Light plays an important role in our daily lives—it helps us see the world around us. In Class 7 Science Ch 15 Light For Oxford Book, students learn key concepts like reflection of light, formation of images by plane mirrors, types of mirrors and lenses, and how shadows and images are formed.
Class 7 Science Ch 15 Light For Oxford Book Full Chapter
Class 7 Science Ch 15 Light
Page 228
A. Fill in the blanks:
- A smooth surface reflects a parallel beam of light in only one direction.
- Irregular reflection is also called diffused reflection.
- A mirror is a regular surface.
- The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual.
B. Answer the following questions orally:
- Why can’t we see a source of light through a hollow bent tube?
Because light travels in straight lines, and it cannot bend to pass through a curved or bent path. - Which expression is used to convey that ‘light travels in straight lines’?
The expression is “rectilinear propagation of light.” - How are we able to see things around us?
We can see things when light reflects off objects and enters our eyes. - Why can we see our image in some surfaces and not in other surfaces?
We can see our image in smooth and shiny surfaces (like mirrors) that reflect light regularly. Rough surfaces scatter light and do not form clear images. - What property is common between the images of the following letters? ‘O’, ‘I’, ‘M’, and ‘A’?
These letters look the same or similar when seen in a mirror — they have symmetry.
Another letter and a digit with the same property: ‘T’ and ‘8’.
Page 235
Fill in the blanks
Ans:
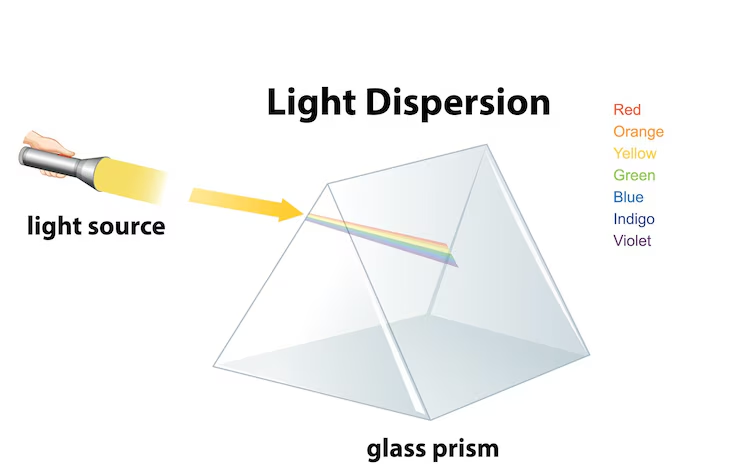
1. White light can be split into its constituent colours.
2. When white light is split, it splits into a band of colours called the visible spectrum.
3. A coloured disc, painted with the constituent colours of white light in equal proportion, appears white when rotated.
Page 236
1. Objective type questions
A .Fill in the blanks with the correct words:
- ‘Rectilinear propagation of light’ means light travels in straight lines.
- A bumpy, rough surface is also referred to as a diffused surface.
- A convex mirror can only form virtual images.
- A concave lens is a diverging lens.
- A virtual image cannot be formed on a screen
B. Choose the correct option.
1. What is bouncing of light from a surface called?
a. Refraction
b. Diffusion
c. Dispersion
d. Reflection
Ans:
✅ d. Reflection
2. Which phenomenon is responsible for the formation of shadows?
a. Rectilinear propagation of light
c. Circular propagation of light
d. Regular reflection
Ans:✅ a. Rectilinear propagation of light
3. What is the reflection from an irregular surface called
a. Spherical reflection
b. Diffused reflection
c. Irregular reflection
d. Both b and c
✅ d. Both b and c (Diffused reflection and Irregular reflection)
4. Which of the following are the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror?
a. Real, upright image
b. Real, inverted image
c. Virtual, upright image
d. Virtual, inverted image
✅ c. Virtual, upright image
5. At which surface does reflection of light take place?
a. Only mirrors
b. Only metals
c. All sorts of surfaces
d. Both a and b
✅ c. All sorts of surfaces (though mirrors reflect more clearly, some amount of reflection occurs on all surfaces)
6. What is correct about a virtual image?
a. It can be formed on a screen.
b. It cannot be formed on a screen.
c. It can be formed on a rough surface.
d. Both a and c
✅ b. It cannot be formed on a screen
7. What type of image(s) does a concave mirror form?
a. Only virtual images
b. Only diminished images
c. Only real and magnified images
d. Both virtual and real images
✅ d. Both virtual and real images
8. What type of image(s) does a convex mirror form?
a. Only virtual images
b. Only diminished images
c. Only real images
d. Virtual and diminished images
✅ d. Virtual and diminished images
9. What does a magnifying glass consist of?
a. Convex mirror
b. Concave mirror
c. Convex lens
d. Concave lens
✅ c. Convex lens
10. Which of these is used as a ‘dentist mirror’?
a. Concave mirror
b. Convex mirror
c. Concave lens
d. Convex lens
✅ a. Concave mirror
II. Very short answer type questions
Give one word for the following.
