Welcome to the Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Oxford Book Solution. This page provides clear and simple answers to all the textbook questions, making it easy for students from any part of the world to learn and revise. The solutions explain important topics such as sources of food, ingredients, and the role of food in daily life. Whether you are studying in India, the UK, the Middle East, Africa, or anywhere else, these solutions will help you understand concepts better, complete homework on time, and prepare confidently for exams.

Section 1: Introduction and Basic Concepts of Food
What is Food?

Food is the basic need of all living beings. Every living organism, whether a plant, animal, or human being, requires food to survive. Food provides us with energy to do work, materials to grow, and substances to repair damaged parts of the body. Without food, no life can exist on Earth.
When we eat food, our body digests it and breaks it down into simpler substances. These substances provide energy, keep us active, and protect us from diseases.
In simple words:
👉 Food = Energy + Growth + Protection
Why Do We Need Food?
Students all over the world have the same question – “Why is food so important?”
The answer can be understood through four main reasons:

- Protection – Food protects us from diseases. Fruits and vegetables give vitamins and minerals that make our immune system strong.
- Energy – Food gives us energy to play, study, walk, talk, and even to breathe.
- Example: A football player eats a good meal before the game so that he can run for 90 minutes without getting tired.
- Growth – Food helps children grow taller, stronger, and healthier.
- Example: Milk, eggs, and pulses help in body growth.
- Repair – When we fall down and get injured, our body repairs the wound. This repairing process is possible because of the nutrients in food.
Sources of Food

Food comes mainly from two sources:
- Plants
- Animals
Food from Plants
- Spices: Pepper, cardamom, turmeric
- Cereals: Rice, wheat, maize, barley
- Pulses: Gram, beans, peas, lentils
- Fruits: Mango, apple, banana, orange
- Vegetables: Potato, tomato, carrot, spinach
- Oil seeds: Mustard, groundnut, sunflower
👉 Plants are the primary source of food. They not only provide food directly (like fruits and vegetables) but also indirectly (plants feed animals, and animals provide food to us).
Food from Animals
- Milk and milk products: Milk, cheese, butter, curd
- Meat: Chicken, mutton, fish
- Eggs: Hen eggs, duck eggs
- Honey: Made by bees from flower nectar
Ingredients of Food

Every dish we eat is made from different raw materials called ingredients.
- Example 1: To prepare rice and dal, we need rice, water, salt, and pulses.
- Example 2: To prepare chapati, we need wheat flour, water, and sometimes oil.
- Example 3: To make cake, ingredients are flour, sugar, milk, butter, and eggs.
👉 Learning about ingredients helps us understand how food is prepared and where the raw materials come from.
Food Variety Around the World

- Different countries have different eating habits. But the purpose of food everywhere is the same: to provide energy and nutrition.
- In America: Burgers, pizza, pasta, but also cereals, fruits, and milk are common.
- In India: Rice, chapati, dal, vegetables, and spices are common.
- In China & Japan: Rice, noodles, fish, and soy products are widely eaten.
- In Europe: Bread, cheese, meat, and salads are common.
- In Africa: Maize, millet, cassava, and beans are staple foods.
👉 Though the dishes differ, the nutrients remain similar.
Quick Recap (for Section 1)
- Food habits differ across the world, but all serve the same purpose.
- Food is essential for life.
- We need food for energy, growth, repair, and protection.
- Food comes from plants and animals.
- Ingredients are raw materials used in cooking.
Section 2: Sources of Food in Detail
In the previous section, we learned why food is important and how it comes from plants and animals. Now, let’s study these sources in detail with examples that students across the world can relate to.
1. Food from Plants 🌱
Plants are the primary producers in nature. They prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis, using sunlight, carbon dioxide, water, and chlorophyll. Because plants can make their own food, they are called autotrophs.
Humans and animals depend on plants directly or indirectly for food.

(a) Cereals and Grains
Cereals are the main source of carbohydrates. They give energy to our body.
- Examples in India: Rice, wheat, maize, barley
- Examples in Africa: Maize (corn), millet, sorghum
- Examples in Europe: Wheat (bread, pasta), oats
- Examples in America: Corn, wheat, rice
👉 Rice is the staple food for billions of people in Asia. Wheat is used for making chapatis in India and bread in Western countries.
(b) Pulses
Pulses are rich in proteins. They are also called legumes.
- Common pulses: Lentils (masoor dal), chickpeas, green gram (moong), black gram (urad dal), kidney beans (rajma), peas.
- In Africa, beans and lentils are widely eaten.
- In Europe and America, baked beans, peas, and lentil soups are common.
👉 Pulses are called the “vegetarian’s meat” because they are an excellent source of protein.

