 3 mL of H₂SO₄, how many mL of NaOH did she add to the test tube initially?
OR
Sara takes 10 drops of dilute H₂SO₄ in a test tube and adds two drops of phenolphthalein solution to it. Then she adds NaOH dropwise. Sara observes a change in colour after adding 20 drops of NaOH. What change in colour would she observe and why?
C. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the above experiment. Which of the following is true and why?
(a) Neutralisation and double displacement reaction
(b) Neutralisation and precipitation reaction
(c) Precipitation and double displacement reaction
(d) Neutralisation, double displacement as well as precipitation reaction
Ans:
A.
Correct option: (b) < 40 drops
Because concentrated H₂SO₄ has more H⁺ ions per drop than dilute acid, it will neutralise the base faster, so fewer drops are needed
B.
From the table: 40 drops (2 mL NaOH) = 2 mL H₂SO₄
→ Ratio is 1:1.
If 3 mL of H₂SO₄ is used, then 3 mL of NaOH was added initially.
OR (alternate subpart)
When NaOH is added to H₂SO₄ with phenolphthalein, the solution changes from colourless to pink because the solution becomes basic (phenolphthalein is pink in base).
C)
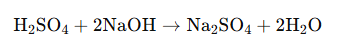
The reaction is a neutralisation as well as a double displacement reaction, because acid and base react to form salt and water.
✅ Correct option: (a) Neutralisation and double displacement reaction
29. Attempt either option A or B
(A) A hydrocarbon with the formula CₓHᵧ undergoes complete combustion as shown in the following equation:
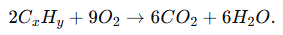
(a) What are the values of ‘x’ and ‘y’?
(b) Give the chemical (IUPAC) name of the hydrocarbon.
(c) Draw its electron dot structure.
(d) Name the alcohol which on heating with conc. H2SO4 will produce the above hydrocarbon CxHy.
(e) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of CxHy with hydrogen gas in presence of Nickel.
(a) By balancing the equation, we find the values: 2x=6⟹x=3. 2y=12⟹y=6. The values are x=3 and y=6.
(b) The hydrocarbon is C3H6, which is propene.
(c) (d) The alcohol is propanol.
(e) The balanced chemical equation is: C3H6+H2→C3H8.
OR
B. The electronic structures of atoms P and Q are shown below…
(a) If P and Q combine to form a compound, what type of bond is formed between them?
(b) Give the chemical formula of the compound formed.
(c) The compound so formed is dissolved in water. Is the resultant solution acidic or basic in nature? Justify your answer.
(d) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between ‘Q’ and ethanol.
(e) What will be the formula of the compound formed when ‘P’ undergoes bonding with carbon?
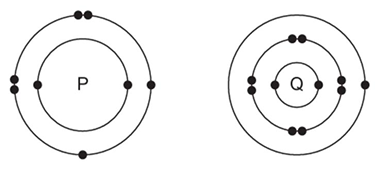
(a) Atom P has 6 valence electrons (non-metal), and Q has 1 valence electron (metal). They will form an ionic bond.
(b) The chemical formula is Q2P.
(c) The solution will be basic. The compound formed is a metallic oxide, which reacts with water to form a base.
(d) Assuming Q is Sodium (Na), the equation is: 2Na+2CH3CH2OH→2CH3CH2ONa+H2.
(e) P is similar to Oxygen, with a valency of 2. Carbon has a valency of 4. The formula for the compound is CO2.
Section C: Physics
30. Arnav was making notes and he wrote down the following statements about reflection from curved surfaces.
I. Concave mirrors can produce both real and virtual images depending on the position of the object.
II. Convex mirrors always produce real, inverted images regardless of the object’s position.
III. In both concave and convex mirrors, the image location can be determined using the mirror formula

Choose the correct option that lists the correct statements.
A. I and II
B. I, II and III
C. II and III
D. I and III
The correct answer is D. I and III .
Statement I is correct as concave mirrors can form both real and virtual images. Statement III is also correct, as the mirror formula is applicable to both types of curved mirrors. Statement II is incorrect because convex mirrors always form virtual, erect, and diminished images.
31: Choose the correct option which explains the reason for us to perceive the day sky as blue.
A. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, shorter wavelengths, such as blue are scattered more than other colors.
B. The sky appears blue because all colors are scattered equally, but blue light is stronger and more visible to the human eye.
