The CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2022–23 is designed to help students understand the latest exam pattern, question types, and marking scheme introduced by the board. Practicing this sample paper allows students to assess their preparation, improve time management, and boost confidence before the actual board exams.

On this page, you’ll find the complete set of questions along with well-explained answers in plain text format — making revision simple and effective. Whether you’re focusing on Physics, Chemistry, or Biology, this paper gives a balanced mix of conceptual and application-based questions aligned with the CBSE syllabus.
CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2022–23 With Answers
Science (086)
Class X
Sample Question Paper 2022-23
Max. Marks: 80 Time Allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
i. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
ii. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is
expected to attempt only one of these questions.
iii. Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
iv. Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions
should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
v. Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these
questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words
vi. Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these
questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
vii. Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts
SECTION A
Select and write one most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1 – 20
Q1. The change in colour of moist litmus paper in the given setup is due to:
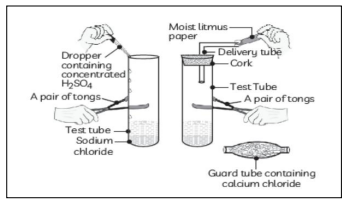
i. presence of acid
ii. presence of base
iii. presence of H⁺(aq) in the solution
iv. presence of Litmus which acts as an indicator
(a) i and ii
(b) Only ii
(c) Only iii
(d) Only iv.
Answer: (c) presence of H⁺(aq) in the solution
Litmus changes colour in presence of hydrogen ions released in an acidic solution. Moisture helps release H⁺, causing the colour change.
Q2. In the redox reaction
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
(a) MnO2 is reduced to MnCl2& HCl is oxidized to H2O
(b) MnO2 is reduced to MnCl2& HCl is oxidized to Cl2
(c) MnO2 is oxidized to MnCl2 & HCl is reduced to Cl2
(d) MnO2 is oxidized to MnCl2 & HCl is reduced to H2O
Answer: (b) MnO₂ is reduced to MnCl₂ and HCl is oxidized to Cl₂
Here, Mn⁴⁺ becomes Mn²⁺ (reduction), and Cl⁻ becomes Cl₂ (oxidation).
Q3. What is the correct observation of the reaction shown in the setup?
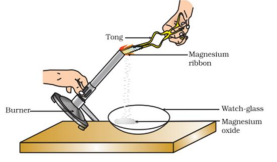
(a) Brown powder of Magnesium oxide is formed.
(b) Colourless gas which turns lime water milky is evolved.
(c) Magnesium ribbon burns with brilliant white light.
(d) Reddish brown gas with a smell of burning Sulphur has evolved.
Answer: (c) Magnesium ribbon burns with brilliant white light
Magnesium reacts with oxygen, releasing energy and forming white magnesium oxide.
Q4. Which gas combination is correct?
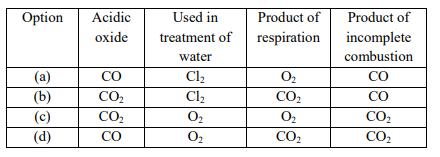
Answer: (b) CO₂, Cl₂, CO₂, CO
CO₂ is acidic and a respiration product; Cl₂ is used in water treatment; CO₂ is again a product of respiration; CO from incomplete combustion.
Q5. On placing a copper coin in a test tube containing green ferrous sulphate solution, it will
be observed that the ferrous sulphate solution
(a) turns blue, and a grey substance is deposited on the copper coin.
(b) turns colourless and a grey substance is deposited on the copper coin.
(c) turns colourless and a reddish–brown substance is deposited on the copper coin.
(d) remains green with no change in the copper coin
Answer: (c) turns colourless and reddish brown substance is deposited
Copper displaces iron forming reddish brown copper and colourless iron sulphate.
Q6. Anita added a drop each of diluted acetic acid and diluted hydrochloric acid on pH paper
and compared the colors. Which of the following is the correct conclusion?
(a) pH of acetic acid is more than that of hydrochloric acid.
(b) pH of acetic acid is less than that of hydrochloric acid.
(c) Acetic acid dissociates completely in aqueous solution.
(d) Acetic acid is a strong acid
Answer: (a) pH of acetic acid is more than that of hydrochloric acid
Acetic acid is weak and less ionized than strong HCl, so pH is higher.
Q7.The formulae of four organic compounds are shown below. Choose the correct option.