(c) Fruits
Fruits provide vitamins, minerals, and fibre.
- Tropical fruits: Mango, banana, papaya, pineapple (India, Brazil, Africa).
- Temperate fruits: Apple, orange, pear, grapes (USA, Europe).
- Berries: Strawberry, blueberry, raspberry (Europe, USA).
(d) Vegetables
- Vegetables are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and roughage.
- Fruit vegetables: Tomato, brinjal, cucumber, pumpkin.
- Root vegetables: Carrot, beetroot, radish, potato.
- Leafy vegetables: Spinach, cabbage, lettuce.
- Flower vegetables: Cauliflower, broccoli.
👉 Vegetables are eaten raw, cooked, or as salads. They are essential for balanced diet.

(e) Spices and Oil Seeds
- Spices like turmeric, black pepper, cardamom, and cloves not only add taste but also have medicinal value.
- Oil seeds like groundnut, mustard, sunflower, and soybean give us edible oils.
(f) Beverages from Plants
- These drinks are popular worldwide for refreshment.
- Tea (from tea leaves), coffee (from coffee beans), cocoa (from cocoa seeds).
2. Food from Animals 🐓🐟🐄
Animals are another important source of food. They provide us with proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
(a) Milk and Milk Products
- Animals like cow, buffalo, goat, and camel give us milk.
- Milk products include butter, cheese, curd, paneer, ghee, and yogurt.
- In Western countries, cheese is very popular. In India, paneer is common. In the Middle East, camel milk is consumed.
👉 Milk is considered a complete food because it contains almost all essential nutrients.
(b) Eggs
- Hens are the main source of eggs, but ducks and quails also give edible eggs.
- Eggs are rich in protein and fat.
- In many countries, eggs are a common breakfast item (boiled eggs, omelets).

(c) Meat and Fish
- Meat from goat, sheep, chicken, and pigs is eaten in many cultures.
- Fish is an important food in coastal regions (Japan, India, Norway, USA).
- Sea food includes prawns, crabs, lobsters, etc.
👉 Meat and fish are rich in protein, fats, and minerals like iron and phosphorus
(d) Honey
- It is widely used in Asia, Africa, and Europe as food and medicine.
- Honey is made by bees from the nectar of flowers.
- It is a natural sweetener and also has medicinal properties.
3. Other Sources of Food
Apart from plants and animals, humans also use some other sources for food:
- Fungi: Mushrooms are eaten as vegetables.
- Algae: Seaweed is eaten in Japan and Korea.
- Microorganisms: Yeast is used in baking bread, curd is made by bacteria.
4. Regional Food Habits 🌎
Food habits differ across regions due to climate, culture, and availability.
- India: Rice in the south, wheat in the north, fish in coastal areas.
- China & Japan: Rice, noodles, soy products, fish.
- Middle East: Bread, meat, milk, dates.
- Europe: Bread, cheese, meat, pasta, potatoes.
- Africa: Maize, millet, cassava, beans.
- America: Burgers, pizza, cereals, milk, beef.
👉 Even though food habits are different, the nutrients required are the same everywhere.
5. Concept of Ingredients 🔎
An ingredient is a raw material used to prepare food.
- For khichdi: rice + dal + salt + spices.
- For bread: wheat flour + yeast + water + salt.
- For salad: cucumber + tomato + onion + lemon.
👉 By learning ingredients, students understand how raw food is turned into cooked food.
Quick Recap (Section 2)
- Plants give us cereals, pulses, fruits, vegetables, oils, and spices.
- Animals give us milk, eggs, meat, fish, and honey.
- Other sources include fungi, algae, and microorganisms.
- Food habits differ regionally but all serve the same purpose – nutrition.
- Ingredients are the basic raw materials for making dishes.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Oxford Book Solution