1. A mirror whose reflecting surface is the inner surface of a sphere
Ans: Concave mirror – A mirror whose reflecting surface is the inner surface of a sphere.
2. A lens that is thicker at the edges than at the middle
Ans: Concave lens – A lens that is thicker at the edges than at the middle.
3. An image that is upside down
Ans: Inverted image – An image that is upside down.
4. A band of colours that is formed when white light is passed through a prism
Ans: Spectrum – A band of colours that is formed when white light is passed through a prism.
5. The property of our eyes that makes us perceive a rotating coloured disc as white
Ans: Persistence of vision – The property of our eyes that makes us perceive a rotating coloured disc as white.
III. Short answer type questions
1. Here are a few words and numbers. Write down how they will look in a plane mirror.
a. AMBULANCE
b. LEFT
c. 12345678
d. 8888
Ans: a. AMBULANCE → ƎƆИ∀⅃∩qW∀
(Note: This is how it is written on real ambulances so drivers can read it correctly in rear-view mirrors.)
b. LEFT → ⊥ᖵƎ⅃
c. 12345678 → 87654321
d. 8888 → 8888
(Symmetrical digits like 8 look the same in a mirror.)
2. If sunlight is streaming in through a window in a room, how could we make it fall on a wall which is on the same side as the window?
Ans: Redirecting Sunlight
If sunlight is streaming in through a window, and you want to make it fall on a wall on the same side as the window:
- Use a plane mirror to reflect the light.
- Position the mirror so that it reflects the sunlight toward the desired wall, making use of the law of reflection.
3. How can we find out if an image formed (either by a mirror or a lens) is real or virtual?
To find out whether an image is real or virtual:
- Try to capture it on a screen:
- Real image: Can be formed on a screen.
- Virtual image: Cannot be projected on a screen.
- You can also check the orientation:
- Real images are usually inverted.
- Virtual images are upright.
- Use of Convex Mirrors in Cars
4. Why are convex mirrors used as car wing mirrors?
- Use of Convex Mirrors in Cars
- To find out whether an image is real or virtual:
- Convex mirrors are used as car wing mirrors because:
- They provide a wider field of view than plane mirrors, allowing drivers to see more of the road and traffic behind.
- They form virtual, upright, and diminished images, making it easier to judge the presence and movement of other vehicles.
IV. Long answer type questions
1. Difference Between Regular and Irregular Reflection
| Feature | Regular Reflection | Irregular (Diffused) Reflection |
| Surface | Smooth and polished (e.g., mirror) | Rough and uneven (e.g., wall) |
| Direction of reflection | All reflected rays are parallel | Reflected rays scatter in different directions |
| Image formation | Forms a clear image | Does not form a clear image |
| Example | Plane mirror | Paper, unpolished wood |
2. Methods to Form Diminished and Enlarged Images
To form diminished images:
- Convex Mirror – Always forms a diminished, virtual image.
- Concave Lens – Always forms a diminished, virtual image.
To form enlarged images:
- Concave Mirror – Forms a real, enlarged image when the object is between the focus and center of curvature; virtual, enlarged image when the object is between the pole and focus.
- Convex Lens – Forms a real, enlarged image when the object is between focus and 2F; virtual, enlarged image when the object is between the lens and focus.
3. What is a Newton’s Disc?
A Newton’s Disc is a circular disc divided into segments painted in the seven colours of the rainbow (VIBGYOR).
- When the disc is rotated rapidly, it appears white to the human eye.
- This demonstrates the concept of persistence of vision and that white light is made up of all seven colours of the visible spectrum.
- It shows that mixing all the colours of the rainbow in the right proportions gives white light.
Class 7 Science Ch 15 Light For Oxford Book – Activity
1. Let us understand rectilinear propagation of light with the help of the following activity.
Activity
Aim: To verify that light travels in a straight line
Materials needed: A flexible rubber or plastic tube/straw of length 10 inches (used for drinking cold drinks), and a light bulb/candle/ lamp
Method:
1. Hold the tube absolutely straight and point one open end to the source of light.
2. Put your eye to the other hole. What do you see?
3. Now, bend the tube and look through the hole. What do you see this time?
Observation: When the tube is held straight, the source of light can be seen. However, when the tube is bent, the source of light cannot be seen.
Conclusion: This indicates that light travels in a straight line.
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
For the official Class 7 Science Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 7):
