In this chapter Class 8 Science Ch 10 Force and Friction Oxford, students explore the fundamental concepts of force and friction, which are essential in understanding the motion of objects. A force is a push or a pull that can change the speed, direction, or shape of an object. The chapter explains different types of forces—contact and non-contact, as well as balanced and unbalanced forces.
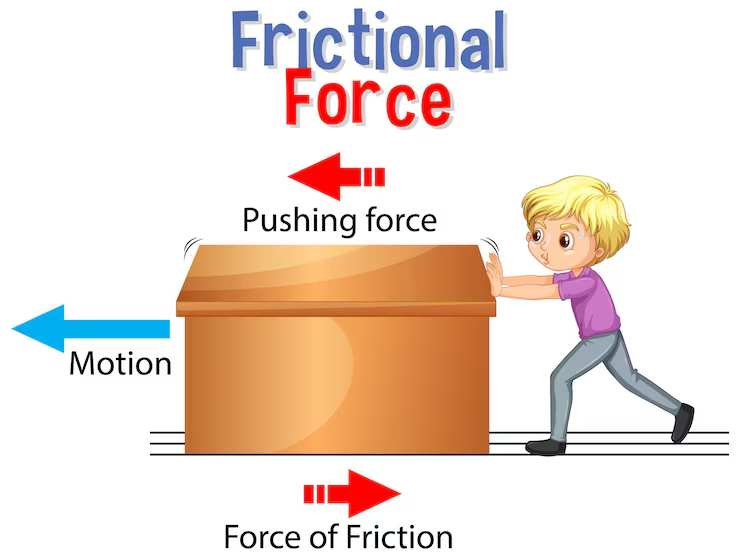
It also introduces friction as a force that opposes motion between two surfaces in contact. Students learn about types of friction (static, sliding, rolling, and fluid friction), factors affecting friction, and how friction can be both useful and undesirable. Methods to reduce or increase friction and real-life applications are also discussed.
This chapter builds a strong foundation for understanding how things move and interact in the physical world.
Class 8 Science Ch 10 Force and Friction Oxford -Textbook
1. Objective Type Questions
A. Choose the correct option.
1.When two forces in the same direction act on an object, then the resultant magnitude of the forces acting on the object is:
a. the sum of the two forces
b. equal to the smaller force
c. the difference between the two forces
d. equal to the larger force
Answer: a. the sum of the two forces
2. Gravitational force:
a. is a ‘non-contact force’
b. opposes motion of a body, just like friction
c. can act only if a body is charged
d. is zero on the Moon
Answer: a. is a ‘non-contact force’
3. This is an example of a contact force:
a. Electrostatic force
b. Magnetic force
c. Friction
d. Gravitational force
Answer: c. Friction
4. This force is our weight:
a. Electrostatic force
b. Magnetic force
c. Friction
d. Gravitational force
Answer: d. Gravitational force
5. Static friction acts when a body is:
a. moving
b. stationary
c. rolling
d. sliding
Answer: b. stationary
6. The SI unit of force is:
a. meters per second
b. newton
c. pascal
d. newton per meter
Answer: b. newton
7. We can expect the force of friction to be greater for an object moving on a surface if the surfaces in contact are:
a. smooth and the object is heavier
b. rough and the object is heavier
c. smooth and the object is lighter
d. rough and the object is lighter
Answer: b. rough and the object is heavier
8. This force makes the Earth go around the Sun:
a. Electrostatic force
b. Frictional force
c. Gravitational force
d. Magnetic force
Answer: c. Gravitational force
9. A ‘streamlined’ shape is given to automobiles in order to:
a. increase friction
b. reduce drag
c. reduce gravitational force
d. get greater electrostatic force
Answer: b. reduce drag
10. Ball bearings are used to:
a. give a streamlined shape
b. increase grip
c. increase drag
d. reduce friction
Answer: d. reduce friction
B. Write T for True and F for False. Correct the false statements and give a short explanation.
1.Frictional force between two surfaces depends on the nature of the two surfaces.
Answer: T
Explanation: Rough surfaces create more friction, while smooth surfaces reduce it.
2. Rolling friction is greater than sliding friction.
Answer: F
Explanation: Rolling friction is less than sliding friction, which is why wheels help reduce resistance.
3. Ball bearings are used to increase friction.
Answer: F
Explanation: Ball bearings reduce friction by converting sliding motion into rolling motion.
4.Fluid friction acts between two solid surfaces in contact that are moving.
Answer: F
Explanation: Fluid friction occurs when objects move through fluids like air or water, not between solids.
t5.Tyres of vehicles have treads to reduce speed.
