Class 8 Science Ch 16 Light-NCERT Solution
Question 1.
Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects out¬side the room? Explain.
Answer:
When we are in a dark room then we cannot see objects in the room. We can see the objects outside the room, because out of the room the light is available and the rays of light can enter our eyes after reflection from the objects.
Question 2.
Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection?
Answer:
| Regular Reflection | Diffused Reflection |
| (i) All the reflected rays are parallel. | (i) The reflected rays are not parallel. |
| (ii) It occurs on a smooth and polished surface. | (ii) It occurs on the rough surface. |
| (iii) Reflected rays are in one direction. | (iii) Reflected rays are scattered in different directions. |
No, diffuse reflection doesn’t mean the failure of laws of reflection.
Question 3.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
- Polished wooden table
- Chalk powder
- Cardboard surface
- Marble floor with water spread over it
- Mirror
- Piece of paper
Answer:
- Regular reflection will take place because the surface is plane and polished.
- Diffused reflection will take place because the surface is rough.
- Diffused reflection will take place because the surface is rough.
- Regular reflection will take place because the surface is smooth and plane.
- Regular reflection will take place because the surface is plane and polished.
- Diffused reflection will take place because the surface is rough.
Question 4.
State the laws of reflection.
Answer:
The laws of reflections are:
- The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane.
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Question 5.
Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Answer:
Activity: To show that the incident ray, reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Materials Required: Plane mirror, holder, ray box, etc.
Procedure: Fix sheet of white paper, a little beyond the edge of the board. Place a plane mirror strip vertically to the paper using a stand. Throw light from a ray box on the mirror. Look at the reflected ray. Mark the incident ray, normal ray and reflected ray. Fold the paper which is beyond the edge of the board. You will observe that the reflected ray is not seen in the folded portion of the chart paper. Now bring the folded portion back to its original position. The reflected ray of light is again seen on the page.
Conclusion: The sheet on the board can be considered as a plane. The incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
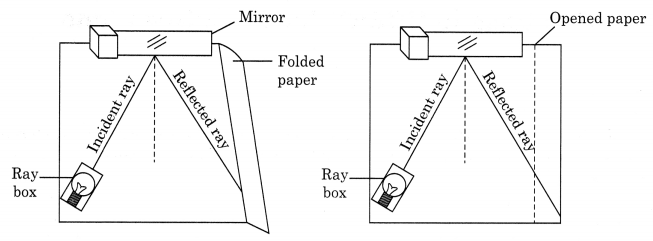
Incident ray, reflected ray and normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane
Question 6.
Fill in the blanks in the following.
(a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be ______ m away from his image.
(b) If you touch your ______ ear with a right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with _____
(c) The size of the pupil becomes _______ when you see in dim light.
(d) Night birds have _______ cones than rods in their eyes.
Answer:
(a) 2
(b) left, left hand
(c) larger
(d) lesser
Choose the correct option in Questions 7-8.
Question 7.
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
(a) Always
(b) Sometimes
(c) Under special conditions
(d) Never
Answer:
(a) Always
Question 8.
Image formed by a plane mirror is:
(a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged.
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
(c) real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged.
(d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Answer:
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Question 9.
Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.
Answer:
Kaleidoscope is a device based on the principle of multiple reflections. It consists of three long and narrow strips of plane mirrors inclined at an angle of 60° to one another forming prism. This is fitted in a tube. One end of this tube is closed by a cardboard disc having a hole at its centre. To the other end touching the mirrors plane glass plate is fixed on which broken pieces of coloured bangles are placed. This end of the tube is closed by a ground glass plate.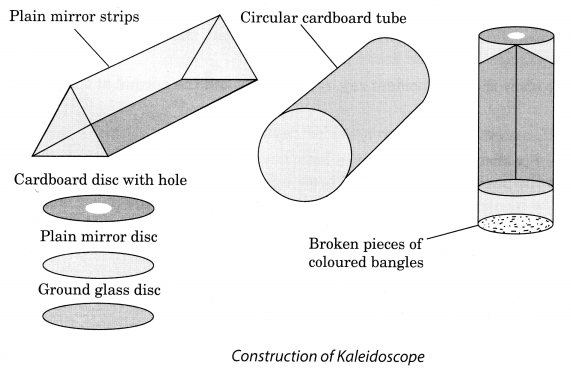
Question 10.
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye.
Answer: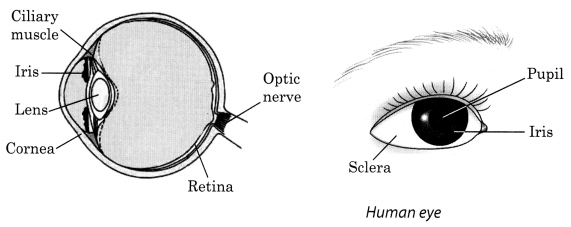
Question 11.
Gurmit wanted to perform Activity 16.8 using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teacher’s advise?
Answer:
Teacher has advised Gurmit not to do so because laser light is very harmful for her eyes and can cause a permanent defect in the eye. Person can even lose his or her eyesight if laser torch is directed over the eyes.