C. The blue color of the sky is due to longer wavelengths like red and orange scattering more than shorter wavelengths, making blue stand out more.
D. The atmosphere contains blue-colored particles that give the sky its blue appearance.
Ans:
The correct answer is A. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, shorter wavelengths, such as blue are scattered more than other colors . This is known as Rayleigh scattering, where the shorter wavelength blue light is scattered in all directions by the fine particles in the atmosphere, making the sky appear blue.
32. This question has two statements — Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Answer by selecting the correct option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true.
Assertion (A): A point object is placed at a distance of 26 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 26 cm. The image will not form at infinity.
Reason (R): For the above system, the equation
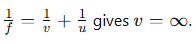
Answer:
The correct option is C. A is true but R is false. The assertion is true because a convex mirror always forms a virtual image behind the mirror, and it cannot form an image at infinity. The reason is false because the focal length of a convex mirror is positive, and the calculation using the mirror formula does not result in v=∞.
33. The above image shows the formation of an image with an optical instrument…
A. Identify the optical instrument (shown schematically as a rectangle) in the image.
B. What type of image is formed in this case?
C. Based on the measurements given in the image, calculate the focal length of the instrument.
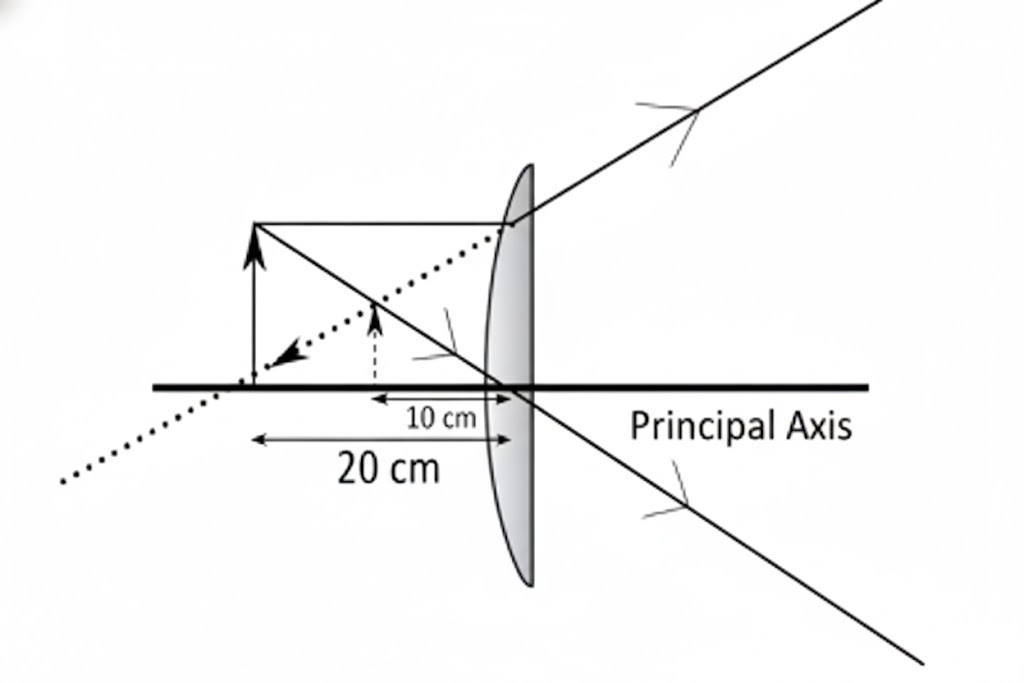
Answer:
A. The optical instrument is a concave lens.
B. The image formed is virtual, erect, and diminished.
C . Ans:
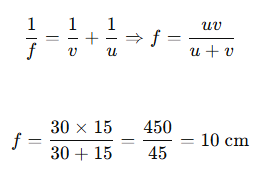
For visually impaired students A. Under what conditions can a convex lens form a virtual image?
A convex lens can form a virtual image when the object is placed between the optical center and the principal focus of the lens.
B. Why does a piece of paper catch fire if we allow sunlight to pass through a convex lens onto the paper?
Answer: A convex lens converges parallel rays of sunlight to a single point called the principal focus. This concentration of light energy produces a large amount of heat at that point, causing the paper to burn.
34. Attempt either option A or B.
A. Find out the following in the electric circuit given in the figure-
(i) Effective resistance of two 8 ohm resistors in the combination.