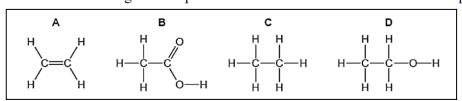
(a) A and B are unsaturated hydrocarbons
(b) C and D are saturated hydrocarbons
(c) Addition of hydrogen in presence of catalyst changes A to C
(d) Addition of potassium permanganate changes B to D
Answer: (c) Addition of hydrogen in presence of catalyst changes A to C
This is hydrogenation — alkyne/alkene becomes alkane with hydrogen and catalyst.
Q8. In the given transverse section of the leaf identify the layer of cells where maximum
photosynthesis occurs.
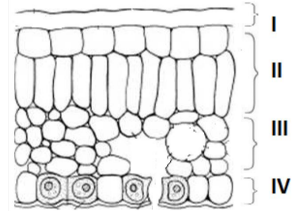
(a) I, II
(b) II, III
(c) III, IV
(d) I, IV
Answer: (b) II, III (Palisade and mesophyll cells)
These cells are packed with chloroplasts, where photosynthesis happens.
Q9. Observe the experimental setup shown below. Name the chemical indicated as ‘X’ that
can absorb the gas which is evolved as a byproduct of respiration.
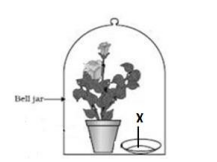
(a) NaOH
(b) KOH
(c) Ca (OH)2
(d) K2CO3
Answer: (b) KOH
Potassium hydroxide absorbs CO₂ produced during respiration.
Q10. If a tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant then, what percentage of F1 and
F2 generation respectively will be tall?
(a) 25%, 25%
(b) 50%, 50%
(c) 75%,100%
(d) 100%, 75%
Answer: (d) 100%, 75%
F₁ = 100% tall (Tt); F₂ (Tt × Tt) = 75% tall: 1 TT, 2 Tt, 1 tt.
Q11. Observe the three figures given below. Which of the following depicts tropic movements
appropriately?
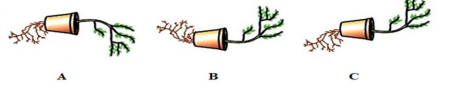
(a) B and C
(b) A and C
(c) B only
(d) C only
Answer: (b) A and C
They show plant bending towards/away from stimulus (light or touch).
Q12. The diagram shown below depicts pollination. Choose the options that will show a
maximum variation in the offspring.
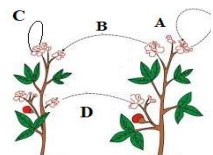
(a) A, B and C
(b) B and D
(c) B, C and D
(d) A and C
Answer: (c) B, C and D
Cross-pollination between different plants causes maximum genetic variation.
Q13. A complete circuit is left on for several minutes, causing the connecting copper wire to
become hot. As the temperature of the wire increases, the electrical resistance of the wire
(a) decreases.
(b) remains the same.
(c) increases.
(d) increases for some time and then decreases .
Answer: (c) increases
With heat, vibrations in atoms increase, opposing flow of electrons.
Q14. A copper wire is held between the poles of a magnet.
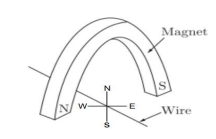
The current in the wire can be reversed. The pole of the magnet can also be changed
over. In how many of the four directions shown can the force act on the wire?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer: (b) 2
According to Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, force can act in two directions.
Q15.
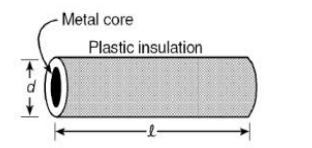
Plastic insulation surrounds a wire having diameter d and length l as shown above. A
decrease in the resistance of the wire would be produced by an increase in the
(a) length l of the wire
(b) diameter d of the wire
(c) temperature of the wire
(d) thickness of the plastic insulation
Answer: (b) diameter d is increased
Resistance ∝ 1/area. Larger diameter = lower resistance.
Q16. Which of the following pattern correctly describes the magnetic field around a long
straight wire carrying current?
(a) straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) concentric circles centred around the wire.
Answer: (d) Concentric circles
Field lines form concentric circles centered on the wire.
Q. no 17 to 20 are Assertion – Reasoning based questions.
These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the
appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is False but R is true
17 Assertion: Silver bromide decomposition is used in black and white photography.
Reason: Light provides energy for this exothermic reaction.
18 Assertion: Height in pea plants is controlled by efficiency of enzymes and is thus
.genetically controlled.
Reason: Cellular DNA is the information source for making proteins in the cell.
19. Assertion: Amphibians can tolerate mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Reason: Amphibians are animals with two chambered heart
20. Assertion: On freely suspending a current – carrying solenoid, it comes to rest in
Geographical N-S direction.