1. Objective type questions.– Exercises
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
- 1. Green plants are known as their own food. (producers/consumers) because they prepare
- 2. The stems of (sugar cane/bamboo) plant is used to make sugar.
- 3. (Honey/Milk) is collected from beehives and has medicinal value.
- 4. (Cheese/Butter) is made by churning fresh cream.
- 5. A……..(scavenger/decomposer) feeds on the flesh of dead animals.
Ans:
- Green plants are known as producers because they prepare their own food.
- The stems of sugar cane plant are used to make sugar.
- Honey is collected from beehives and has medicinal value.
- Butter is made by churning fresh cream.
- A scavenger feeds on the flesh of dead animals.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Oxford Book Solution-MCQs
B. Choose the correct option.
1. The flowers of which of these plants are eaten as vegetables?
a. Broccoli and cauliflower b. Banana
c. Cabbage and Ginger d. Both a. and b.
Ans:→ a. Broccoli and cauliflower
2. The seeds of this plant are used as spices.
a. Wheat b. Cumin
c. Maize d. Chickpea
Ans: → b. Cumin
3. Which of these is made if you put a few drops of lemon juice in hot milk?
a. curd b. butter
c. Ghee d. Paneer
Ans: → d. Paneer
4. Which of these do herbivores depend on for their food?
a. Plants b. flesh of other animals
c. Dead plants and animals d. All of these
→ a. Plants
5. Which of the following animals is a carnivore?
a. Butterfly b. Spider
c. Honey Bee d. Squirrel
Ans→ b. Spider
6. This food product is obtained from beehives.
a. Honey c. nectar
b. Eggs d. Milk
Ans: → a. Honey
7. Which of these animals swallow their prey whole?
a. Eagle b. Snakes
c. Butterflies d. None of them
8. Which of the following birds has a sharp and pointed beak?
a. Eagle b. Hawk
c. Crow d. None of them
Ans: B. Choose the correct option
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Oxford Book Solution – 1 mark
II. Very short answer type questions.
A. Give one word for the following.
- 1. The green pigment present in leaves of green plants………….
- 2. The process by which plants prepare their own food……………..
- 3. Products obtained from milk………………
- 4. The process by which milk gets separated into solid and liquid parts……………
- 5. Organisms that decompose dead plants and animals………………
Ans:
- Chlorophyll
- Photosynthesis
- Dairy products
- Curdling
- Decomposers
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Oxford Book Solution- 1 Mark
B. Give two examples for the following.
- 1. Roots that we eat as vegetables ………….. …………….
- 2. Stems that we eat as vegetables………………. ………………
- 3. Leaves that we eat as vegetables…………. ………………..
- 4. Seeds that are eaten after sprouting…………. ……………..
- 5. Animals that give us eggs………………. ……………………
Ans:
- 1. Roots that we eat: Carrot, Radish
- 2. Stems that we eat: Potato, Sugar cane
- 3. Leaves that we eat: Spinach, Cabbage
- 4. Sprouted seeds we eat: Moong, Chickpea
- 5. Animals that give us eggs: Hen, Duck
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Oxford Book Solution- 2 Marks
III. Short Answer Questions
- What are the main sources of food?
→ Plants and animals are the main sources of food. - What is sprouting?
→ Sprouting is the process where seeds start to grow tiny roots and shoots when soaked in water. - Why do we need to have calcium-rich foods?
→ Calcium-rich foods help in making our bones and teeth strong. - How do we commonly make curd at home?
→ We add a small amount of curd to warm milk and leave it for a few hours to set. - Define:
- Herbivores: Animals that eat only plants.
- Carnivores: Animals that eat only other animals.
- Omnivores: Animals that eat both plants and animals.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Oxford Book Solution-4 marks
IV. Long Answer Questions
1.Describe, with examples, how plants are an important source of food.
Ans: Plants are one of the most important sources of food for both humans and animals. They provide us with fruits, vegetables, cereals, pulses, and nuts. Different parts of a plant are used as food. For example, we eat the roots of carrots and radishes, the stems of sugar cane and potatoes, the leaves of spinach and cabbage, the flowers of cauliflower and broccoli, and the fruits of mango and banana plants.
Cereals like rice, wheat, and maize are the seeds of plants and are the main food in many countries. Pulses such as moong and gram are also seeds and are rich in proteins. Spices like cumin, coriander, and black pepper are also obtained from plants. These make our food tasty and healthy.
Plants also give us edible oils like mustard oil, coconut oil, and groundnut oil, which are used for cooking. Tea, coffee, and sugar also come from plants. Animals that give us milk, like cows and goats, depend on plants for their food, so indirectly, plants help us get milk and dairy products too.
Thus, plants are very important for our survival as they are the base of the food chain and give us a variety of foods to stay healthy.
2.What are dairy products? With the help of paneer and curd, explain how we get them.
Ans: Dairy products are food items made from the milk of mammals, such as cows, buffaloes, goats, and sheep. They include products like milk, cheese, butter, ghee, curd, and paneer. These products are rich in nutrients like protein, calcium, and vitamins, making them essential for a healthy diet.
- Paneer and Curd:
- Curd:
- Curd is made by fermenting milk with the help of bacterial cultures. When milk is heated and then cooled to a lukewarm temperature, a small amount of curd (previously prepared) is added to it. The bacteria in the curd ferment the lactose in the milk, causing it to thicken and form curd.
- Paneer:
- Paneer, also known as Indian cottage cheese, is made by curdling milk with an acidic substance like lemon juice or vinegar. First, milk is heated and then the acid is added to curdle the milk. The solid curds that form are separated from the whey (the liquid part) and then pressed into a block to form paneer.
- In summary, curd is made through bacterial fermentation, while paneer is made by curdling milk using an acid, followed by pressing. Both are common and nutritious dairy products enjoyed in various cuisines.
3.Classify animals based on the type of food they eat. Explain each group.
Ans:

Animals are grouped according to the food they eat:
- Herbivores – Eat plants, grass, and leaves.
- Examples: Cow, goat, deer, elephant.
- Carnivores – Eat flesh of other animals.
- Examples: Lion, tiger, eagle.
- Omnivores – Eat both plants and flesh.
- Examples: Humans, bear, crow.
- Scavengers – Eat dead animals and help clean the environment.
- Examples: Vulture, hyena, jackal.
- Parasites – Live on or inside other animals and take food from them.
4. Write a note on the type of teeth in different animals.
Ans: Animals have different kinds of teeth depending on the food they eat. Their teeth are specially designed to suit their feeding habits. These teeth help them gnaw seeds, nuts, and wood.
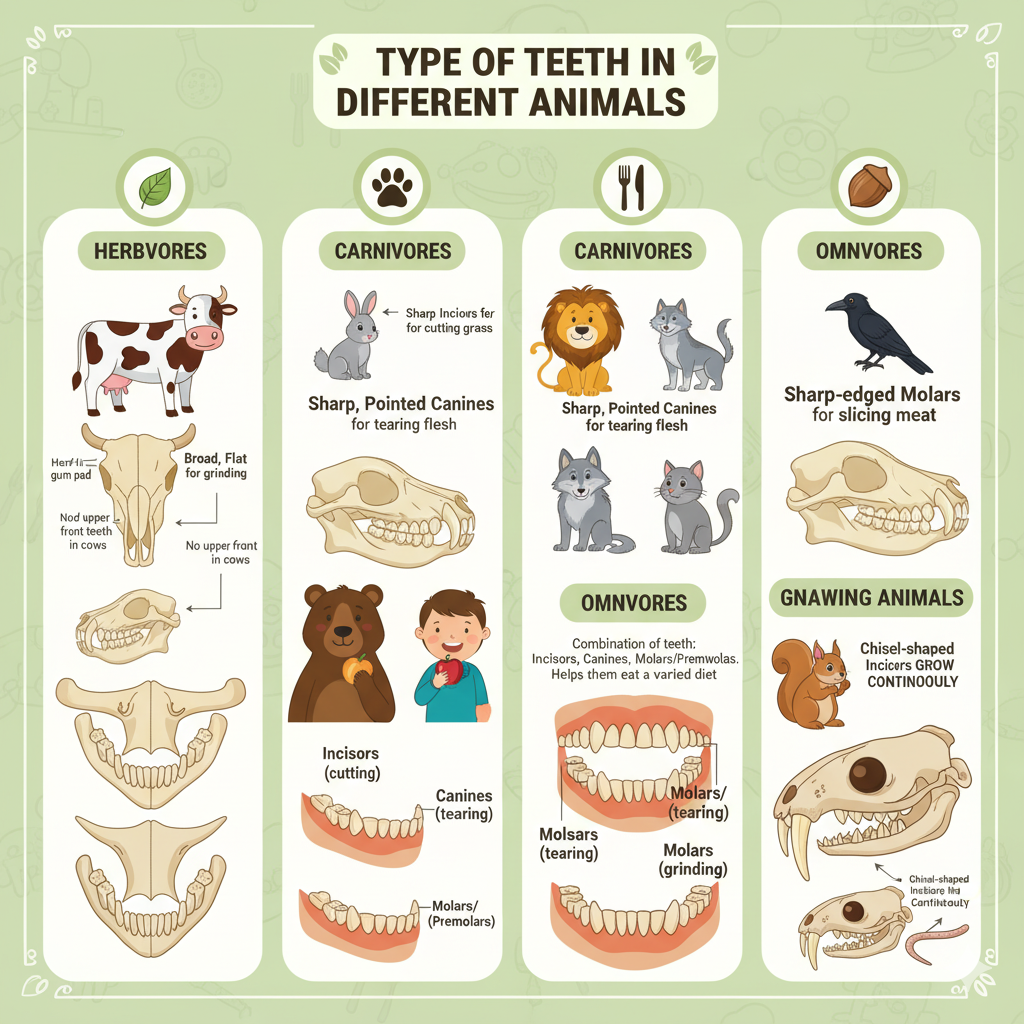
Herbivores (Plant-eating animals)
Examples: Cow, goat, horse, rabbit.
- They have sharp front teeth (incisors) for cutting grass and leaves.
- Their back teeth (molars) are broad and flat to grind plant material.
- Cows do not have upper front teeth; instead, they use their lower incisors and a hard upper gum pad to bite grass.
Carnivores (Flesh-eating animals)
Examples: Lion, tiger, cat, dog.
- They have sharp, pointed canines for tearing flesh.
- Their incisors help in cutting meat.
- Their molars are sharp-edged and act like scissors to slice meat and bones.
Omnivores (Animals that eat both plants and flesh)
Examples: Humans, bear, crow.
- They have a combination of teeth:
- Incisors for cutting food.
- Canines for tearing.
- Molars and premolars for grinding.
- This helps them eat a variety of food.
5.Differentiate between scavengers and decomposers with examples.
Ans:
- Scavengers eat the flesh of dead animals. Example: vultures, crows.
- Decomposers break down dead plants and animals into simple substances. Example: fungi, bacteria.
| Feature | Scavengers | Decomposers |
| Definition | Animals that feed on dead and decaying bodies of other animals. | Microorganisms that break down dead plants and animals into simpler substances. |
| Mode of Action | Eat and tear the dead organisms into pieces. | Break down complex organic matter chemically. |
| Type of Organism | Mostly animals (larger in size). | Mostly fungi and bacteria (microscopic). |
| Example Organisms | Vultures, hyenas, jackals, crows. | Fungi, bacteria, actinomycetes. |
| Role in Ecosystem | Help in cleaning the environment by removing dead bodies. | Help in nutrient recycling by converting dead matter into simple substances. |
| Visible to Naked Eye | Yes | Mostly no (microscopic). |
Worksheet – Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Oxford Book Solution
A. Fill in the blanks.
- Animals that eat only plants are called __________.
- Animals that eat flesh of other animals are called __________.
- Honey is made by __________ from the nectar of flowers.
- __________ is the staple food of South India.
- The raw materials used to prepare a dish are called __________.
B. Match the following.
- Cow → (a) Flesh-eating
- Lion → (b) Plant-eating
- Human → (c) Makes honey
- Vulture → (d) Eats both plants and animals
- Honeybee → (e) Scavenger
C. Very Short Answer Questions.
- Why do living beings need food?
- Name two food items we get from plants.
- Name two food items we get from animals.
- Give one example of an omnivore.
- What are ingredients?
D. Short Answer Questions.
- Classify animals based on the type of food they eat.
- Write a short note on the teeth of herbivores and carnivores.
- Mention any three methods of food preservation.
- Give three examples of food variety in different countries.
E. True or False.
- Tiger is a herbivore. (_____)
- Wheat and rice are cereals. (_____)
- Humans are omnivores. (_____)
- Pickling is a method of food preservation. (_____)
- Cows give us eggs. (_____)
F. Activity/Think & Answer.
- List the food items you ate yesterday. Identify which are plant products and which are animal products.
- Visit your kitchen and note at least five preserved foods. Write how they are preserved.
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
