Class 7 Science Ch 1 Nutrition in plant is one of the most important chapters in your science syllabus. It explains how plants prepare their own food and support all life on Earth. In many international curriculums, this topic is also studied in Grade 7 Science or Year 7 Biology as Plant Nutrition or Photosynthesis.
Plants are called the producers of the ecosystem because they can make their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, water, and chlorophyll through the process of photosynthesis. Besides photosynthesis, some plants follow other modes of nutrition such as parasitic, saprophytic, symbiotic, or insectivorous nutrition.

photosynthesis explanation, revision notes, and practice worksheets.
This chapter is important not only for NCERT/Oxford Class 7 students but also for learners across the world who study middle school science.
Concept Summary – Class 7 Science Ch 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition is the process by which living organisms take in food and use it for growth, energy, and repair.
- Plants are called autotrophs because they prepare their own food by photosynthesis.
- Raw materials needed for photosynthesis:
- Carbon dioxide from the air
- Water from the soil
- Sunlight as the energy source
- Chlorophyll in the leaves
- Photosynthesis equation:
6CO2+6H2O→C6H12O6+6O2 - The food produced is stored in the form of starch.
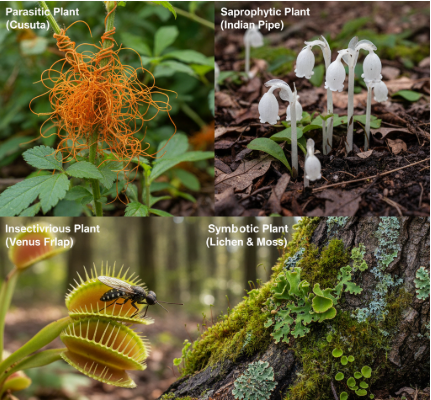

- Some plants cannot make their own food and follow heterotrophic nutrition:
- Parasitic plants – depend on other plants (e.g. Cuscuta).
- Saprophytic plants – absorb nutrients from dead organisms (e.g. mushrooms).
- Symbiotic plants – live in partnership with other organisms (e.g. lichens).
- Insectivorous plants – trap insects to supplement their nutrition (e.g. pitcher plant).
- Plants are the primary producers in the food chain, supporting all life on Earth.
Class 7 Science Ch 1 Nutrition in plant Oxford Book-1 mark
1. Objective type questions
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
1. The mode of nutrition in which an organism makes its own food is called (autotrophic/heterotrophic) nutrition.
Ans: The symbiotic association between Rhizobium and leguminous plants replenishes the soil with nitrogen.
2. The green pigment found in leaves is present in structures called (chloroplasts/chlorophyll).
Ans: The mode of nutrition in which an organism makes its own food is called autotrophic nutrition.
3. Water and other nutrients absorbed by the roots are transported from the roots to other parts of the plant through structures called the (xylem/ phloem).
Ans: The green pigment found in leaves is present in structures called chlorophyll.
4. The roots of saprophytic plants contain convert dead and decaying matter into (fungi/bacteria) that (nutrients/oxygen).
Ans: Water and other nutrients absorbed by the roots are transported from the roots to other parts of the plant through structures called the xylem.
5. The (symbiotic/parasitic) association between Rhizobium and leguminous plants replenishes the soil with (oxygen/nitrogen).
Ans: The roots of saprophytic plants contain fungi that convert dead and decaying matter into nutrients.
Class 7 Science Ch 1 Nutrition in plant Oxford Book-1 mark
B. Write T for the True and F for the False statements. Correct the false statements
1.All plants are autotrophic in nature.
- Answer: F
- Correction: Most plants are autotrophic, but some, like the pitcher plant and dodder, are parasitic or insectivorous.
2. Plants make food in the form of starch as a result of photosynthesis.
- Answer: T
3. The leaf of the pitcher plant is modified into a tubular pitcher to trap insects.
- Answer: T
4. Lichens are a parasitic relationship between a fungus and a bacteria.
- Answer: F
- Correction: Lichens are a symbiotic association between a fungus and an alga or a cyanobacterium.
5. Farmers grow leguminous plants alternately with other crops to restore potassium and phosphorus content of the soil.
Correction: Farmers grow leguminous plants to restore the nitrogen content of the soil.
