Electricity plays a vital role in our daily lives—from lighting our homes to powering devices. In Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Electricity and Circuit, students are introduced to the basic concepts of electric current, circuits, switches, conductors, and insulators. Understanding how simple electric circuits work builds the foundation for learning advanced science in later classes.
This page provides complete Oxford book solutions for Chapter 14, including fill in the blanks, multiple choice questions (MCQs), short and long answer type questions, and labeled diagrams where needed. These answers are explained in a simple, student-friendly manner to help you understand the concepts easily and prepare well for exams.
Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Electricity and Circuit Textbook Answers
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct word – Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Electricity and Circuit
1…… (Pencil cell/flowing water) is used for the large-scale generation of electricity.
2. Solar cells use……. (Chemicals/sunlight) to produce electric current.
3. By convention, electric current flows from the….. (positive/negative) terminal.
4. An electric switch is used to open or close an electric…… (Bulb/circuit).
5. People operating electrical equipment are asked to wear rubber gloves to safeguard against electric……… (Wastage/shocks).
Answer:
- Flowing water is used for the large-scale generation of electricity.
- Solar cells use sunlight to produce electric current.
- By convention, electric current flows from the positive terminal.
- An electric switch is used to open or close an electric circuit.
- People operating electrical equipment are asked to wear rubber gloves to safeguard against electric shocks.
B. Choose the correct option – Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Electricity and Circuit
1. Which of these is a part of a dry cell?
a. Filament
b. Terminals
c. Inert gas
d. Glass mount
Answer: b. Terminals
Explanation: A dry cell has two terminals — one positive and one negative — which are used to connect the cell to a circuit.
2. Which of these produces electricity?
a. Car battery
b. Ceiling fan
c. Light bulb
d. Refrigerator
Answer: a. Car battery
Explanation: A car battery stores and produces electrical energy through chemical reactions. Other options only use electricity.
3. Which of these is necessary for an electric current to flow through a circuit?
a. Switch
b. Light bulb
c. Insulation tape
d. Source of electricity
Answer: d. Source of electricity
Explanation: A power source like a dry cell or battery is required to provide energy for current to flow.
4. A dry cell has
a. Two positive terminals
b. Two negative terminals
c. Two negative and one positive terminal
d. One positive and one negative terminal
Answer: d. One positive and one negative terminal
Explanation: These two terminals are necessary for completing the circuit and allowing current to flow.
5. Which of these is a good conductor of electric current?
a. Wood
b. Graphite
c. Pure water
d. Rubber
Answer: b. Graphite
Explanation: Graphite, a form of carbon, allows electric current to pass through and is used in pencil leads and dry cells.
6. Which of these works when an electric current flows through it?
a. An electric torch
b. A chair
c. A book
d. A wax candle
Answer: a. An electric torch
Explanation: An electric torch uses current from cells to light up a bulb. The other items don’t use electricity to function.
7. Support wires, filament, glass mount, inert gas, would be components of
a. an electric fan
b. an incandescent bulb
c. a dry cell
d. an electric switch
Answer: b. an incandescent bulb
Explanation: These are internal parts of a traditional electric bulb that help produce light when current passes through.
8. An electric switch is a device that is used to
a. produce electricity
b. open or close an electric circuit
c. fuse an electric bulb
d. produce heat
Answer: b. open or close an electric circuit
Explanation: A switch helps control the flow of current by either connecting or disconnecting the circuit.
9. A material that is not a conductor of electricity is called a/an
a. filament
b. switch
c. insulator
d. bulb
Answer: c. insulator
Explanation: Insulators like rubber or plastic block the flow of electricity and are used for safety.
10. Which of these devices is also referred to as a ‘key’?
a. an electric torch
b. an electric switch
c. a filament
d. a dry cell
Answer: b. an electric switch
Explanation: In science, a switch is often called a ‘key’ because it opens or closes the electric circuit just like a key opens or closes a lock.
II. Very Short answer type questions
A. Give two examples of places where the following could be used.
- A dry cell:
- In a wall clock
- In a TV remote control
- A secondary cell:
- In mobile phone batteries
- In inverter systems
- Electric switch:
- In room light control
- In a fan regulator
- Conductors:
- In electric wiring (e.g., copper wires)
- In metal bodies of appliances for grounding
- Insulators:
- Plastic coating on electric wires
- Handle of electric irons or screwdrivers
B. Explain the following terms:
- Electrical appliances:
Devices that work using electricity to perform a specific function are called electrical appliances. Examples include fans, refrigerators, electric kettles, and irons. - A source of electric current:
A device or system that provides a continuous flow of electrons (electricity) is called a source of electric current. Examples: dry cell, battery, generator. - Electrical circuit:
A complete path through which electric current can flow is called an electrical circuit. It includes components like a power source, wires, switches, and electrical appliances. - An electric switch:
A device used to open or close an electric circuit is called an electric switch. It helps in controlling the flow of current in a circuit. - Insulator:
A material that does not allow electric current to pass through it is called an insulator. Examples: rubber, plastic, glass.
