Are you nervous about the upcoming Class 10 Science Board Exam 2026? You are not alone. With a vast syllabus covering Physics, Chemistry, and Biology, it is impossible to memorize every single line of the NCERT textbook.
But here is the secret: CBSE repeats concepts. so Class 10 Science Important Questions 2026
After analyzing the last 10 years of question papers, we have identified 30 specific questions that appear almost every year. If you master these, you are guaranteed to secure high marks. Below is the list of the most important, high-weightage questions for 2026.
Section A: Chemistry (Most Important Questions)
Chemistry is the most scoring part of the Science paper if you know the reactions. Focus on Chemical Reactions and Carbon and its Compounds.
Q1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Answer: Magnesium is a reactive metal. When kept in the open, it forms a layer of magnesium oxide (MgO) on its surface. This layer prevents further burning. We clean it with sandpaper to remove this oxide layer so it can burn properly.
Q2. Explain the versatile nature of Carbon. (Repeated 5+ Times)
Answer: Carbon forms millions of compounds due to two unique properties:
- Catenation: Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other carbon atoms, giving rise to large molecules (chains, branches, or rings).
- Tetravalency: Carbon has a valency of 4, allowing it to bond with four other atoms of carbon or other elements.
Q3. Write the chemical formula and two uses of Plaster of Paris.
Answer:
- Formula: CaSO₄·½H₂O (Calcium Sulphate Hemihydrate).
- Uses:
- Used by doctors for supporting fractured bones in the right position.
- Used for making toys and materials for decoration.
Q4. What is an Amphoteric Oxide? Give two examples.
Answer: Metal oxides that show both acidic and basic behavior are called amphoteric oxides. They react with both acids and bases to produce salt and water.
- Examples: Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃) and Zinc Oxide (ZnO).
Q5. Explain the formation of Scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer: Hard water contains Calcium and Magnesium salts. When soap reacts with these salts, it forms an insoluble substance called “Scum” (precipitate). This limits the cleaning action of soap. (Note: Detergents do not form scum).
Q6. What is a Homologous Series?
Answer: A series of compounds in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain is called a homologous series.
- Key Feature: Successive members differ by a -CH₂ unit and 14u mass unit.
- Example: CH₄ (Methane) and C₂H₆ (Ethane).
Q7. Differentiate between Roasting and Calcination. Answer:
- Roasting: Heating sulphide ores in the presence of excess air (e.g., ZnS → ZnO).
- Calcination: Heating carbonate ores in limited air (e.g., ZnCO₃ → ZnO).
Q8. Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Answer: Ionic compounds are made of positive and negative ions held together by a strong force of attraction (electrostatic force). A large amount of energy is required to break these strong bonds, resulting in high melting points.
Q9. State the Modern Periodic Law.
Answer: “The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers.” (Remember: Mendeleev used atomic mass, Modern table uses atomic number).
Q10. What is a Redox Reaction? Give an example.
Answer: A reaction in which both oxidation (gain of oxygen/loss of hydrogen) and reduction (loss of oxygen/gain of hydrogen) take place simulate
Section B: Physics (Theory & Numericals)
Physics requires understanding formulas and rules. Pay special attention to Light and Electricity chapters.
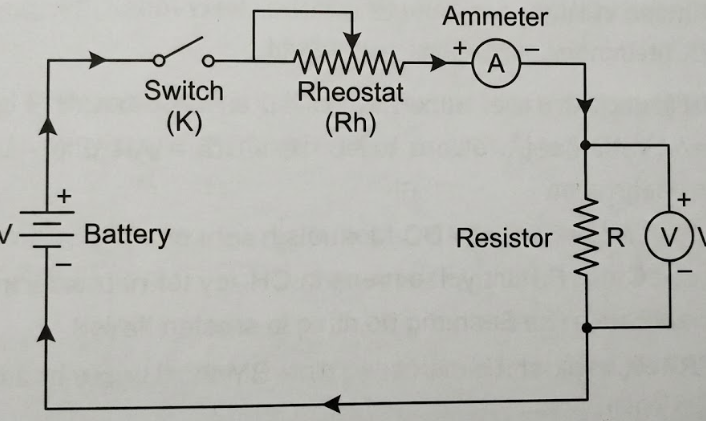
Q11. State Ohm’s Law. Draw a circuit diagram to verify it.
