In this chapter , you will learn how plants reproduce through both asexual and sexual methods. Topics like pollination, fertilization, seed dispersal, and vegetative propagation are explained with examples. This chapter helps you understand how new plants grow and how different parts of a plant play a role in reproduction.
Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plant-Oxford Book
1. Objective type questions
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
1. The male and female reproductive cells called. ……(gametes/zygote) fuse to form a single cell called.. ..(gametes/zygote)
2…….(Spores/Fragments) are microscopic single-celled or several-celled reproductive bodies that are mostly spherical in shape.
3…….. (Grafting /Tissue culture) is a method used for large scale multiplication to develop better variety of crops and to save endangered species of plants.
4……(Pollination/Fertilization) is the first step in the process of seed formation.
5. The…….(fruit/flower) is the seed-bearing part of a flowering plant.
Ans:
- The male and female reproductive cells called gametes fuse to form a single cell called zygote.
- Spores are microscopic single-celled or several-celled reproductive bodies that are mostly spherical in shape.
- Tissue culture is a method used for large-scale multiplication to develop better variety of crops and to save endangered species of plants.
- Pollination is the first step in the process of seed formation.
- The fruit is the seed-bearing part of a flowering plant.
Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plant-Oxford Book-1 Mark
B. Write T for the True and F for the False statements. Correct the false statements.
1. Plants can only reproduce by asexual methods.
Ans: F – Plants can reproduce both by asexual and sexual methods.
2. An algae multiplies by the process of layering.
Ans: F – Algae multiply by fragmentation, not layering.
3. The pistil bears the anthers that contain female gametes.
Ans: F – The stamen, not the pistil, bears the anthers which contain male gametes.
4. After successful pollination, the stigma secretes nutrients.
Ans: F – The stigma does not secrete nutrients; it receives pollen during pollination.
5. Wind blows away pollen grains from anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower.
Ans: T
Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plant-Oxford Book-
C. Choose the correct option.
1. By which of these processes, does the yeast multiply?
a. Budding
b. Fragmentation
c. Spore formation
d. Grafting
Ans: a. Budding
2 . In which of these processes is a young plant lowered towards the ground and covered by moist soil forming a layer?
a. Grafting
b. Layering
c. Cutting
d. Tissue culture
Ans: b. Layering
3. Which of these is an underground stem with fleshy scales that serve as sites of food storage?
a. Rhizome
b. Bulb
c. Tuber
d. Corm
Ans: b. Bulb
4. Which of these parts of a flower contain male gametes?
a. Anthers
b. Stigma
c. Style
d. Ovary
Ans: a. Anthers
5. Which of these is known as the ripened ovary?
a. Sepals and petals
b. Fruit
c. Seed
d. Embryo
Ans: b. Fruit
6. Which of these is an example of a bulb?
a. Potato
b. Onion
c. Gladiolus
d. Ginger
Ans: b. Onion
7. In which of these processes does the adult organism breaks up into two or more pieces?
a. Budding
b. Grafting
c. Fragmentation
d. Spore formation
Ans: c. Fragmentation
8. Which of these have buds in the eyes that give rise to new plants?
a. Bulbs
b. Tubers
c. Rhizomes
d. Ovary
Ans: b. Tubers
9. Which of these is not a part of the pistil of a flower?
a. Stigma
b. Stamen
c. Style
d. Corm
Ans: b. Stamen
10. Which of these have buds from which outgrowths are produced which give rise to new plants?
a. Rhizome
b. Bulb
c. Corm
d. Both a. and b.
Ans: d. Both a. and b.
Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plant-Oxford Book-
II. Very short answer type questions
Give two examples for the following.
1. Plants that multiply by fragmentation
Ans: Spirogyra, Algae
2. Plants that multiply by their tuberous roots
Ans: Sweet potato, Dahlia
3. Plants that have corms
Ans: Colocasia, Gladiolus
4. Plants that multiply by cutting
Ans: Rose, Hibiscus
5. Plants that multiply by layering
Ans: Jasmine, Strawberry
6. Plants that pollinate by wind
Ans: Grass, Wheat
7. Plants that pollinate by water
Ans: Vallisneria, Hydrilla
8. Plants whose seeds disperse through explosion
Ans: Balsam, Pea
Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plant-Oxford Book-
III. Short answer type questions
1.Why are underground stems swollen?