Answer: F
Explanation: Treads improve grip and channel water away, helping control—not reduce—speed.
II. Very short answer type questions
A. Answer the following.
1.Give an example of one contact force.
Friction is a good example of a contact force.
It occurs when two surfaces are in direct contact.
2.What is the SI unit of force?
The SI unit of force is called the newton (N).
It is named after Sir Isaac Newton.
3.What is a spring balance used for?
A spring balance is used to measure force or weight.
It works based on the stretching of a spring.
4.Give an example of one non-contact force.
Gravitational force is an example of a non-contact force.
It acts without any physical contact between objects.
5.Give two advantages of friction.
Friction helps us walk without slipping.
It also allows vehicles to brake and stop safely
B. Define the following (Two marks each):
Applied forces
An applied force is a force that is exerted on an object by another object or person from the outside.
It can cause the object to move, stop, or change direction depending on the strength and direction of the force.
Static friction
Static friction is the frictional force that acts between two surfaces when there is no relative motion between them.
It must be overcome to start the motion of an object and is usually greater than kinetic friction.
Rolling friction
Rolling friction is the resistance that occurs when a round object like a wheel or ball rolls over a surface.
It is usually smaller than both static and sliding friction, which is why wheels help reduce overall resistance.
Sliding friction
Sliding friction is the force that opposes the motion of two surfaces sliding past each other.
It generates heat and slows down the movement of objects in contact, requiring effort to keep motion going.
Wear and tear
Wear and tear refer to the gradual damage or deterioration of materials due to repeated use or constant friction.
It often results in reduced performance or failure of machines or tools over time.
1. What is the dominant force that acts between two electrically charged objects called?
Ans: The dominant force that acts between two electrically charged objects is called the electrostatic force. This force can either pull them together (attract) or push them apart (repel) depending on their charges.
2. Write down two factors on which the magnitude of frictional force between two surfaces depends.
Ans: Two factors on which the magnitude of frictional force between two surfaces depends are:
- The nature of the surfaces in contact: Rougher surfaces have more friction than smoother surfaces.
- How hard the surfaces are pressed together: If you press two surfaces together with more force, the friction between them increases.
3. How can we change the shape of an object? Give an example.
Ans: We can change the shape of an object by applying a force to it.
Example: When you squeeze a sponge, its shape changes. When you push on a lump of clay, you can mold it into different shapes.
4. Give one condition necessary for frictional force to act.
Ans: One condition necessary for frictional force to act is that there must be contact between two surfaces. If two surfaces are not touching, there can be no friction between them.
5. Why is friction a disadvantage?
Ans: Friction is a disadvantage because it often opposes motion and causes things to wear out. For example, friction makes it harder to push a heavy box, and it causes the soles of our shoes to wear thin over time. It also produces unwanted heat.
6. Why are oils and grease used in machinery?
Ans: Oils and grease are used in machinery to reduce friction between moving parts. When oil or grease is applied, it forms a thin layer between the surfaces, making them smoother and allowing the parts to slide past each other more easily. This helps to prevent wear and tear and keeps the machine running smoothly
IV. Long answer type questions
1. Discuss the effects of force.
Ans: A force is a push or a pull, and it can do many things to an object. Here are the main effects of force:
- Change the state of motion: A force can make a stationary object move. For example, if you kick a football, it starts moving. A force can also stop a moving object, like when a goalkeeper catches a ball. It can also change the speed of a moving object, making it faster or slower.
- Change the direction of motion: When you hit a cricket ball, you not only change its speed but also its direction. A force can make an object turn or move in a different path.
- Change the shape and size of an object: If you press on a rubber ball, its shape changes. Similarly, when you stretch a rubber band, both its shape and size change. Forces can deform objects.
So, forces are very powerful and can cause a lot of changes in the world around us!
2. Describe an activity to show that the force of friction between two surfaces depends on the nature of the two surfaces in contact.
Ans: We can do a simple activity to show that friction depends on the nature of the surfaces.
Activity:
- Materials needed: A small toy car or a book, a smooth table, a piece of sandpaper, and a piece of cloth.
- Procedure:
- First, place the toy car (or book) on the smooth table. Gently push it and observe how far it travels before stopping. You will notice it travels quite a distance.
- Next, place the piece of sandpaper on the table. Now, place the toy car on the sandpaper and gently push it with the same amount of force you used earlier. Observe how far it travels. You will find that it stops much quicker.