Answer: F
Class 7 Science Ch 1 Nutrition in Plants – MCQs with Answers & Reasons
C. Choose the correct option.
1. Which of these absorbs light energy?
a. Chlorophyll
b. Stomata
c. Guard cells
d. Veins
Answer: a. Chlorophyll
Reason: Chlorophyll is the green pigment in leaves that traps light energy from the Sun, which is essential for photosynthesis.
2. Which of these increases the surface area to absorb water and minerals through the roots?
a. Rootlets
b. Secondary roots
c. Root hair
d. Primary root
Answer: c. Root hair
Reason: Root hairs are tiny, hair-like structures that greatly increase the surface area of roots, helping in better absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
3. Which of these is the reason for heterotrophic nutrition in certain plants?
a. They do not contain chlorophyll.
b. They grow in places where there isn’t enough light.
c. They depend on other organisms for certain specific nutrients.
d. All of these
Answer: d. All of these
Reason: Some plants lack chlorophyll, some live in shady areas with less light, and some cannot make certain nutrients on their own — so they depend on other organisms.
4. Which of these plants live in association with other organisms in such a way that both gain from each other?
a. Insectivorous plants
b. Saprophytic plants
c. Symbiotic plants
d. Parasitic plants
Answer: c. Symbiotic plants
Reason: In symbiosis, two organisms live together and both benefit. Example: lichens (algae + fungi), Rhizobium bacteria in legume roots.
5. Which of these does a sundew plant have for trapping and digesting insects?
a. Tentacles and mucilage
b. Pitcher and digestive fluid
c. Short, stiff hair and leaves that snap shut
d. Bladder structures that snap shut
Answer: a. Tentacles and mucilage
Reason: Sundew plants have sticky tentacles that secrete mucilage. This traps insects, which are later digested to obtain nitrogen.
6. Which of these is needed for photosynthesis?
a. Chlorophyll
b. Sunlight and water
c. Carbon dioxide
d. All of these
Answer: d. All of these
Reason: Photosynthesis requires chlorophyll (to trap sunlight), carbon dioxide (from air), water (from soil), and sunlight (as energy source).
7. Which of these helps leaves to get carbon dioxide for photosynthesis?
a. Xylem
b. Phloem
c. Stomata
d. Thylakoid
Answer: c. Stomata
Reason: Stomata are small pores on the surface of leaves. They open to allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaf and oxygen to leave.
8. Which of these tissues help in conducting prepared food from leaves to the roots?
a. Xylem
b. Phloem
c. Guard cells
d. Both a and b
Answer: b. Phloem
Reason: Phloem is the tissue that transports prepared food (like glucose) from the leaves to other parts of the plant, including roots.
9. Which of these plants live off dead and rotting material?
a. Parasitic
b. Saprophytic
c. Insectivorous
d. Symbiotic
Answer: b. Saprophytic
Reason: Saprophytic plants like mushrooms feed on dead and decaying matter, absorbing nutrients from them.
10. Which of the following do pea plants get into a symbiotic relationship with?
a. Fungus
b. Algae
c. Rhizobium
Answer: c. Rhizobium
Reason: Pea plants form a symbiotic relationship with Rhizobium bacteria, which live in their root nodules and fix nitrogen, helping the plant grow.
Class 7 Science Ch 1 Nutrition in plant Oxford Book-1 mark
II. Very short answer type questions
Give two examples for the following.
- Plants that have autotrophic mode of nutrition
- Plants that have heterotrophic mode of nutrition
- Plants that grow in nitrogen-deficient soil
- Plants that harm their host plant
- Symbiotic plants
Ans:
- Autotrophic plants: Mango, Neem
- Heterotrophic plants: Cuscuta, Pitcher plant
- Plants in nitrogen-deficient soil: Venus flytrap, Sundew
- Plants that harm hosts: Cuscuta, Mistletoe
- Symbiotic plants: Lichen, Pea plant with Rhizobium
Class 7 Science Ch 1 Nutrition in plant Oxford Book-2 marks
III. Short answer type questions
1. Define heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Name the four types of heterotrophic nutrition in plants.
Ans: Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms or organic matter for energy.
The four types of heterotrophic nutrition in plants are: Insectivorous/Carnivorous: Plants that capture and digest insects to supplement their diet (e.g., Venus flytrap).