Reason : One end of current carrying straight solenoid behaves as a North pole and
the other end as a South pole, just like a bar magnet
SECTION – B
Q. no. 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.
21. A clear solution of slaked lime is made by dissolving Ca(OH)2in an excess of water.
This solution is left exposed to air. The solution slowly goes milky as a faint white
precipitate forms. Explain why a faint white precipitate forms, support your
response with the help of a chemical equation.
OR
Keerti added dilute Hydrochloric acid to four metals and recorded her observations
as shown in the table given below:
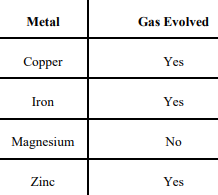
Select the correct observation(s) and give chemical equation(s) of the reaction
involved.
22 How is the mode of action in beating of the heart different from reflex actions?
Give four examples.
23 Patients whose gallbladder are removed are recommended to eat less oily food.
Why?
24 Name the substances other than water, that are reabsorbed during urine formation.
What are the two parameters that decide the amount of water that is reabsorbed in
the kidney?
Q25.
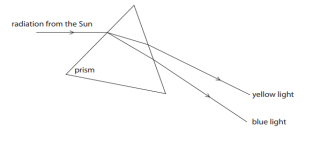
State the phenomena observed in the above diagram. Explain with reference to the
diagram, which of the two lights mentioned above will have the higher wavelength?
OR
How will you use two identical prisms so that a narrow beam of white light incident
on one prism emerges out of the second prism as white light? Draw the diagram
Answer:
Homologous organs have the same structure but different functions. Example: arm of human, wing of bat.
They show common ancestry and support the theory of evolution.
Q26. A lot of waste is generated in neighborhood. However, almost all of it is
biodegradable. What impact will it have on the environment or human health?
Answer:
The magnetic field created by current depends on its direction. Reversing battery terminals changes current direction, hence reversing the magnetic field, making the needle deflect oppositely.
Q27.
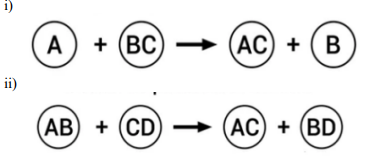
Identify the types of reaction mentioned above in (i) and (ii). Give one example for
each type in the form of a balanced chemical equation.
Answer:
Q28.
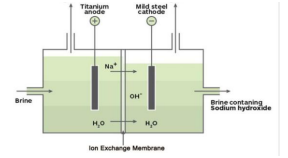
(a) Identify the gasses evolved at the anode and cathode in the above
experimental set up.
(b) Name the process that occurs. Why is it called so?
(c) Illustrate the reaction of the process with the help of a chemical equation.
Answer:
Q29. The leaves of a plant were covered with aluminium foil, how would it affect the
physiology of the plant?
OR
How is lymph an important fluid involved in transportation? If lymphatic vessels
get blocked, how would it affect the human body? Elaborate
Answer:
Q30. Rohit wants to have an erect image of an object using a converging mirror of focal
length 40 cm.
(a) Specify the range of distance where the object can be placed in front of the
mirror. Justify.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show image formation in this case.
(c) State one use of the mirror based on the above kind of image formation
Answer:
Q31.(a) A lens of focal length 5 cm is being used by Debashree in the laboratory as a
magnifying glass. Her least distance of distinct vision is 25 cm.
(i) What is the magnification obtained by using the glass?
(ii) She keeps a book at a distance 10 cm from her eyes and tries to read. She is
unable to read. What is the reason for this?
(b) Ravi kept a book at a distance of 10 cm from the eyes of his friend Hari. Hari is
not able to read anything written in the book. Give reasons for this?
32. A student fixes a white sheet of paper on a drawing board. He places a bar magnet
in the centre and sprinkles some iron filings uniformly around the bar magnet. Then
he taps gently and observes that iron filings arrange themselves in a certain pattern.
(a) Why do iron filings arrange themselves in a particular pattern?
(b) Which physical quantity is indicated by the pattern of field lines around the
bar magnet?
(c) State any two properties of magnetic field lines.
OR
A compass needle is placed near a current carrying wire. State your observations for
the following cases and give reasons for the same in each case-
(a) Magnitude of electric current in wire is increased.
(b) The compass needle is displaced away from the wire.
33 Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern? What are its causes and
what steps are being taken to limit this damage?
SECTION – D
Q.no. 34 to 36 are Long answer questions.
34 Shristi heated Ethanol with a compound A in presence of a few drops of
concentrated sulphuric acid and observed a sweet smelling compound B is formed.
When B is treated with sodium hydroxide it gives back Ethanol and a compound C.
(a) Identify A and C
(b) Give one use each of compounds A and B.
(c) Write the chemical reactions involved and name the reactions.
