Class 6 Science Ch 8 Getting to Know Plants Oxford Solution, takes students on a journey into the world of plants. It introduces the different types of plants—herbs, shrubs, and trees—as well as the structure and functions of various plant parts like roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. This chapter helps build a strong foundation in plant biology by encouraging observation and hands-on learning. Our Oxford-based solutions provide clear, step-by-step answers to all textbook questions, making it easier for students to understand concepts and prepare effectively for exams.
Class 6 Science Ch 8 Getting to Know Plants Oxford Solution Full Chapter
Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Getting to Know Plants
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
- Fibrous roots are thin and almost equal in size, having a bushy appearance.
- Stems of jade swell up to store water in them.
- Leaves arise from the nodes of the stem.
- Transpiration helps in cooling the leaves.
- Stamens are the male reproductive parts of a flower.
- Cotyledons contain food for the baby plant.
B. Write T for the True and F for the false statement. Correct the False statements.
- Lateral roots branch out from the primary root in a tap root system.
- Roots can be modified for protection and strength but never for reproduction.
- Stems can never carry out photosynthesis.
- Plants breathe with the help of tiny holes called spines.
- In pollination, the pollen grains are transferred from the carpel to the sepal of a flower.
Ans:
- Lateral roots branch out from the primary root in a tap root system.
True - Roots can be modified for protection and strength but never for reproduction.
False
Correction: Roots can be modified for protection, strength, and also for reproduction. - Stems can never carry out photosynthesis.
False
Correction: Some stems, like those of cactus, can carry out photosynthesis. - Plants breathe with the help of tiny holes called spines.
False
Correction: Plants breathe with the help of tiny holes called stomata. - In pollination, the pollen grains are transferred from the carpel to the sepal of a flower.
False
Correction: In pollination, the pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of a flower.
1. Which of these are special roots that help the plant to absorb nutrients from another plant called the host?
a. Prop roots
b. Parasitic roots
c. Tendrils
d. Rhizomes
Answer: b. Parasitic roots
2. Which of these plants can multiply through stem cuttings?
a. Potato, ginger, and onion
b. Jasmine and hibiscus
c. Grapes and passion flower
d. Banyan and Dodder
Answer: b. Jasmine and hibiscus
3. Which of these modifications help a plant to reduce loss of water from it?
a. Tendrils
b. Spines
c. Bulbs
d. Parasitic roots
Answer: b. Spines
4. Which of these forms a carpel?
a. Stamens, filaments, and stalk
b. Stigma, style, and ovary
c. Sepals, petals, and anthers
d. None of these
Answer: b. Stigma, style, and ovary
5. Which of these would a seed need to become a baby plant?
a. Air and water
b. Water and warmth
c. Air, water, and warmth
d. None of these
Answer: c. Air, water, and warmth
6. Which of these plants bears a taproot system?
a. Grass
b. Neem
c. Onion
d. Sugar cane
Answer: b. Neem
7. Which of these plants has roots modified for reproduction?
a. Turnip
b. Dahlia
c. Dodder
d. Banyan
Answer: b. Dahlia
8. The stem of which of these plants is modified for water storage?
a. Rose
b. Cactus
c. Bougainvillea
d. Potato
Answer: b. Cactus
9. The leaves of which of these plants have parallel venation?
a. Mango
b. Peepal
c. Banana
d. Rose
Answer: c. Banana
10. Which of these parts later becomes the seed?
a. Stigma
b. Style
c. Ovary
d. Ovule
Answer: d. Ovule
II. Very short answer type questions.
A. Give one word for the following:
- Roots that grow from branches and give extra support to the stem of the plant
Answer: Prop roots - Part of the stem from which leaves or new buds arise
Answer: Node - Structures that grow from the stem of climber plants to support them
Answer: Tendrils - Underground stem of potato
Answer: Tuber - Transfer of pollen grains from an anther to a stigma
Answer: Pollination
III. Short answer type questions.
1. Differentiate between tap root system and fibrous root system.
| Feature | Tap Root System | Fibrous Root System |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Arises from the radicle of the seed | Arises from the base of the stem |
| Structure | Has one main root with smaller branches | All roots are thin, similar in size, and bushy |
| Example | Neem, Mango | Grass, Wheat |
2. What are prop roots?
Answer:
Prop roots are special types of roots that grow from the branches of certain plants and grow downward into the soil to provide extra support to the plant. They are commonly seen in banyan trees.
