Class 6 Science Water and Its Importance Oxford is one of the most essential natural resources for all living beings. Without water, life on Earth cannot exist. In Class 6 Science, the chapter “Water and Its Importance” (Oxford) explains how water exists in nature, the processes of the water cycle, and the importance of saving this precious resource. This chapter also highlights problems like droughts, floods, and pollution, and teaches us methods such as rainwater harvesting and conservation practices.
On this page, you will find complete solutions to the Oxford Class 6 Science chapter “Water and Its Importance” including fill in the blanks, multiple-choice questions, very short answers, short answers, and long answer type questions. These solutions will help students understand the concepts clearly and prepare well for exams.
Class 6 Science Water and Its Importance Oxford Textbook Answers
I. Objective Type Questions
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
- Water exists in the form of gas in nature as water vapour (from water, snow) and as steam (from boiling water).
- Water cycle is the cyclic movement of water from the atmosphere to the Earth and back to the atmosphere through various processes.
- Drought is the condition when the ground is submerged under water, due to heavy rain and overflowing of rivers.
(Correction: actually Flood is the right answer here). - Dam is a structure built on a river to store and hold back water.
- Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting and storing rainwater from roofs or surface catchments.
B. Choose the correct option.
Q1. How much of the Earth’s water is present in seas and oceans as salt water?
a) 3%
b) 97%
c) 0.003%
d) 29.97%
Answer: b) 97%
Q2. Water found in rivers, lakes, and ponds used for domestic and commercial purposes is called:
a) potable water
b) sea water
c) fresh water
d) salt water
Answer: c) fresh water
Q3. The conversion of water vapour into its liquid form happens by the process of:
a) condensation
b) evaporation
c) transpiration
d) precipitation
Answer: a) condensation
Q4. Abnormally long period of insufficient or no rainfall is:
a) flood
b) epidemic
c) famine
d) drought
Answer: d) drought
Q5. What are the tiny crystals of water droplets floating in the air called?
a) Rivers
b) Clouds
c) Precipitation
d) Water cycle
Answer: b) Clouds
Q6. Which of the following is not the result of drought?
a) Water logging
b) Lack of food
c) Thirst and dehydration
d) Crop failure
Answer: a) Water logging
Q7. Which one of the following is an outcome of a flood?
a) Water shortage
b) No rainfall
c) Drought
d) Water-borne diseases
Answer: d) Water-borne diseases
Q8. The plants give off water vapour through their leaves by the process of:
a) condensation
b) evaporation
c) transpiration
d) precipitation
Answer: c) transpiration
Q9. Which of the following is not a method of conservation of water?
a) Avoiding wastage of water
b) Building dams
c) Rainwater harvesting
d) Pollution of water
Answer: d) Pollution of water
Q10. Which of the following will lead to wastage of water?
a) Watering plants in the morning
b) Repair of leaky pipes and taps
c) Using a wet cloth to clean the car
d) Leaving the tap open while brushing
Answer: d) Leaving the tap open while brushing
II. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Watering crops by artificial means is called?
Answer: Irrigation
Q2. Water fit for human consumption is called?
Answer: Potable water
Q3. Release of water vapour into the atmosphere through plant leaves is called?
Answer: Transpiration
Q4. Lack of food in a region for a long period is called?
Answer: Famine
Q5. A disease affecting thousands of people at the same time is called?
Answer: Epidemic
III. Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Explain the following with the help of simple activities:
a) Condensation of water vapour present in air.
Answer: When a chilled glass of water is kept outside on a hot day, water droplets form on the glass surface. This happens due to condensation of water vapour present in the air.
b) Condensation of steam.
Answer: When steam comes in contact with a cool surface, it changes into water droplets. This shows condensation of steam into water.
Q2. How are clouds formed?
Answer: Clouds are formed when water vapour rises up, cools down at high altitudes, and condenses into tiny water droplets or ice crystals. These droplets cluster together to form clouds.
Q3. State four ways to avoid wastage of water at home.
Answer:
- Close taps properly after use.
- Repair leaking taps and pipes.
- Use a bucket instead of a shower for bathing.
- Water plants in the morning or evening to reduce evaporation.
Q4. Explain the formation of water cycle.
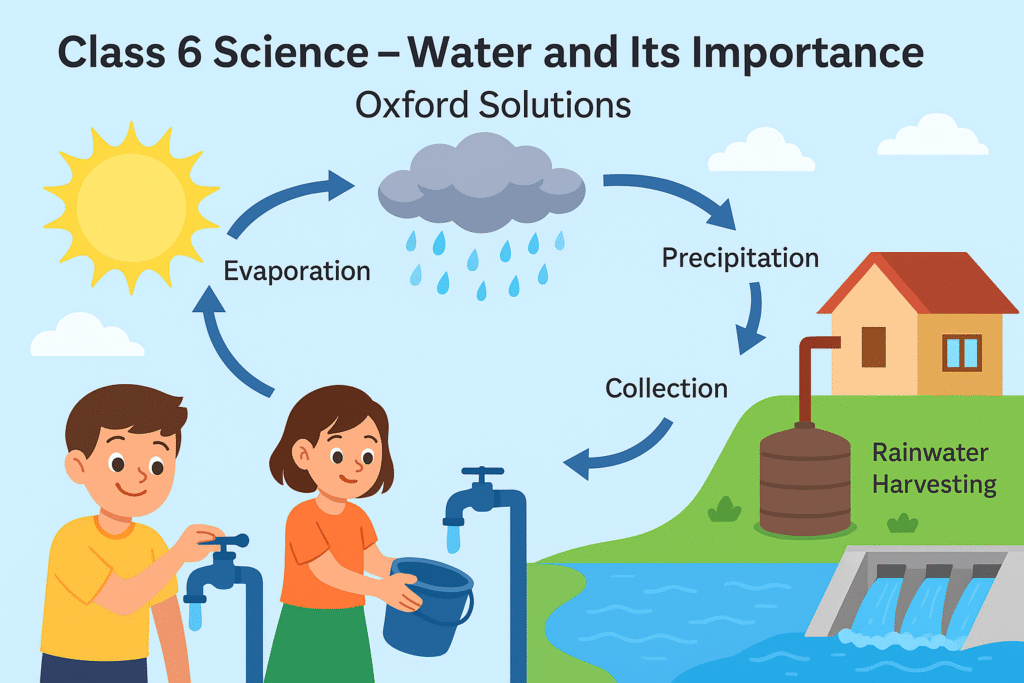
Answer: The water cycle involves the continuous movement of water on Earth. Water evaporates from oceans, rivers, and lakes due to heat, rises as vapour, cools down to form clouds (condensation), and returns as rain (precipitation). This cycle repeats endlessly.
Q5. Label the diagram of water cycle:
Answer:
- Sun (provides heat)
- Evaporation (from water bodies)
- Condensation (cloud formation)
- Precipitation (rainfall)
- Collection (rivers, lakes, seas)
IV. Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. Explain how water is used for various purposes in India.
Answer: Water in India is used for drinking, cooking, bathing, and washing. It is also used for agriculture (irrigation), industries (cooling, cleaning, and processing), generating electricity (hydroelectric dams), and maintaining ecosystems.
Q2. What are natural disasters? Explain any two natural disasters.
Answer: Natural disasters are sudden natural events causing damage to life and property.
- Floods: Occur due to heavy rainfall and overflowing rivers, causing destruction and spread of diseases.
- Droughts: Occur when there is little or no rainfall for a long time, leading to crop failure, shortage of food and water.
Q3. Describe how dams, water harvesting, and prevention of water pollution help in conservation of water.
Answer:
- Dams: Store water for irrigation, electricity generation, and drinking purposes.
- Rainwater harvesting: Collects and stores rainwater for later use, reduces groundwater depletion.
- Prevention of water pollution: Keeps water sources clean and fit for human and agricultural use.
Class 6 science oxford book Solutions-All Chapters
Welcome to the solutions for the Oxford Class 6 science oxford book Solutions-All Chapters! Below is a list of all the chapters with links to their solutions. Click on any chapter to access detailed answers, explanations, and helpful study notes.
- Chapter 1: Food
- Chapter 2: Components of Food
- Chapter 3: Separation of Substances
- Chapter 4: Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 5: Sorting Materials into Groups
- Chapter 6: Changes Around Us
- Chapter 7: Things Around Us
- Chapter 8: Getting to Know Plants
- Chapter 9: Form and Body Movements
- Chapter 10: Habitat of the Living
- Chapter 11: Measurement and Motion
- Chapter 12: Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 13: Light, Shadows and Reflections
- Chapter 14: Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 15: Water and its importance
- Chapter 16: Air Around Us
- Chapter 17: Garbage In, Garbage Out
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
