Based on the solutions Class 6 science Light Shadow and Reflection-Oxford, users can access and understand different methods of separating substances from mixtures. In our everyday life, we often deal with mixtures—like tea with leaves, salt in water, or grains mixed with stones. To make these mixtures useful, we need to separate the unwanted or harmful substances.

This chapter Class 6 science Light Shadow and Reflection-Oxford explains why separation is important and teaches us different methods such as hand picking, sieving, filtration, decantation, evaporation, and condensation. Each method is explained with simple examples and activities so that students can easily understand how to use them in real life. This helps us make substances clean, pure, and fit for use
Page 175| Exercises – Class 6 science Light Shadow and Reflection-Oxford
I. Objective type questions
- Choose the correct option
1. Light enable us to
a. hear b. see
c.taste d. None of the above
2. Which of these is not a natural source of light?
a. A star b. Firefly
c. Tubelight d. The sun
3. Pick out the opaque material from the following.
a. Grass b. Air
c. Clear glass d. Clean water
4. Which of these is not necessary to form a shadow?
a. The sun b. A source of light
c. An opaque object d. A screen or surface
5. A pinhole camera produces which of the following?
- Coloured inverted image
- Black and white inverted image
- Black and white upright image
- Coloured upright image
6. Which of these is not a source of light?
a. A star c. A lit candle
b. A lit light bulb d. A book
7. Which of these is transparent?
a. Butter paper b. Pure air
c. Mud d. A mirror
8. What happens when we look at an object through a translucent material?
a. We can see it very clearly.
b. Can not see it at all.
c. We can see it, but not very clearly.
d. We can see its image.
9. The shadow of an object shows its
a. size b. colour
c. shape or outline d. all of these
10. Unlike its shadow, the image of an object shows its.
a, outline b. shape
d. none of these c. colour
Objective Type Questions – Class 6 science Light Shadow and Reflection-Oxford
A. Choose the correct option
- Light enables us to
b. see - Which of these is not a natural source of light?
c. Tubelight - Pick out the opaque material from the following.
a. Grass - Which of these is not necessary to form a shadow?
a. The sun - A pinhole camera produces which of the following?
b. Black and white inverted image - Which of these is not a source of light?
d. A book - Which of these is transparent?
b. Pure air - What happens when we look at an object through a translucent material?
c. We can see it, but not very clearly. - The shadow of an object shows its
c. shape or outline - Unlike its shadow, the image of an object shows its
c. colour
B. Write T for the true statement and F for the false one. Correct the false statement(s).
- We cannot see an object through a transparent material.
F – Correction: We can see through a transparent material. - Clear air is opaque.
F – Correction: Clear air is transparent. - Shadows cannot be formed without a source of light.
T - The shadow of an object shows its colour.
F – Correction: The shadow of an object shows its shape or outline, not its colour. - The image formed by a pinhole camera is coloured.
F – Correction: The image formed by a pinhole camera is black and white.
II. Very short answer type questions. – Class 6 science Light Shadow and Reflection-Oxford
A. Give two examples of the following.
- 1. Human-made sources of light
- 2. Opaque materials
- 3. Objects that can form a shadow
- 4. Irregular surfaces (with respect to reflection)
- 5. Regular surfaces (with respect to reflection)
Ans:
- 1.Electric bulb and Candle
- 2. Wood and Metal
- 3. A chair and A book
- 4. Rough wall and Wooden surface
- 5. Mirror and Still water
B. Define the following terms.– Class 6 science Light Shadow and Reflection-Oxford
- 1. A natural source of light
- 2. Transparent material
- 3. Translucent material
- 4. Opaque material
- 5. Shadow
- 6. Diffused reflection
Ans:
- A natural source of light:
A natural source of light is something that produces its own light naturally, without the need for an external power source. Example: The sun. - Transparent material:
A transparent material allows light to pass through it so that objects behind can be clearly seen. Example: Glass. - Translucent material:
A translucent material allows some light to pass through but scatters it, making objects on the other side appear blurry. Example: Butter paper. - Opaque material:
An opaque material does not allow light to pass through it, and as a result, objects behind it cannot be seen. Example: Wood - Shadow:
A shadow is a dark area created when an opaque object blocks light from a light source. - Diffused reflection:
Diffused reflection occurs when light strikes a rough surface, and the reflected rays scatter in many directions, leading to a blurry or diffused image.
III. Short answer type questions.– Class 6 science Light Shadow and Reflection-Oxford
1. Classify the following as ‘luminous’ and ‘non-luminous’:
A table, a cup, a star in the night sky, candle flame, a cupboard, a book, water
Ans:
- Non-luminous: A table, a cup, a cupboard, a book, water
- Luminous: A star in the night sky, candle flame
2. What are natural sources of light? Give two examples.
Ans: Natural sources of light are those that produce light naturally.
Example 2: A star
Example 1: The Sun
3. If you want a wall, so that you can see clearly on the other side, what kind of material would you use to build it?
Ans: To see clearly through the wall, the material should be transparent, such as glass.
4. What property of light is demonstrated by formation of shadows and pinhole camera?
Ans: The rectilinear propagation of light is demonstrated by the formation of shadows and images in a pinhole camera.
5. Write down any two characteristics of a shadow.
- A shadow is always formed in the opposite direction of the light source.
- The size of a shadow depends on the distance between the light source and the object.
IV. Long answer type questions.– Class 6 science Light Shadow and Reflection-Oxford
1. Can you see clearly through a transparent material? Give two examples of transparent materials. Describe an activity to determine whether a given material is transparent or not.
Yes, you can see clearly through a transparent material because it allows light to pass through it without scattering, making objects on the other side visible.
Examples of Transparent Materials:
- Glass
- Water
Activity to Determine if a Material is Transparent:
Objective: To check if a material is transparent.
Materials Required:
- A piece of paper with a simple drawing (like a letter “A”)
- A transparent material (like a glass sheet)
- An opaque material (like a book or cardboard)
Procedure:
- Place the paper with the drawing (the letter “A”) on a table.
- Hold the transparent material (glass sheet) above the paper.
- If you can clearly see the drawing of the letter “A” through the glass, it means the material is transparent.
- Repeat the same procedure with an opaque material like a book or cardboard. If you cannot see the drawing through the material, then it is opaque.
Conclusion: If you can see through the material and clearly view the object on the other side, the material is transparent. If the material blocks the view, it is opaque.
This simple activity helps determine whether a material is transparent, allowing light to pass through and making objects visible behind it.
2. Why is it that we cannot see a reflected image on a rough wall?
Ans: We cannot see a reflected image on a rough wall because of diffused reflection.
Explanation: When light strikes a smooth surface, such as a mirror, it reflects at a uniform angle, and the rays remain parallel. This produces a clear, distinct image because all the reflected light rays follow the same path.
However, when light hits a rough surface, like a rough wall, the surface does not reflect the light uniformly. Instead, the light rays are scattered in many different directions. This scattering of light is called diffuse reflection.
Since the reflected rays are scattered in various directions, they do not come together to form a clear, focused image. Instead, the reflected light is spread out, and we cannot see a sharp or distinct image as we would on a smooth surface.
Conclusion: A rough surface scatters the reflected light in many directions, preventing the formation of a clear, reflected image, unlike a smooth surface like a mirror that reflects light uniformly to form an image.
3. Draw a diagram to illustrate reflection of a parallel beam of light from a smooth surface.
Diagram:
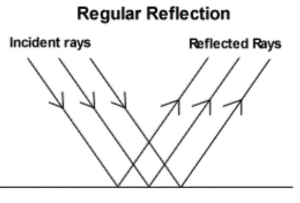
4. Draw a diagram to show how an image is formed in a pinhole camera. Label all the parts of the pinhole camera.
Ans:
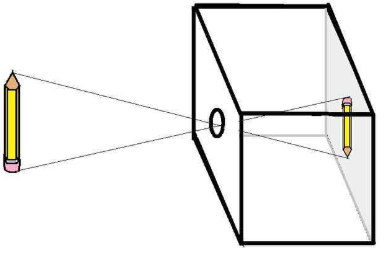
Labels:
- Object: The object outside the pinhole camera.
- Camera Box: The outer casing of the camera.
- Pinhole: The small hole that allows light to enter the camera.
- Screen: The surface where the inverted image is formed.
- Light Rays: Straight lines of light passing through the pinhole to form the image.
Conclusion: The pinhole camera forms an inverted and reversed image of the object on the screen inside. The image quality can be affected by the size of the pinhole and the distance between the pinhole and the screen.
Class 6 science Light Shadow and Reflection-Oxford – Explore More chapters
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