- Finally, replace the sandpaper with the piece of cloth. Push the toy car with the same force again and observe its distance. It will likely travel an even shorter distance than on the sandpaper.
- Observation and Conclusion: We observe that the toy car travels the longest distance on the smooth table, a shorter distance on the sandpaper, and the shortest distance on the cloth. This is because the smooth table offers less friction, while the rough sandpaper and even rougher cloth offer more friction. This activity clearly shows that the force of friction depends on how smooth or rough the surfaces in contact are.
3. What is ‘streamlined shape’? Explain and give two examples.
Ans: A streamlined shape is a special kind of shape that is designed to reduce the drag or resistance caused by fluids like air or water. Objects with streamlined shapes have smooth, tapering (getting thinner at the ends) bodies that allow the fluid to flow easily over them without creating much turbulence. This helps them move through the fluid with less effort.
Explanation: Imagine you are trying to push a flat board through water versus pushing a pointed boat. The flat board would be very hard to push because it creates a lot of resistance. The pointed boat, however, cuts through the water easily. This is because the boat has a streamlined shape. When air or water flows over a streamlined object, it separates smoothly and then comes back together, minimizing the force that tries to slow the object down.
Two examples of streamlined shapes:
- Birds and fishes: Most birds have streamlined bodies that help them fly through the air with less resistance. Similarly, fish have streamlined bodies that allow them to swim through water very efficiently.
- Aeroplanes and rockets: The bodies of aeroplanes and rockets are designed to be streamlined. This helps them cut through the air at high speeds without too much air resistance, saving fuel and allowing them to travel faster.
this design is streamline

4. Describe how friction can be reduced. In what way will it help if friction is reduced?
Ans: Friction is very useful in many situations, but sometimes it’s a disadvantage because it causes wear and tear, wastage of energy, and slows down motion. Here’s how friction can be reduced:
- Using lubricants: Applying substances like oil, grease, or graphite between moving parts of machines reduces friction. These lubricants form a thin layer between surfaces, making them slide past each other more easily.
- Using rollers or wheels (rolling friction): Instead of sliding objects, using rollers, wheels, or ball bearings changes sliding friction into rolling friction, which is much smaller. This is why it’s easier to move heavy luggage with wheels than to drag it.
- Polishing surfaces: Making surfaces very smooth by polishing them reduces the interlocking of irregularities between them, thereby decreasing friction.
- Using ‘streamlined’ shapes: For objects moving through fluids (like air or water), designing them with streamlined shapes reduces fluid friction (drag).
How reducing friction helps: Reducing friction is very helpful in many ways:
- Reduces wear and tear: When friction is reduced, the surfaces rub less against each other, which means machines and parts last longer and don’t get damaged quickly.
- Saves energy: Less friction means less energy is wasted as heat or resistance, making machines more efficient and saving fuel or electricity.
- Allows for smoother movement: Machines work more smoothly and easily when friction is reduced, making their operation quieter and more effective.
- Increases speed: In vehicles like cars, trains, or aeroplanes, reducing friction allows them to achieve higher speeds with the same amount of power.
5. How can we increase friction between two surfaces?
Ans: While reducing friction is often desired, sometimes we need to increase it for safety or to make things work better. Here are ways to increase friction between two surfaces:
- Making surfaces rougher: Increasing the roughness of the surfaces in contact increases the interlocking between them, which leads to more friction. For example, sports shoes have rough soles (spikes or patterns) to provide a better grip on the ground. Car tyres also have treads for this reason.
- Increasing the pressing force: When two surfaces are pressed together with greater force, the friction between them increases. This is why brake pads in vehicles are pressed hard against the wheels to stop them.
- Using materials with high coefficient of friction: Some materials naturally have more friction when rubbed against others. For example, rubber provides a good grip, which is why it’s used in tyres and shoe soles.
- Removing lubricants: If lubricants like oil or water are present, removing them will increase friction because the surfaces will come into direct contact again.
So, making surfaces rougher or pressing them harder together are the main ways to increase friction for practical purposes.
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
For the official Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks ):
Class 8 Science Ch 10 Force and Friction Oxford explains how different types of forces affect the motion of objects around us. It helps us understand that friction, though sometimes unwanted, is essential in many activities like walking, writing, and driving. Class 8 Science Ch 10 Force and Friction Oxford also shows how to control friction using lubricants or smooth surfaces. The examples and exercises in Class 8 Science Ch 10 Force and Friction Oxford make it clear that these forces are a part of our everyday experiences. By learning from Class 8 Science Ch 10 Force and Friction Oxford, students gain a strong foundation in the science behind motion and resistance.