(ii) Current flowing through the 4-ohm resistor.
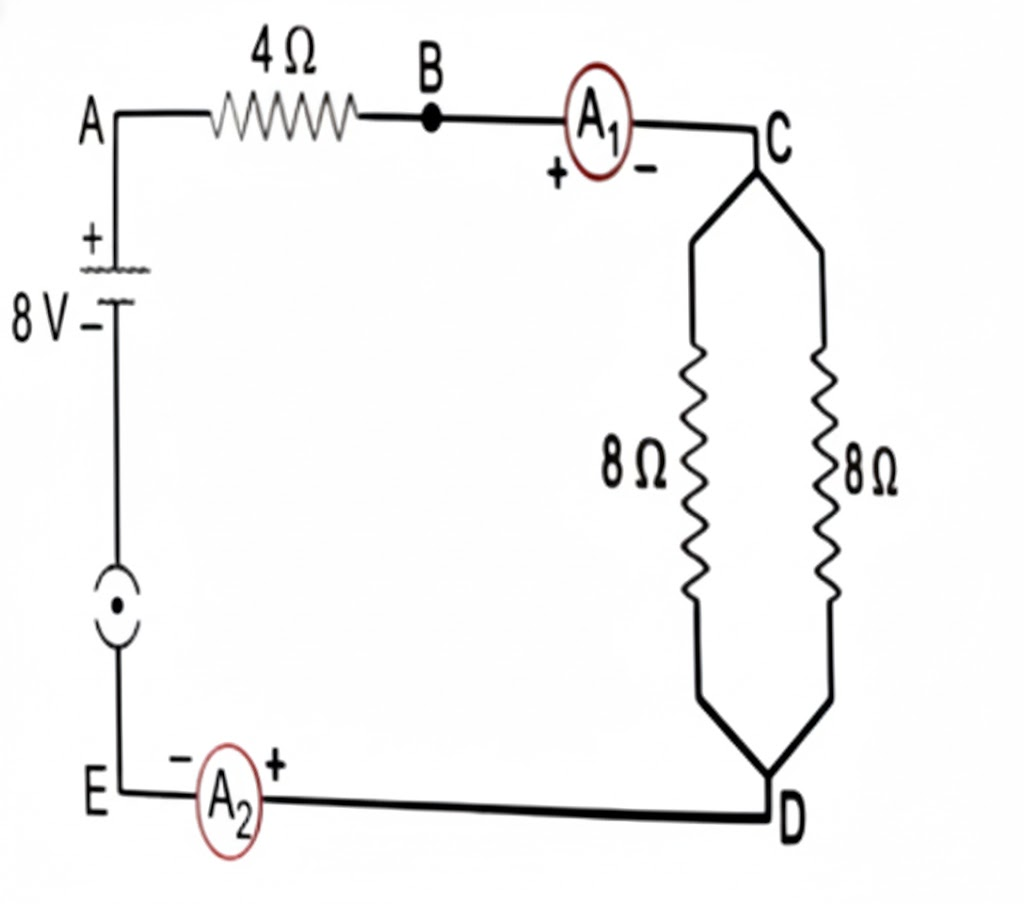
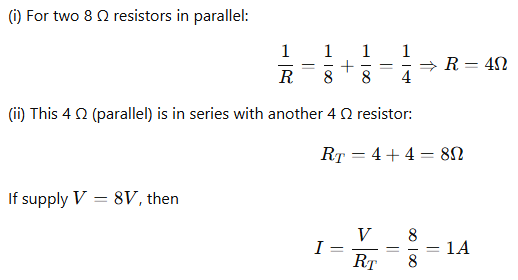
OR
B. Study the circuit and find out-
(i) Current in 12 ohm resistor.
(ii) Difference in the readings of ammeter A1 and A2 if any.
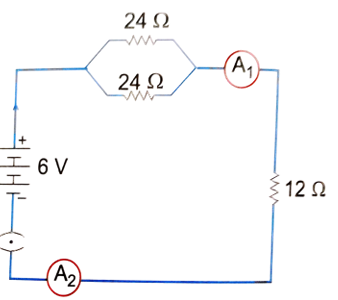
34. B .1 Answer:
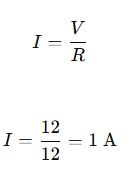
(ii) In a parallel circuit, total current divides among the branches, but the potential difference across each branch is the same.
Hence, the sum of currents through all branches equals the total current.
Therefore, ammeter A₁ (main current) and A₂ (branch current) will show different readings.
Difference = A₁ – A₂ = current in the other branch.
Readings of A₁ and A₂ are different (A₁ > A₂).
(For visually impaired students)
A. You are given four resistors each having resistance R ohm. Find the maximum and minimum resistance that can be made with these four resistors.
OR
B. A copper wire has length L = 2 m, cross-sectional area A = 0.5 mm², and resistivity ρ = 1.7 × 10⁻⁸ Ωm. Calculate the resistance of another wire made of the same material whose length is twice the first but has the same cross-sectional area.
Answer:
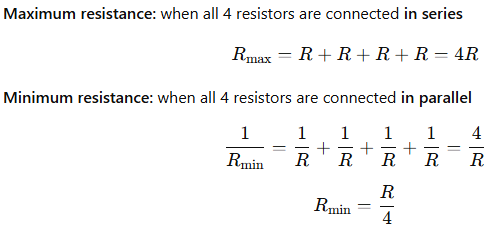
34. B .Answer
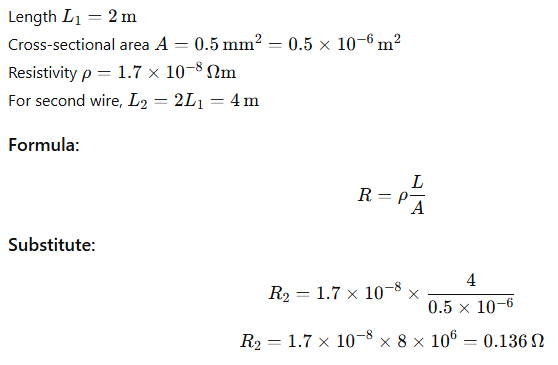
35.
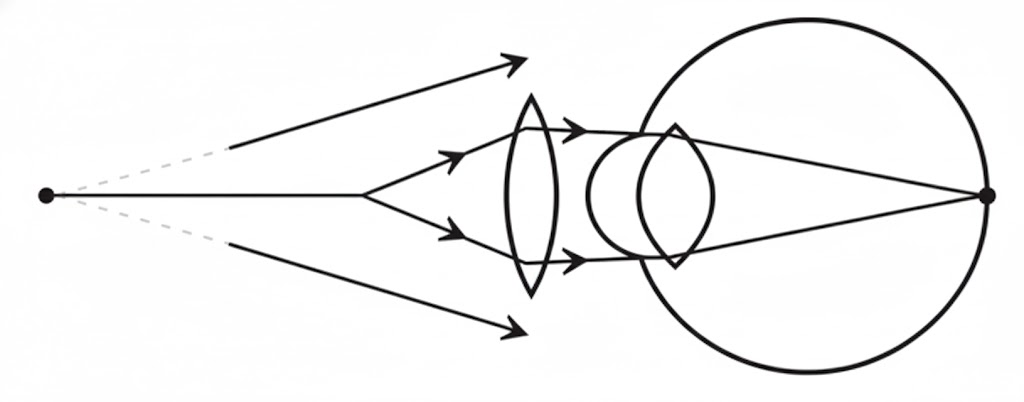
The above image shows a corrective measure for a particular defect of vision…
(i) Identify the defect of vision and state what kind of lens is used to correct this deficiency.
Answer: (i) The defect of vision is Hypermetropia or farsightedness. A convex lens is used to correct this deficiency.
(ii) Draw and label a ray diagram that shows the defect of vision in the above case before correction.
Answer: (ii) Before correction, the image of a nearby object is formed behind the retina.
(For visually impaired students)
(i) What is dispersion of light?
Dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colors (VIBGYOR) when it passes through a transparent medium like a prism.
(ii) Explain the condition under which dispersion happens?
Dispersion occurs because the refractive index of the medium is different for different wavelengths (colors) of light.
(iii) Give one reason that causes presbyopia.
Presbyopia is caused by the weakening of the ciliary muscles and the loss of flexibility of the eye lens with age.
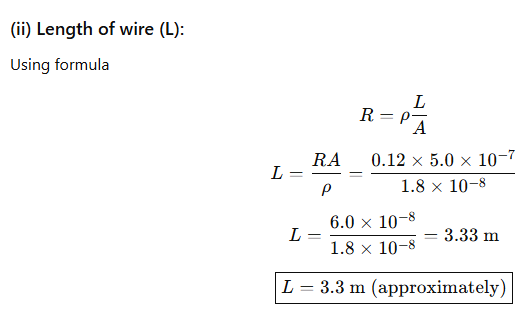
36.A student needs to make a 0.12 Ω resistor. She has some copper wire of 0.80 mm diameter. The resistivity of copper is 1.8 × 10⁻⁸ Ω·m.