Answer: Ohm’s Law states that the potential difference (V) across the ends of a metallic wire is directly proportional to the current (I) flowing through it, provided the temperature remains constant.
- Formula: V = IR (where R is Resistance).
- Graph: The V-I graph is a straight line passing through the origin.
Q12. Why is a parallel arrangement used in domestic circuits instead of series?
Answer: Parallel arrangement is preferred because:
- Independent Operation: Each appliance has its own switch. If one fails, others keep working.
- Voltage Stability: Each appliance gets the same voltage (220V) as the power supply.
- Resistance: The total resistance decreases in parallel, ensuring proper current flow.
Q13. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What is the defect of vision and how is it corrected?
Answer:
Correction: It is corrected using a Concave Lens of suitable power.
Defect: Myopia (Near-sightedness). The student can see nearby objects (notebook) clearly but not distant objects (blackboard).
Cause: Excessive curvature of the eye lens or elongation of the eyeball.
Q14. State Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule.
Answer: Stretch the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of your left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular.
- Forefinger: Points in the direction of the Magnetic Field.
- Middle Finger: Points in the direction of Current.
- Thumb: Points in the direction of Force (Motion) acting on the conductor.(Tip: Remember “FBI” -> Force, B-field, I-current).
Q15. An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
Answer:
Given:
- Object distance, u = -10 cm (Object is placed in front of the mirror)
- Focal length of convex mirror, f = +15 cm
To find:
- Position of the image (v)
- Nature of the image
Formula:
According to the mirror formula:
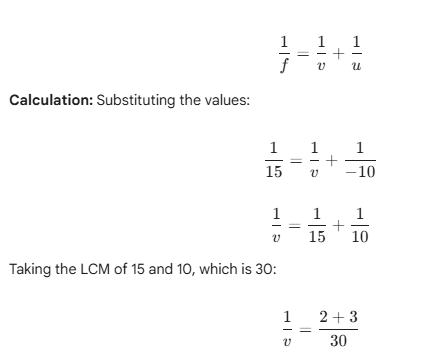

Conclusion:
- Position: The image is formed at a distance of 6 cm behind the mirror.
- Nature: Since $v$ is positive and magnification ($m$) is positive and less than 1, the image is virtual, erect, and diminished.
Q16. Why does the sky appear blue?
Answer: This is due to the Scattering of Light. The fine particles in the atmosphere scatter blue light (shorter wavelength) more strongly than red light (longer wavelength). This scattered blue light enters our eyes.
Q17. Explain the function of an Electric Fuse.
Answer: A fuse is a safety device used to protect circuits from damage due to short-circuiting or overloading. It has a wire with a low melting point. If the current exceeds a safe limit, the fuse wire melts and breaks the circuit, stopping the flow of current.
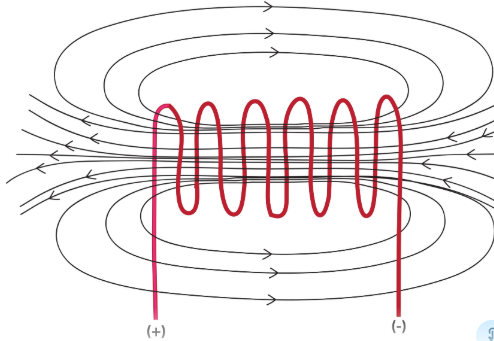
Q18. What is a Solenoid? Draw the magnetic field lines inside a solenoid.
Ans: Definition of a Solenoid: A solenoid is a long, cylindrical coil of insulated copper wire with a large number of circular turns. When an electric current is passed through it, it behaves like a magnet. The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetize a piece of magnetic material, like soft iron, when placed inside the coil.
Magnetic Field Lines Inside a Solenoid: The magnetic field lines inside a solenoid have the following characteristics:
Uniform: This indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid.
Parallel and Straight: The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines.
Q19. Define Power of a Lens. What is its SI unit?
Answer: The power of a lens is the reciprocal of its focal length (in meters). It represents the degree of convergence or divergence of light rays.
- Formula: P = 1/f (where f is in meters).
- SI Unit: Dioptre (D).
Q20. Why do stars twinkle but planets do not?
Answer: Stars are point sources of light very far away. Atmospheric refraction causes the path of starlight to fluctuate, making them appear to twinkle. Planets are closer and appear as extended sources (collection of points); the fluctuations cancel out, so they do not twinkle.
Section C: Biology (Diagrams & Processes)
Biology answers must be precise. Always draw a diagram if the question asks for “Structure” or “Process.”
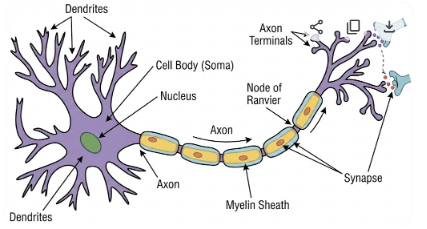
Q21. Draw the structure of a Neuron and explain its function.Answer:
Ans: : Structure of a Neuron:
A neuron (nerve cell) consists of three main parts:
- Cell Body (Cyton/Soma): The central part of the neuron containing the nucleus and cytoplasm. It regulates the growth and metabolism of the neuron.
- Dendrites: Short, branched projections extending from the cell body. They receive chemical signals (impulses) from adjacent neurons and transmit them toward the cell body.
- Axon: A long, thread-like extension that carries electrical impulses away from the cell body to the nerve endings.
Function of a Neuron:
The primary function of a neuron is to transmit information throughout the body in the form of electrical signals called nerve impulses.
Transmission: At the nerve ending, the electrical impulse triggers the release of chemicals (neurotransmitters) that cross the synapse to start a similar impulse in the next neuron.
Reception: Dendrites detect information (stimuli) from the environment or other neurons.
Conduction: The information travels as an electrical impulse from the dendrites, through the cell body, and down along the axon.
Q22. Explain the process of ‘Double Circulation’ in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Answer: In humans, blood flows through the heart twice during one complete cycle of the body.
It consists of two distinct pathways:
- Pulmonary Circulation (Heart $\leftrightarrow$ Lungs):
- Deoxygenated blood from the body is collected in the Right Atrium and moves to the Right Ventricle.
- The Right Ventricle pumps this blood to the lungs via the Pulmonary Artery.
- In the lungs, the blood releases carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen.
- Oxygenated blood returns to the Left Atrium of the heart via the Pulmonary Veins.
- Systemic Circulation (Heart $\leftrightarrow$ Body):
- Oxygenated blood enters the Left Ventricle from the Left Atrium.
- The Left Ventricle pumps this oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body via the Aorta.
- The body cells use the oxygen and produce carbon dioxide.
- The now deoxygenated blood is collected by veins (Vena Cava) and returned to the Right Atrium.
- Necessity: It separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, which provides an efficient supply of oxygen to the body to maintain constant body temperature.
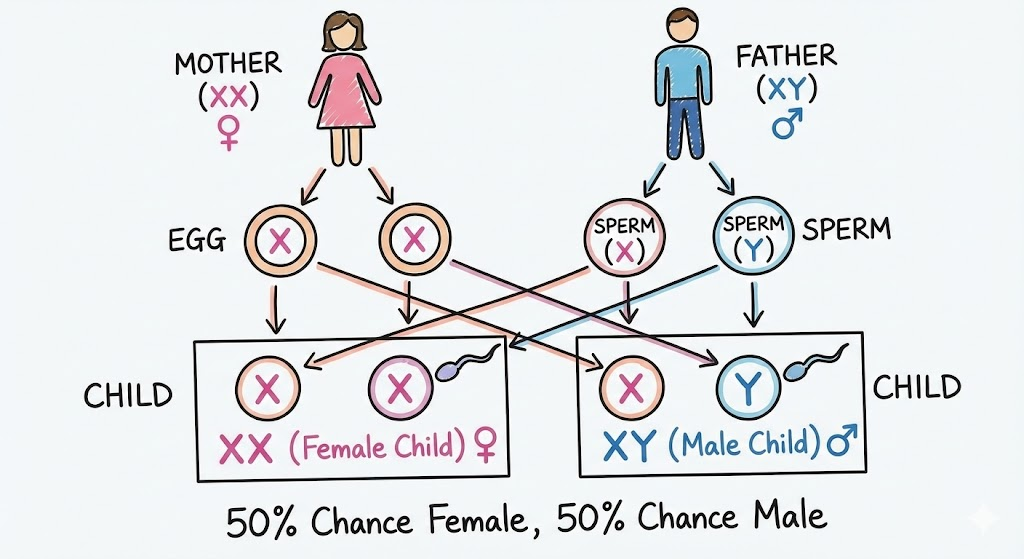
Q23. How is the sex of a child determined in human beings?