- Parasitic: Plants that get nutrients by living on or in another organism (e.g., dodder).
- Saprophytic: Plants that obtain nutrients from dead and decaying organic matter (e.g., Indian pipe plant).
- Symbiotic: Plants that live in a mutually beneficial relationship with another organism (e.g., lichens).
2. How do parasitic plants benefit from their host plants?
Ans: Parasitic plants benefit from their hosts by directly stealing the water, nutrients, and carbohydrates they need to survive. This is an efficient strategy that allows them to bypass the need for a full root system or, in some cases, even the ability to photosynthesize.
3. What is the symbiotic association in lichens?
Ans: A lichen is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic partner, typically an alga or a cyanobacterium. This relationship is a classic example of mutualism, where both organisms benefit. The fungus provides a protected environment, absorbing water and minerals, while the alga or cyanobacterium produces food through photosynthesis for both partners
Class 7 Science Ch 1 Nutrition in plant Oxford Book-4 marks
IV. Long answer type questions
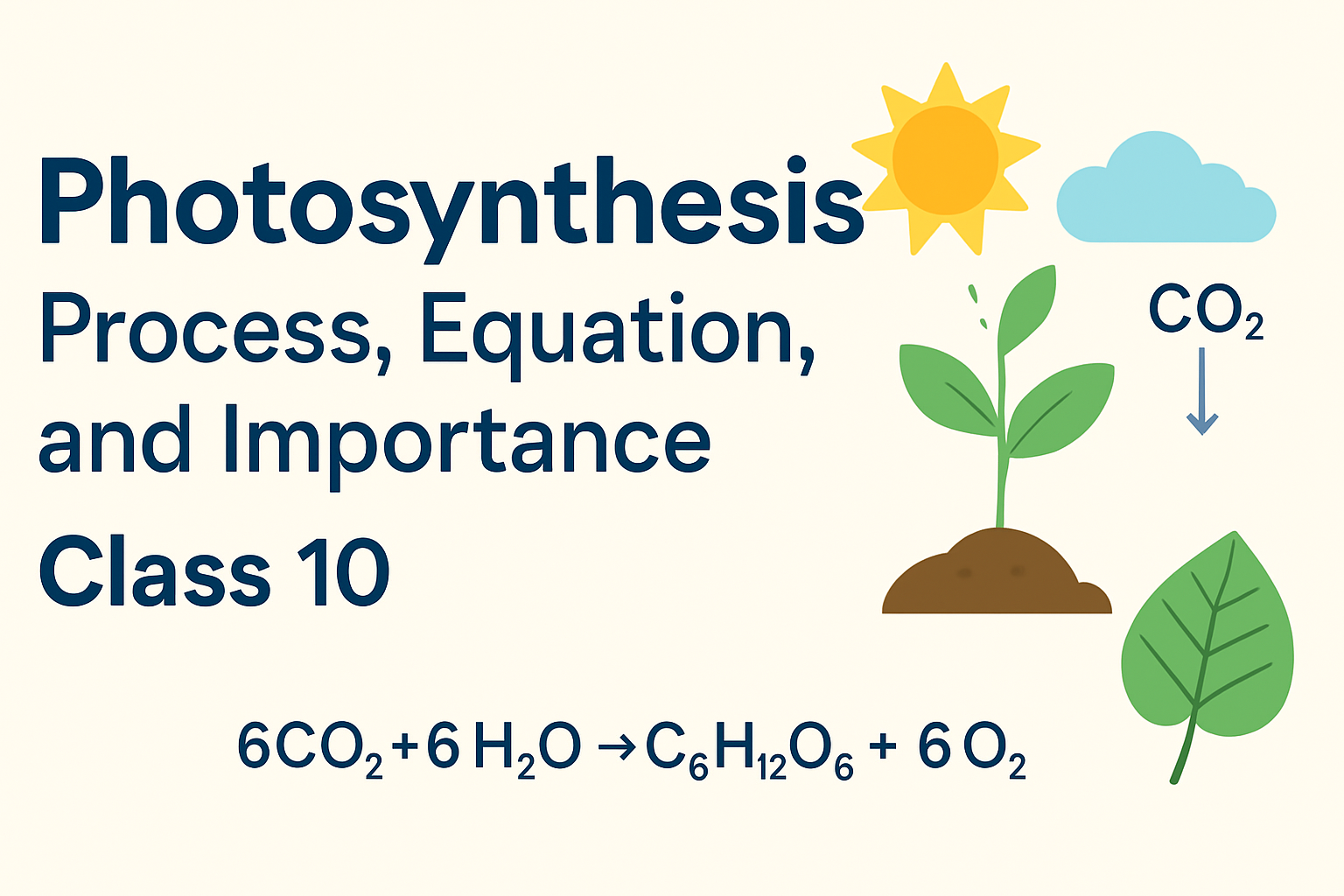
1.With the help of a labelled diagram, describe the process of photosynthesis in autotrophs.