Answer: Underground stems are swollen because they store food and nutrients. This storage helps the plant survive unfavorable conditions and aids in vegetative reproduction.
2. Differentiate between the following:
a. Asexual and sexual reproduction
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| Involves only one parent. | Involves two parents (male and female). |
| No formation of gametes. | Involves fusion of male and female gametes. |
| Offspring are genetically identical. | Offspring show genetic variation. |
b. Self-pollination and cross-pollination
Ans:
| Feature | Self-Pollination | Cross-Pollination |
| Number of Plants | Occurs within the same flower or plant | Occurs between two different plants of the same species |
| Transfer of Pollen | From anther to stigma of the same flower or plant | From anther of one plant to stigma of another |
| Genetic Variation | No genetic variation; offspring are identical | Increases genetic variation in offspring |
| Pollinating Agents | Often does not require agents like wind or insects | Requires agents like wind, insects, water, or animals |
3. Why do seeds need to disperse?
Answer: Seed dispersal helps in reducing competition for sunlight, water, and nutrients between the parent plant and the new plant. It also allows plants to colonize new and favorable environments.
Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plant-Oxford Book
IV. Long Answer Type Questions
1. Describe the various steps involved in tissue culture.
Answer:
Tissue culture involves the following steps:
- A small piece of plant tissue (explant) is taken from a healthy plant.
- The tissue is placed in a sterilized nutrient medium containing hormones.
- The cells grow and divide to form a mass called callus.
- The callus is transferred to another medium where it develops roots and shoots.
- The new plantlets are then transferred to soil for growth.
2. What are the advantages of vegetative reproduction?
Answer:
- Produces genetically identical plants (clones).
- Faster and easier than seed-based reproduction.
- Can produce plants without seeds.
- Helps maintain desired traits in plants.
- Useful for propagating plants that do not produce viable seeds.
3. What happens after successful pollination?
Answer:
After successful pollination:
- Pollen grains germinate on the stigma.
- A pollen tube forms and grows down the style.
- Male gametes travel through the tube and fuse with the ovule in the ovary.
- Fertilization occurs, forming a zygote.
- The zygote develops into an embryo, and the ovule becomes a seed.
- The ovary becomes the fruit.
4. Explain with examples the different ways in which seeds disperse.
Answer:
Seeds are dispersed in different ways to reduce competition and help plants grow in new places. The main methods of seed dispersal are:
- By Wind: Seeds are light or have wings/hairs to float in the air.
Example: Dandelion, Maple. - By Water: Seeds float on water and travel to new locations.
Example: Coconut, Lotus. - By Animals: Some seeds stick to animal fur or are eaten and later excreted.
Example: Xanthium (sticks), Guava (eaten). - By Explosion: Some fruits burst open, throwing seeds away from the plant.
Example: Balsam, Castor. - By Animals: Seeds have hooks or are eaten and excreted, e.g., xanthium, guava.
- By Explosion: Fruits burst open to scatter seeds, e.g., balsam, castor.
Class 7 Science Reproduction in Plant-Oxford Book-Picture Based Questions
LET’S OBSERVE
1. Look at the picture and answer the following questions.
a. This is a…………..(bulb/rhizome/tuber).
b. It is an underground……..(root/stem/leaf).
c. This is a …..(sexual/asexual) method of reproduction.
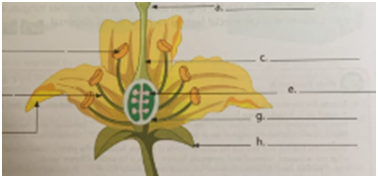
2. Label the organs in the complete flower given below. Circle the female parts.
Ans:
1. Assuming the picture is of onion:
a. This is a bulb.
b. It is an underground stem.
c. This is an asexual method of reproduction.
2. Label the parts:
a. Stigma
b. Anther
c. Style
d. Filament
e. ovules
f. petals
g. ovary
h. sepals
Class 7 Science Chemical and Chemical Change-Oxford
For the official Class 7 Science Solutions, you can visit:
