Chapter 10 of Class 7 Science, Transport of Substances, introduces students to the vital processes through which water, minerals, and food are transported in plants and animals. This chapter explains key concepts such as diffusion, osmosis, the circulatory system in humans, and the role of xylem and phloem in plants.
Understanding these processes helps students appreciate how living organisms survive and function efficiently. The Oxford textbook provides a clear framework for these topics, and our step-by-step solutions aim to make learning easier by offering accurate answers, simple explanations, and helpful diagrams to support your understanding.
Class 7 Science Ch 10 Transport of Substance Oxford Book Solutions From Textbook
1. Objective type questions
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
- 1. In unicellular organisms, every part gets nutrients and oxygen directly through …… (Diffusion/translocation).
- 2. Blood contains several cells floating in a straw-coloured liquid called the …….. (Platelets/plasma).
- 3. Diffusion of gases and chemical substances takes place through the walls of the……… (Arteries/capillaries).
- 4………… (Valves/Auricles) separate the chambers of the heart so that there no mixing of blood.
- 5…….. (Right/Left) ventricle pumps blood to the farthest parts of the body through the aorta.
- 6. The larger the leaf, the…….. (faster/slower) is the rate of transpiration.
Ans:
- In unicellular organisms, every part gets nutrients and oxygen directly through diffusion.
- Blood contains several cells floating in a straw-coloured liquid called the plasma.
- Diffusion of gases and chemical substances takes place through the walls of the capillaries.
- Valves separate the chambers of the heart so that there is no mixing of blood.
- Left ventricle pumps blood to the farthest parts of the body through the aorta.
- The larger the leaf, the faster is the rate of transpiration.
B. Write T for the True and F for the false statements. Correct the false statements
- 1. The human circulatory system is made up of the heart and blood.
- 2. White blood cells contain haemoglobin that helps to transport oxygen.
- 3. Blood consists of two types of blood cells.
- 4. Kidneys are always working separately to get rid of wastes.
- 5. All arteries always carry oxygenated blood.
- 6. When blood enters the kidney, useful substances are absorbed or filtered back into the blood
Ans:
- The human circulatory system is made up of the heart and blood. – F
Correct statement: The human circulatory system is made up of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. - White blood cells contain haemoglobin that helps to transport oxygen. – F
Correct statement: Red blood cells contain haemoglobin that helps to transport oxygen. - Blood consists of two types of blood cells. – F
Correct statement: Blood consists of three types of blood cells – red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. - Kidneys are always working separately to get rid of wastes. – F
Correct statement: Both kidneys work together to filter blood and remove wastes. - All arteries always carry oxygenated blood. – F
Correct statement: Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. - When blood enters the kidney, useful substances are absorbed or filtered back into the blood. – T
C. Choose the correct option.
- Which of these substances need to be transported within a living organism?
a. Food and oxygen
b. Water and minerals
c. Waste products
d. All of these ✅ - Which of these constitute the blood in human beings?
a. Red blood cells
b. White blood cells
c. Blood platelets
d. All of these ✅ - Which of these increases the rate of transpiration in leaves?
a. Warmer air and lesser amount of moisture
b. Larger size of the leaf
c. Cold and humid air
d. Both a. and b. ✅ - Which of these parts of the excretory system stores urine?
a. Kidneys
b. Ureters
c. Urinary bladder ✅
d. Urethra - Which of these does transpiration help in?
a. Cooling the plant body
b. Helping in exchange of gases
c. Creating a low pressure to pull up water and minerals up the stems
d. All of these ✅ - Which of these is not a part of the transport system in human beings?
a. Blood and plasma
b. Arteries, veins and capillaries
c. Brain and nerves ✅
d. Four-chambered heart - Which of these brings back oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pours into the left auricle?
a. Aorta
b. Pulmonary vein ✅
c. Pulmonary artery
d. Ventricles - Which of these helps plants to continuously lose water from their leaves?
a. Transportation
b. Transpiration ✅
c. Respiration
d. Translocation - Which of these organisms get rid of all kinds of body wastes by direct diffusion through their cells?
a. Amoeba and paramecium ✅
b. Amphibians and leeches
c. Insects and earthworms
d. All of these - Which of these are common plant wastes?
a. Latex
b. Gum
c. Resins
d. All of these ✅
I. Very short answer type questions
Give two examples for the following.
- 1. Organisms that do not require any special transport system inside them
- 2. Wastes formed inside the human body
- 3. Animals that have tubular structures to help them excrete wastes
- 4. Toxic wastes of plants
- 5. Things manufactured using plant secretions
Ans:
- Organisms that do not require any special transport system inside them
→ Amoeba, Paramecium - Wastes formed inside the human body
→ Urea, Carbon dioxide - Animals that have tubular structures to help them excrete wastes
→ Earthworms, Insects - Toxic wastes of plants
→ Resins, Latex - Things manufactured using plant secretions
→ Gum, Latex products (like rubber)
III. Short Answer Type Questions
- How do substances get transported in hydra?
→ In hydra, substances like oxygen, nutrients, and wastes are transported from cell to cell by diffusion because it is a simple organism with only two layers of cells. - What is blood? Describe what blood is made up of.
→ Blood is a fluid connective tissue that transports nutrients, oxygen, and waste in the body. It consists of:- Plasma (the liquid part),
- Red blood cells (RBCs) – carry oxygen,
- White blood cells (WBCs) – fight infections,
- Platelets – help in clotting.
- Define the following:
a. Translocation – The process of transport of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
b. Excretion – The process of removal of metabolic wastes like urea, carbon dioxide, etc., from the body.
- How do plants get rid of toxic wastes produced in them?
→ Plants remove wastes by:- Storing them in cell vacuoles,
- Shedding old leaves,
- Releasing them as gums, resins, or through stomata in gaseous form.
IV. Long Answer Type Questions
- Explain the main differences between arteries, veins, and capillaries.
| Feature | Arteries | Veins | Capillaries |
| Direction | Carry blood away from the heart | Carry blood toward the heart | Connect arteries and veins |
| Blood carried | Mostly oxygenated (except pulmonary) | Mostly deoxygenated (except pulmonary) | Both, for exchange of gases |
| Wall thickness | Thick and elastic | Thin walls with valves | Very thin (one cell thick) |
| Pressure | High pressure | Low pressure | Moderate pressure |
- Describe how the heart acts as the pumping station of the body.
Ans: The human heart is a muscular organ with four chambers – two auricles (upper) and two ventricles (lower).
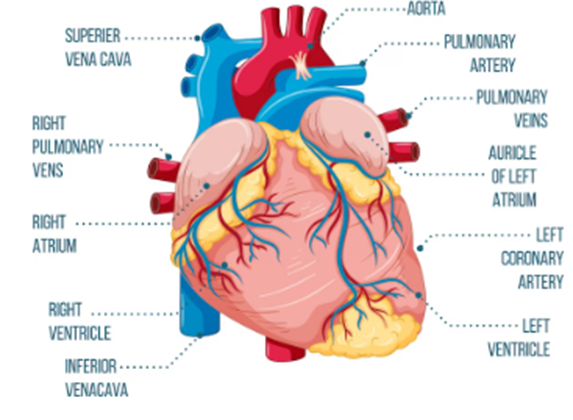
The human heart circulates blood through two main loops: pulmonary and systemic circulation. The step-by-step path is:
- From the Body to the Heart:
Deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cava. It then flows into the right ventricle. - From the Heart to the Lungs (Pulmonary Circulation):
The right ventricle pumps the deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery, where carbon dioxide is removed and oxygen is absorbed. - From the Lungs to the Heart:
Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs via pulmonary veins into the left atrium, then into the left ventricle. - From the Heart to the Body (Systemic Circulation):
The left ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood to the entire body through the aorta. Body cells use the oxygen, and the deoxygenated blood returns to the heart — completing the cycle.
- What is transpiration? Discuss the role that transpiration plays in a plant and the factors that affect the rate of transpiration.
Ans: Transpiration is the process by which water is lost in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of a plant, mainly through the stomata of the leaves.
Role of Transpiration in Plants:
- Cooling effect: Transpiration cools the plant by releasing water vapour, especially in hot weather.
- Water movement: It helps in pulling water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves through the xylem (transpiration pull).
- Maintains water balance: It regulates the water content in plant tissues.
- Mineral transport: It aids in the upward movement of essential minerals from the soil.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Transpiration:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase transpiration.
- Humidity: Low humidity increases the rate, while high humidity slows it down.
- Wind: Fast-moving air carries away water vapour, increasing transpiration.
- Light: More light increases stomatal opening, which raises the rate of transpiration.
- Type and number of stomata: More stomata or open stomata lead to more transpiration.
- With the help of a well-labelled diagram, describe the human excretory system.
4. With the help of a well labelled diagram, describe the human excretory system.
Ans: The human excretory system is responsible for removing waste materials (especially nitrogenous waste like urea) from the body. The main organs involved in this system are:
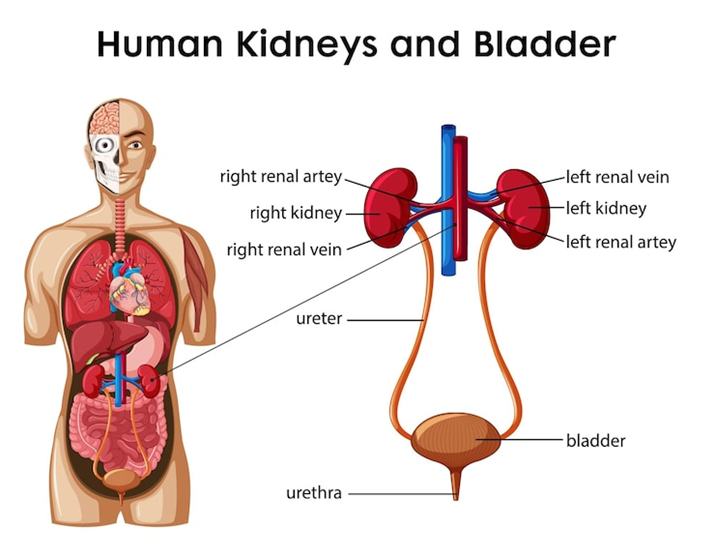
Main Parts of the Human Excretory System:
- Kidneys – Bean-shaped organs that filter blood to remove waste and extra water, forming urine.
- Ureters – Thin muscular tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary Bladder – A sac-like organ where urine is stored temporarily.
- Urethra – A tube through which urine is excreted out of the body.
Functions of Excretory Organs:
- Kidneys: Filter blood, remove urea, excess salts, and water.
- Ureters: Transport urine from kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: Stores urine until it is excreted.
- Urethra: Excretes urine outside the body.
Class 12:
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
NEET BIOLOGY
- Evolution
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Human Health and Disease
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
For the official Class 8 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 8):
