In Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Heat For Oxford Solution, students learn how heat is a form of energy that causes a change in temperature and state of matter. This chapter introduces the concept of temperature, how it is measured, and the different units used—such as Celsius and Fahrenheit. Students also explore the working of clinical and laboratory thermometers.
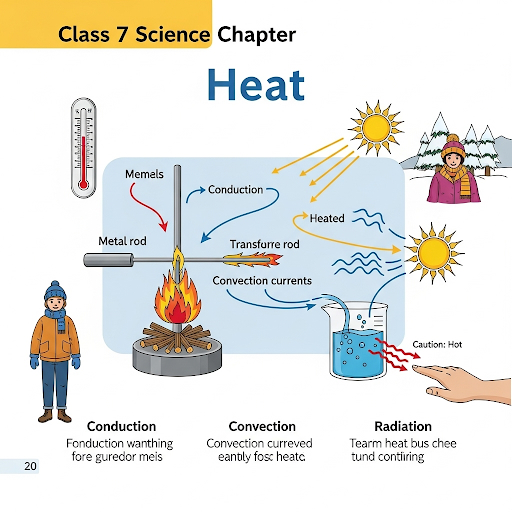
The chapter explains the three modes of heat transfer—conduction, convection, and radiation—through real-life examples, making it easy to understand how heat moves from one object to another. It also discusses the role of good and poor conductors, and how clothing and daily activities are affected by heat transfer.
Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Heat For Oxford Solution
1. Objective type questions
A. Write T for the True and F for the False statements. Correct the false statements.
1. The terms ‘hot’ and ‘cold’ are relative.
Answer: T (True)
2. On the Fahrenheit scale, the difference between the boiling point of water and the melting point of ice is divided into 100 degrees.
Answer: F (False)
Correct Statement: On the Fahrenheit scale, the difference between the boiling point and melting point of water is divided into 180 degrees.
3. Digital thermometers use mercury to measure temperature.
Answer: F (False)
Correct Statement: Digital thermometers do not use mercury; they use electronic sensors to measure temperature.
4. Mercury is used in thermometers because it is relatively easy to see because of its red colour.
Answer: F (False)
Correct Statement: Mercury is used because it expands uniformly with heat and is easily visible due to its silvery appearance, not red colour.
5. Heat energy is measured in degree centigrade.
Answer: F (False)
Correct Statement: Heat energy is measured in joules, while degree centigrade (Celsius) measures temperature.
1. What does temperature measure?
a. Degree of hotness of a body
b. Degree of coldness of a body
c. Volume of a body
d. Both a and b
✅ Correct Answer: a. Degree of hotness of a body
Explanation: Temperature measures how hot an object is. It indicates the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
2. What are the commonly used reference temperatures for constructing temperature scales?
a. Melting point of wax and boiling point of alcohol
b. Melting point of wax and boiling point of water
c. Melting point of ice and boiling point of wax
d. Melting point of ice and boiling point of water
✅ Correct Answer: d. Melting point of ice and boiling point of water
Explanation: These two points are universally used as fixed reference points in Celsius and Fahrenheit scales.
3. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Copper has a higher rate of conduction than iron.
b. Iron has a higher rate of conduction than copper.
c. Aluminium has a higher rate of conduction than iron.
d. Both a. and c
✅ Correct Answer: d. Both a. and c
Explanation: Copper and aluminium are both good conductors, and copper is better than iron. So both a and c are correct.
4. Which of the following is the reason for sea breeze and land breeze to blow?
a. Water heats up much faster than land
b. Land heats up much faster than water
c. Water and land get heated up equally fast
d. None of these
✅ Correct Answer: b. Land heats up much faster than water
Explanation: This difference causes uneven heating and leads to the formation of sea breeze during the day and land breeze at night.
5. Why does an electric heater have a mirror fitted behind its heating coil?
a. Mirror is a good conductor of heat
b. Mirror is a bad conductor of heat
c. To improve convection of heat
d. Mirrors reflect heat radiation to the front of the heater
✅ Correct Answer: d. Mirrors reflect heat radiation to the front of the heater
Explanation: The mirror reflects the heat toward the room, improving efficiency.
6. What are ‘Celsius’ and ‘Fahrenheit’?
a. Scales to measure heat
b. Temperature scales
c. Different types of thermometers
d. Temperature scales used only for mercury thermometers
✅ Correct Answer: b. Temperature scales
Explanation: Celsius and Fahrenheit are units to measure temperature, not heat or thermometer types.
7. In which thermometer is a ‘kink’ added?
a. Clinical thermometer
b. Alcohol Thermometer
c. Laboratory thermometer
d. All of these
✅ Correct Answer: a. Clinical thermometer
Explanation: The kink prevents mercury from falling back immediately, making it easier to read the temperature.
8. ‘Heat’ is a form of what?
a. Energy
b. Thermometer
c. Temperature
d. Scale
✅ Correct Answer: a. Energy
Explanation: Heat is a form of energy that flows from a hotter body to a colder one.
9. ‘Conduction’ is the primary mode of heat transfer in which of the following?
a. Water
b. Solids
c. Liquids
d. Gases
✅ Correct Answer: b. Solids
Explanation: In solids, heat transfers by conduction through particle-to-particle contact.
10. ‘Convection’ is the primary mode of heat transfer in which of the following?
a. Solids and liquids
b. Liquids and gases
c. Gases and solids
d. Only liquids
✅ Correct Answer: b. Liquids and gases
Explanation: Convection occurs in fluids (liquids and gases) where particles move in bulk carrying heat.
II. Very short answer type questions
Name the following.
- The scale in which the melting point of ice and the boiling point of water are taken as 0 and 100, respectively.
Answer: Celsius scale - The silvery grey liquid used in clinical thermometers.
Answer: Mercury - The breeze that flows from the land to the sea during night time.
Answer: Land breeze - The type of waves via which heat and light energy travel.
Answer: Radiation - A unit for measuring heat energy.
Answer: Calorie
III. Short answer type questions
1. Under what conditions does heat flow from a hot body to a cold body by conduction?
Answer:
Heat flows from a hot body to a cold body by conduction when they are in direct contact with each other. Conduction occurs primarily in solids, where particles are closely packed and transfer energy by vibrating and passing it along to neighboring particles.
2. Give one advantage of using alcohol as the liquid in a thermometer as compared to using mercury.
Answer:
Alcohol can be used in very low-temperature conditions as it has a lower freezing point than mercury. Additionally, alcohol can be dyed, making it more visible in the thermometer tube.
3. List two characteristic features of a mercury clinical thermometer.
Answer:
- It has a kink in the capillary tube to prevent the mercury from falling back, allowing an accurate reading even after removing it from the body.
- It usually has a temperature range of 35°C to 42°C, which is suitable for measuring human body temperature.
4. Why do we wear woolen clothes in winter?
Answer:
We wear woolen clothes in winter because wool is a poor conductor of heat and traps a lot of air in its fibers. This trapped air acts as an insulator, preventing body heat from escaping and keeping us warm
IV. Long answer type questions
1. Describe a simple experiment which can demonstrate that the terms ‘hot’ and ‘cold’ as we feel them are only relative.
2. What are temperature scales? Explain how Celsius and Fahrenheit scales are defined.
3. With the help of diagram, explain the working of a thermos flask.
V. Numerical-based questions
1. Express the following temperatures in the Fahrenheit scale.
a. 110°C b. 85°C c. 225°C
2. Express the following temperatures in the Celsius scale.
a. 131°F b. 149°F c. 32°F d. 23°F
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
NEET BIOLOGY
- Evolution
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Human Health and Disease
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
For the official Class 8 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 8):
Understanding the concept of heat is essential in our daily lives, and the Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Heat For Oxford Solution provides a clear and structured explanation of this topic. From learning about temperature measurement to understanding the different modes of heat transfer—Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Heat For Oxford Solution ensures students grasp these fundamental ideas through practical examples and well-explained theory.