(i) Determine the cross-sectional area of the wire.
Answer:
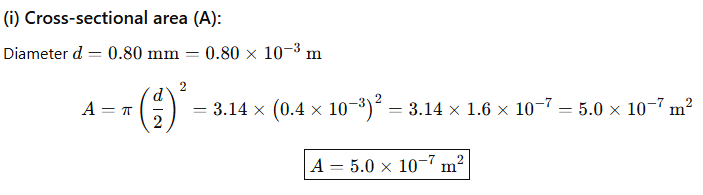
(ii) Calculate the length of wire required for the 0.12 Ω resistor.
37. Magnetic field lines are shown in the given diagram. A student makes a statement that the magnetic field at X is stronger than at Y.
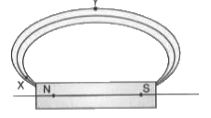
(i) Explain with reason if the student’s claim is correct.
Answer: (i) The student’s claim is correct if the field lines are closer together at X than at Y. Magnetic field strength at a point is indicated by the density (closeness) of field lines — the closer the lines, the stronger the field. So where lines are more crowded (X) the magnetic field is stronger than where they are more spread out (Y).
(ii) Also redraw the diagram and mark the direction of magnetic field lines.
38.
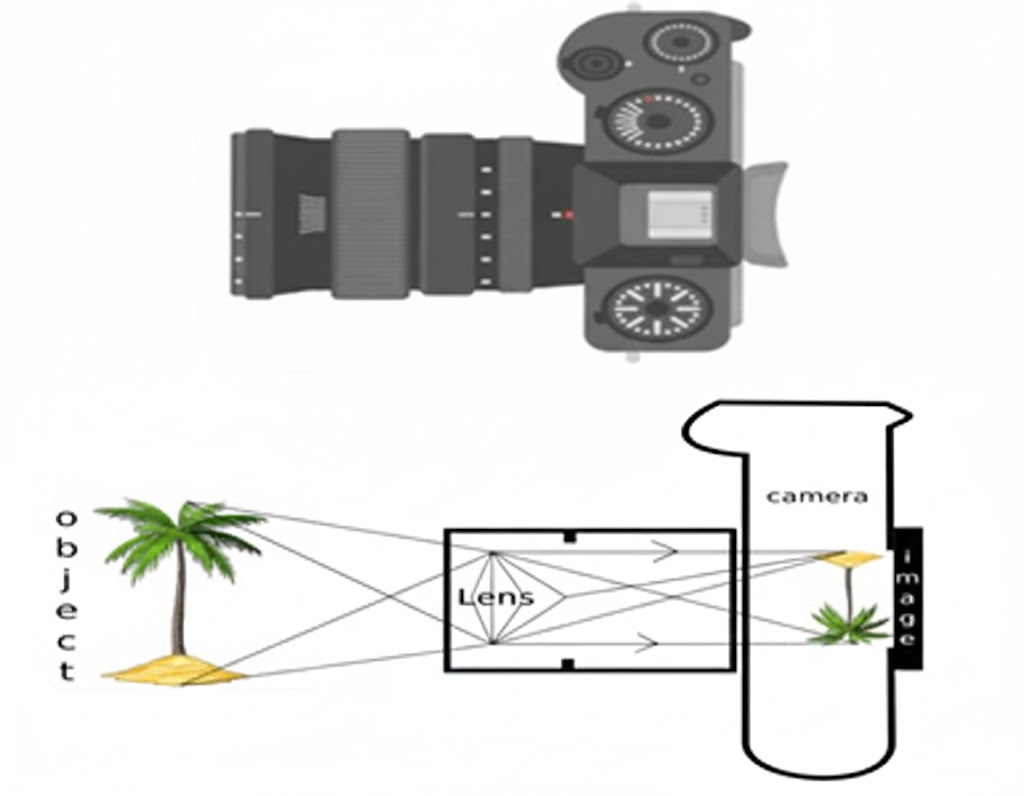
The above image is that of a Digital Single Lens Reflex (DSLR) Camera, which is used to take high-resolution photographs by professional photographers. The second image of the above two is a schematic diagram of how an image is formed on the sensor of the camera.