Answer: Sex is determined by the chromosomes inherited from the father.
- A female has XX sex chromosomes.
- A male has XY sex chromosomes.
- If a sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the child will be a girl (XX).
- If a sperm carrying a Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the child will be a boy (XY). Therefore, the father is responsible for the sex of the child.
Q24. Differentiate between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration. Answer:
- Aerobic: Takes place in the presence of oxygen. End products are Carbon dioxide, Water, and Energy (High energy). Occurs in Mitochondria.
- Anaerobic: Takes place in the absence of oxygen. End products are Ethanol/Lactic acid and a small amount of energy. Occurs in Cytoplasm (e.g., Yeast).
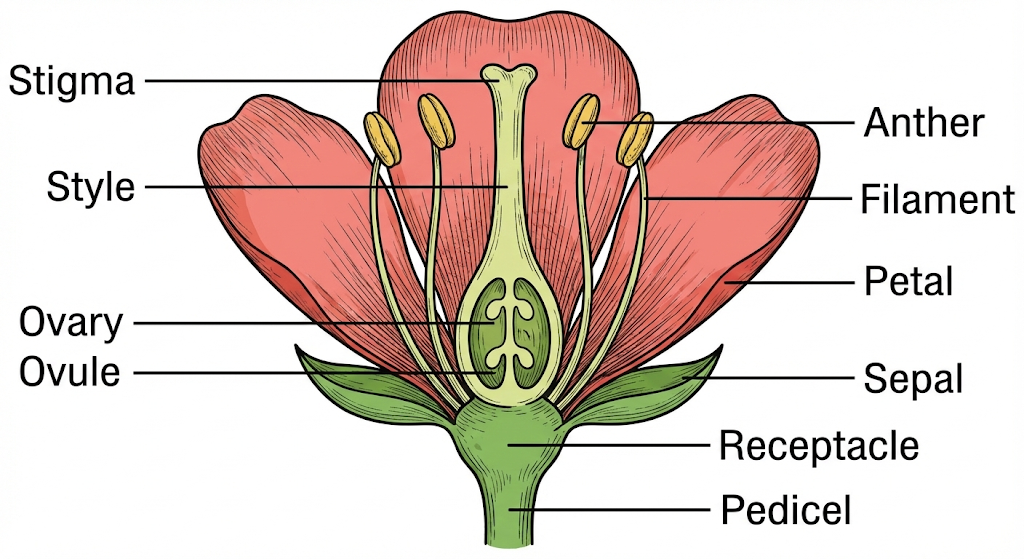
Q25. Draw a longitudinal section of a flower and label its parts.
Answer: The main parts are:
- Stamen (Male): Anther and Filament.
- Pistil (Female): Stigma, Style, and Ovary.
- Petals and Sepals: For attraction and protection.
Q26. What is the role of Acid in our stomach?
Answer: Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) in the stomach serves two purposes:
- It kills bacteria that enter along with food.
- It makes the medium acidic, which is necessary for the action of the enzyme Pepsin to digest proteins.
Q27. State Mendel’s Law of Dominance.
Answer: In a cross between two parents differing in a pair of contrasting characters, only one form of the trait appears in the F1 generation. This trait is called “Dominant” (e.g., Tallness), while the one that remains hidden is called “Recessive” (e.g., Dwarfness).
Q28. What is the 10% Law of energy flow?
Answer: Only 10% of the energy entering a particular trophic level of organisms is available for transfer to the next higher trophic level. The remaining 90% is lost as heat to the environment.
Q29. What are the functions of the following plant hormones?
Answer:
- Auxin: Helps in the growth of cells and elongation.
- Gibberellins: Helps in the growth of the stem.
- Cytokinins: Promotes rapid cell division (present in fruits/seeds).
- Abscisic Acid: Inhibits growth (causes wilting of leaves).
Q30. Explain the role of Nephrons.
Answer: Nephrons are the filtration units of the kidney. They filter the blood to remove waste products like urea and uric acid while reabsorbing useful substances like glucose, amino acids, and water back into the blood.
Conclusion: How to Score Full Marks?
These 30 questions cover nearly 70% of the important concepts for the Class 10 Science Board Exam 2026. However, to score a perfect 100/100, you need to practice solving full-length papers within 3 hours.
👉 [Download FREE CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2018-2025 Here]
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 10):