OR
(a) What is the role of concentrated Sulphuric acid when it is heated with
Ethanol at 443 K. Give the reaction involved.
(b) Reshu by mistake forgot to label the two test tubes containing Ethanol and
Ethanoic acid. Suggest an experiment to identify the substances correctly
35. (a) Why is it not possible to reconstruct the whole organism from a fragment in
complex multicellular organisms?
(b) Sexual maturation of reproductive tissues and organs are necessary link for
reproduction. Elucidate.
OR
(a) How are variations useful for species if there is drastic alteration in the niches?
(b) Explain how the uterus and placenta provide necessary conditions for proper
growth and development of the embryo after implantation?
Q36.
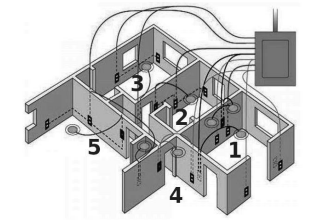
The diagram above is a schematic diagram of a household circuit. The house shown
in the above diagram has 5 usable spaces where electrical connections are made.
For this house, the mains have a voltage of 220 V and the net current coming from
the mains is 22A.
(a) What is the mode of connection to all the spaces in the house from the
mains?
(b) The spaces 5 and 4 have the same resistance and spaces 3 and 2 have
respective resistances of 20Ω and 30Ω. Space 1 has a resistance double that
of space 5. What is the net resistance for space 5.
(c) What is the current in space 3?
(d) What should be placed between the main connection and the rest of the
house’s electrical appliances to save them from accidental high electric
current?
SECTION – E
Q.no. 37 to 39 are case – based/data -based questions with 2 to 3 short sub – parts. Internal choice is
provided in one of these sub-parts.
37. Two students decided to investigate the effect of water and air on iron object under identical experimental conditions. They measured the mass of each object before placing it partially immersed in 10 ml of water. After a few days, the object were removed, dried and their masses were measured. The table shows their results.
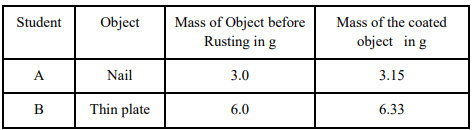
(a) What might be the reason for the varied observations of the two students?
(b) In another set up the students coated iron nails with zinc metal and noted that, iron nails coated with zinc prevents rusting. They also observed that zinc initially acts as a physical barrier, but an extra advantage of using zinc is that it continues to prevent rusting even if the layer of zinc is damaged. Name this
process of rust prevention and give any two other methods to prevent rusting
OR
(b) In which of the following applications of Iron, rusting will occur most?
Support your answer with valid reason.
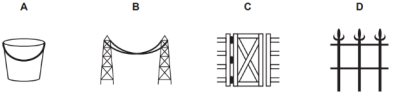
A – Iron Bucket electroplated with Zinc
B – Electricity cables having iron wires covered with aluminium
C – Iron hinges on a gate
D – Painted iron fence
38. Pooja has green eyes while her parents and brother have black eyes. Pooja’s husband Ravi has black eyes while his mother has green eyes and father has black eyes.
(a) On the basis of the above given information, is the green eye colour a dominant or recessive trait? Justify your answer.
(b) What is the possible genetic makeup of Pooja’s brother’s eye colour?
(c) What is the probability that the offspring of Pooja and Ravi will have green
eyes? Also, show the inheritance of eye colour in the offspring with the
help of a suitable cross.
OR
(d) 50% of the offspring of Pooja’s brother are green eyed. With help of cross
show how this is possible
39.

The above images are that of a specialized slide projector. Slides are small transparencies mounted in sturdy frames ideally suited to magnification and projection, since they have a very high resolution and a high image quality. There is a tray where the slides are to be put into a particular orientation so that the viewers
can see the enlarged erect images of the transparent slides. This means that the slides will have to be inserted upside down in the projector tray.
To show her students the images of insects that she investigated in the lab, Mrs. Iyer brought a slide projector. Her slide projector produced a 500 times enlarged and inverted image of a slide on a screen 10 m away.
(a) Based on the text and data given in the above paragraph, what kind of lens must the slide projector have?
(b) If v is the symbol used for image distance and u for object distance then with one reason state what will be the sign for 𝑣/𝑢 in the given case?
(c) A slide projector has a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm. The slide is placed upside down 21 cm from the lens. How far away should the screen be placed from the slide projector’s lens so that the slide is in focus?
OR
(c)When a slide is placed 15 cm behind the lens in the projector, an image is formed 3 m in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is 14 cm, draw a ray diagram to show image formation. (not to scale)
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 10):
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