3. How do stems of grapes help the plant to climb?
Answer:
The stems of grape plants produce tendrils, which are thin, curling structures that coil around nearby objects or supports. These tendrils help the plant climb and stay upright by providing support.
4. What is venation? Name the two types of venations with one example of each.
Answer:
Venation is the pattern of arrangement of veins in the leaf. There are two main types:
- Reticulate venation – The veins form a network.
Example: Mango, Peepal - Parallel venation – The veins run parallel to each other.
Example: Banana, Grass
5. Why are the flowers of some plants brightly coloured and have a sweet smell?
Answer:
Flowers of some plants are brightly coloured and have a sweet smell to attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and other insects. These pollinators help in the process of pollination, which is necessary for the formation of seeds and fruits.
IV. Long answer type questions.
1. Describe with examples how roots are modified for additional functions.
Ans: Roots are not only used for anchoring and absorbing water and minerals, but in some plants, they are modified to perform additional functions:
- Storage of food: In plants like carrot, radish, and sweet potato, roots store food and become thick and fleshy.
- Support: In banyan tree, some roots grow from the branches down to the ground and act as prop roots, providing support.
- Respiration: In plants like mangroves, roots called breathing roots (pneumatophores) grow above the ground to take in oxygen from the air.
- Reproduction: In dahlia and sweet potato, roots can give rise to new plants, helping in vegetative reproduction.
2. Describe the functions of a stem.
Ans: The stem plays many important roles in a plant’s life:
- Support: It holds up leaves, flowers, and fruits to keep them in sunlight and air.
- Transport: It conducts water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and food from the leaves to other parts through xylem and phloem.
- Storage: In some plants like potato (tuber) and ginger (rhizome), the stem stores food and nutrients.
- Photosynthesis: In plants like cactus, the stem is green and performs photosynthesis.
- Propagation: Stems can grow new plants. For example, money plant and rose can grow from stem cuttings.
3. What is transpiration? How does it help the plant?
Ans: Transpiration is the process by which water is lost as water vapour from the surface of leaves through tiny openings called stomata.
Importance/Benefits of transpiration:
- Cooling: It helps to cool the plant just like sweating cools our body.
- Water movement: It creates a suction force that helps in drawing water and minerals from the roots upward through the plant.
- Distribution of nutrients: Helps in transporting essential minerals and nutrients to various parts of the plant.
- Maintains turgidity: Keeps cells firm by maintaining water balance.
4. Define pollination. What happens to the different parts of the flower after pollination?
Ans: Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther (male part) to the stigma (female part) of the same or another flower.
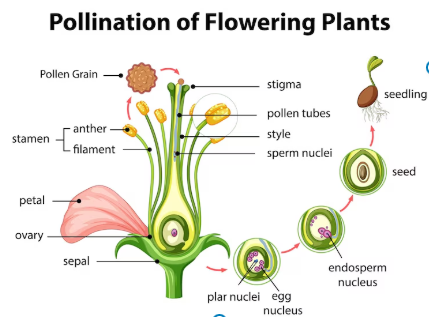
After pollination:
- Pollen grain travels down the style and reaches the ovary.
- Fertilization takes place when the male cell fuses with the female cell (ovule).
- The ovule becomes the seed.
- The ovary turns into the fruit.
- Other parts like petals, sepals, stamens usually dry up and fall off.
5. What are the four main parts of a flower? Describe them in detail, with the help of a labelled diagram.
Ans: The four main parts of a flower are:
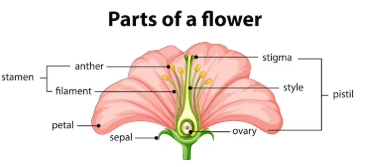
- Sepals: Green leaf-like structures that protect the bud before it opens.
- Petals: Often brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination.
- Stamens (Male part): Made of anther (produces pollen) and filament (holds the anther).
- Carpel (Female part): Made of stigma (receives pollen), style (tube for pollen to travel), and ovary (contains ovules which become seeds after fertilization).
Class 12:
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
NEET BIOLOGY
- Evolution
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Human Health and Disease
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
For the official Class 6 Science Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 6):