Ans: Photosynthesis is the process used by autotrophs, such as plants, to convert light energy into chemical energy. Using chlorophyll to capture sunlight, plants use carbon dioxide and water to synthesize glucose (a sugar) for food.
The overall chemical equation for the process is:
Equation: 6CO2+6H2O→C6H12O6+6O2
2.Describe how insectivorous plants trap and digest insects for nutrition. Support your answer with examples.
Ans: Insectivorous plants grow in nitrogen-deficient soil and trap insects for nutrition:
- Insectivorous plants grow in soil that is poor in nitrogen. To fulfill their nitrogen requirements, they trap and digest insects. These plants have specially modified leaves that act as traps.
- For example, the pitcher plant has a tube-shaped leaf with a lid. Insects are attracted to its color and scent, fall into the pitcher, and are digested by digestive juices.
- The sundew plant has sticky tentacles on its leaves that trap insects. Once an insect is stuck, the tentacles curl around it and secrete enzymes to digest it.
- The Venus flytrap has leaves with sensitive trigger hairs. When an insect touches these hairs, the leaves snap shut, trapping the insect inside. The plant then secretes digestive fluids to break down the insect and absorb the nutrients. These adaptations help insectivorous plants survive in nutrient-deficient environments by supplementing their food through animal protein.
3. Discuss the different ways in which nutrients are replenished into the soil
Ans: Nutrients replenished in soil by: Plants absorb essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from the soil to grow and carry out various life processes. Over time, continuous farming depletes these nutrients, making it necessary to replenish them for healthy plant growth and good crop yield.
- One natural way to restore nutrients is through the decay of organic matter. Dead plants, animals, and animal waste decompose with the help of microbes and fungi, releasing nutrients back into the soil.
- Another effective method is the use of manure and fertilizers. Manure, made from animal dung and organic waste, is rich in nutrients and improves soil texture. Chemical fertilizers contain specific nutrients like urea (rich in nitrogen), superphosphate, and potash, which directly boost soil fertility.
- Crop rotation is also a common practice. Farmers grow leguminous plants like peas and beans in between other crops. These plants have a symbiotic relationship with Rhizobium bacteria, which live in their root nodules and fix atmospheric nitrogen into the soil.
- Additionally, green manure involves growing certain crops and ploughing them back into the soil to enrich it. These sustainable practices help maintain soil health, reduce dependency on chemicals, and ensure long-term agricultural productivity.
Revision Notes – Class 7 Science Ch 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition is the process of obtaining and using food for growth, energy, and maintenance of life.
- Plants are autotrophs because they prepare their own food by photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, water, and chlorophyll.
- The food made during photosynthesis is mainly stored as starch in plants.
- Other modes of nutrition in plants:
- Parasitic plants → depend on other living plants (example: Cuscuta).
- Saprophytic plants → depend on dead and decaying matter (example: mushrooms).
- Symbiotic plants → live in close association with other organisms (example: lichens).
- Insectivorous plants → trap and digest insects (examples: pitcher plant, Venus flytrap).
- Plants are called the producers of the ecosystem because all animals depend directly or indirectly on them for food and oxygen.
Practice Worksheet – Nutrition in Plants (Grade 7 / Year 7 Science)
- Define photosynthesis in your own words.
- Why are green plants called autotrophs?
- Fill in the blanks:
a) Plants are the ______ of the food chain.
b) The green pigment in leaves is called ______. - Name two insectivorous plants.
- Write one difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition.
- Explain the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis.
- Give an example of a symbiotic plant and explain the relationship.
- What are the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
- Why are plants called producers of the ecosystem?
- Differentiate between parasitic and saprophytic plants with examples.
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 10):