Based on your understanding of lenses, answer the following questions:
A. What type of lens is used in the DSLR camera shown in the image?
Answer: A. A convex lens is used in the DSLR camera.
B. What type of image is formed on the sensor?
Answer: B. A real, inverted, and diminished image is formed on the sensor.
Attempt either subpart C or D.
C. A photographer is using a DSLR camera with a lens of focal length f = 50 mm to take a close-up photograph of a small object. The lens projects an image onto the camera sensor that is located 60 mm behind the lens.
Calculate the object distance (i.e., the distance between the object and the lens).
OR
D. A photographer is using a DSLR camera to take a picture of a flower. The flower is positioned 150 mm away from the camera lens. The actual height of the flower is 80 mm, and the image height formed on the camera’s sensor is measured to be 20 mm.
Calculate the focal length of the camera lens.
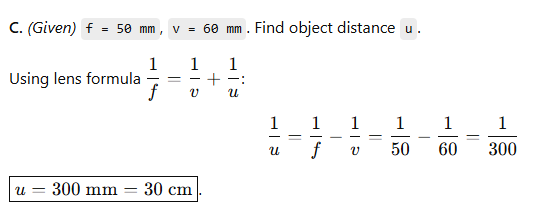
D. A photographer is using a DSLR camera to take a picture of a flower… Calculate the focal length of the camera lens.

39. Attempt either option A or B.
A. The arrangement of resistors shown in the above figure is connected to a battery.
The power dissipation in the 100 Ω resistor is 81 W. Calculate:
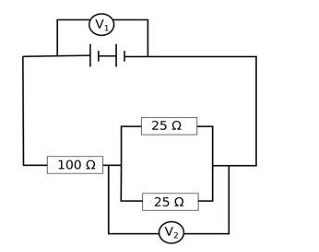
(i) the current in the circuit
Answer:
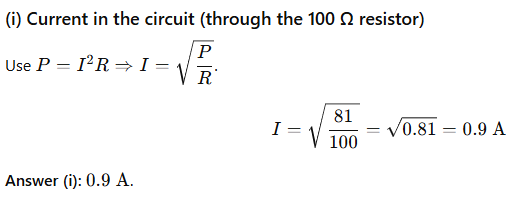
(ii) the reading in the voltmeter V2
Answer:
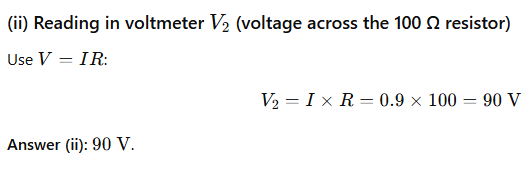
(iii) the reading in the voltmeter V1.
Answer:
OR
B. An electric heater consists of three similar heating elements A, B and C, connected as shown in the figure. Each heating element is rated 1.2 kW, 240 V and has constant resistance. S1, S2 and S3 are respective switches.
The circuit is connected to a 240 V supply.
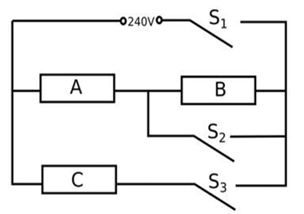
(i) Calculate the resistance of one heating element.
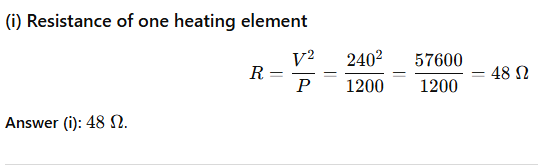
(ii) Calculate the current in each resistor when only S1 and S3 are closed.
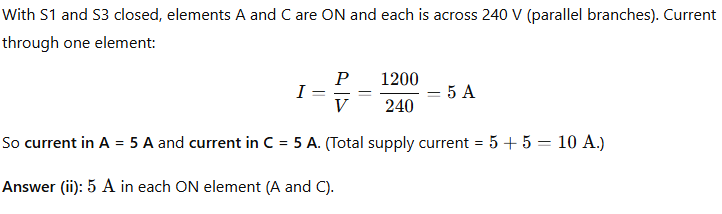
(iii) Calculate the power dissipated across A when S1, S2 and S3 are closed.

For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
NCERT Textbooks (for Class 10):
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