III. Short Answer Type Questions
- Name a source that uses chemical reactions to produce electric current.
Answer: Dry cell - Name an appliance that uses electric current to produce light.
Answer: Electric bulb - Name a kind of cell that uses sunlight to produce electric current.
Answer: Solar cell - Name a device that is used to make or break an electrical circuit.
Answer: Electric switch - What name is given to cells that cannot be recharged?
Answer: Primary cells
IV. Long Answer Type Questions
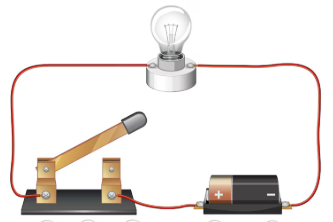
- Draw a simple electrical circuit and label the parts. Explain how we can connect a bulb in a circuit and how it can show us if an electric current is flowing in the circuit or not.
Answer: To create a simple circuit:
- Connect the positive terminal of the cell to one side of the bulb using a wire.
- Connect the other terminal of the bulb to a switch.
- Connect the switch back to the negative terminal of the cell.
If the switch is closed (ON), the bulb glows. This means electric current is flowing. If the switch is open (OFF), the bulb does not glow, showing no current flow.
Diagram:
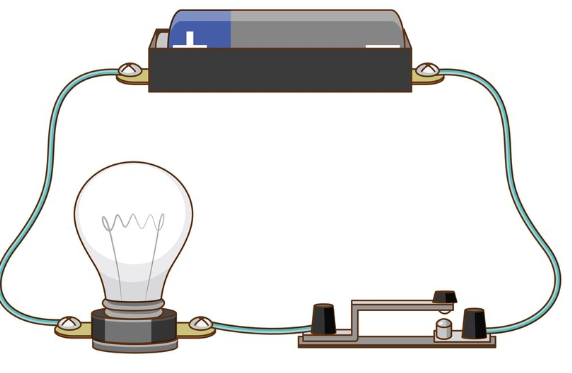
2. Using a bulb, cell and key, draw diagrams and explain the flow of electric current in an ‘open circuit’ and in a ‘closed circuit’.
Ans: Closed Circuit (Bulb Glows)
In a closed circuit, the key or switch is in the closed position. This means the circuit is complete, and electric current flows from the positive terminal of the cell, through the key and the bulb, and returns to the negative terminal. As a result, the bulb receives current and glows.

Open Circuit (Bulb Does Not Glow)
In an open circuit, the key or switch is in the open position. This breaks the path of the current, so the electric current cannot flow through the circuit. Since the bulb does not receive any current, it does not glow.
3. What is a dry cell? What is inside it? Why is it useful to us?
Ans: A dry cell is a type of electric cell that provides a small amount of electricity for use in portable devices. It is called “dry” because it does not contain a free-flowing liquid; instead, it uses a moist paste as the electrolyte.
What is Inside a Dry Cell?
A dry cell consists of:
- A zinc container (which acts as the negative terminal)
- A carbon rod in the center (positive terminal)
- A paste of ammonium chloride and zinc chloride as the electrolyte
- Manganese dioxide surrounding the carbon rod, which acts as a depolarizer
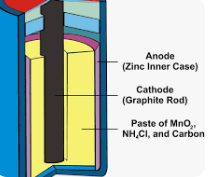
A dry cell is useful because:
- It is small, portable, and easy to use
- It does not spill, unlike liquid cells
- It can be used in everyday devices like wall clocks, remote controls, torches, and toys
Dry cells provide a convenient and safe source of electricity for many household and electronic items.
4. How does an electric torch work? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Answer: An electric torch (also called a flashlight) is a portable device that produces light using electric current. It contains one or more dry cells (batteries), a bulb, a switch, and metal contacts or wires to form an electric circuit.
Working of an Electric Torch:
- Battery (Dry Cell) provides the electrical energy.
- Wires or metal strips connect the positive and negative terminals of the battery to the bulb.
- Switch is used to open or close the circuit.
- Bulb glows when electric current flows through it.
- When the switch is ON, the circuit becomes closed, allowing current to flow from the battery to the bulb.
- The bulb receives current and produces light.
- When the switch is OFF, the circuit becomes open, so no current flows, and the bulb does not glow.
5. One class of materials allow the flow of electric current and some do not. What are these different classes of material called?
Answer: The different classes of materials based on their ability to conduct electric current are called:
- Conductors
- Insulators
*Conductors are materials that allow electric current to flow through them easily.
These materials have free electrons that move and carry current.
Examples: Copper, aluminium, iron, graphite.
*Insulators are materials that do not allow electric current to pass through them.
They resist the flow of electricity and are used for safety.
Examples: Rubber, plastic, wood, glass.
Summary:
- Conductors = allow current to flow
- Insulators = block current flow
These properties help us in designing safe and effective electrical devices.
You can access the official NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics on the NCERT website at the following link:
NCERT Class 10 Mathematics Solutions
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