Question 12.
Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Answer:
Eyes are very precious. We must take proper care of them. We must
- always sit straight while reading or writing.
- if advised, use suitable spectacles.
- wash our eyes with clean water frequently.
- not look at the sun directly.
- always read or write in a proper light.
Question 13.
What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
Answer:
Here, the angle of reflection is 90°. As we know, according to the laws of reflection that angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
Here, the angle between the incident ray and reflected ray is 90°.
i.e., ∠i + ∠r = 90°
Since, ∠i = ∠r
We can write, ∠i + ∠i = 90°
⇒ 2∠i = 90°
⇒ ∠i = 45°
Angle of incidence = 45°.
Question 14.
How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mir¬rors separated by 40 cm?
Answer:
Here, mirrors are placed parallel to each other 40 cm apart. Therefore, the infinite number of images will be formed.
Question 15.
Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° as shown in Fig. 16.19. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.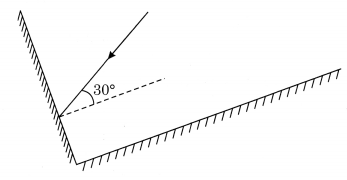
Answer: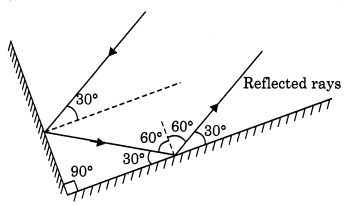
Question 16.
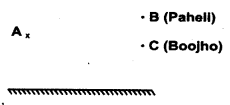
Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror as shown in Fig. 16.21. Can he see himself in the mirror? Also, can he see the image of objects situated at P, Q, and R?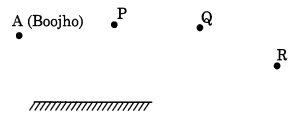
Answer:
No, Boojho can’t see himself in the mirror. He can see the image of the object at P and Q but not of R.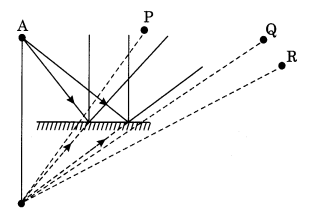
Question 17.
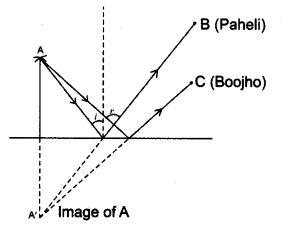
(a) Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror (Fig. 16.23).
(b) Can Paheli at B see this image?
(c) Can Boojho at C see this image?
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?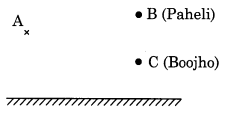
Answer:
(a) It is shown in the following figure.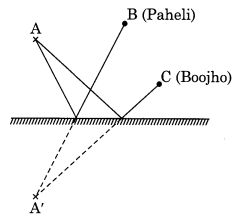
(b) Yes, Paheli can see the image of A.
(c) Yes, Boojho can see the image of A.
(d) Image of the object at A will not move as an object is not moving.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 – 1 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define dispersion of light. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2007]
Answer:
Splitting up of white light into seven colours when it passes through a glass prism is known as dispersion of light.
Question 2.
Name the colours in the order they appear in the spectrum of light. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2005]
Answer:
VIBGYOR – Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red.
Question 3.
Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. [NCERT]
- Always
- Sometimes
- Under special conditions
- Never
Answer:
Always.
Question 4.
Image formed by a plane mirror is [NCERT]
- virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged.
- virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
- real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged.
- real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Answer:
virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Question 5.
What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray ? [NCERT]
Answer:
The angle of incidence = 45°.
Question 6.
What are the two factors responsible for an object to be seen ?
Answer:
To be seen an object, the sense of vision and light are required.
Question 7.
What is meant by normal ?
Answer:
The perpendicular drawn at the point of incidence is known as normal.
Question 8.
Define the angle of incidence.
Answer:
The angle between the incident ray and the normal is known as angle of incidence.
Question 9.
What name is given to the angle between the normal and the reflected ray ?
Answer:
Angle of reflection.
Question 10.
What is meant by lateral inversion ? [NCT2010]
Answer:
Lateral inversion is the phenomenon of the interchange of the left and right sides, between the object and its image.
Question 11.
When the reflected rays are parallel, what type of reflection is taking place ?
Answer:
Regular reflection.
Question 12.
In irregular reflection, are the reflected rays parallel or not ?
Answer:
In irregular reflection the reflected rays are not parallel.
Question 13.
What are illuminated objects ?
Answer:
Objects which reflect the light falling on them and can be seen are known as illuminated objects
Question 14.
What is white light ?
Answer:
Sunlight is a mixture of seven colours also known as white light.
Question 15.
Give one example of natural dispersion.
Answer:
Formation of rainbow.
Question 16.
What is function of iris ?
Answer:
Iris controls the amount of light entering into the eyes.
Question 17.
What is meant by visually challenged people ?
Answer:
Visually challenged people have limited vision to see things.
Question 18.
What are non-optical aids ?
Answer:
Non-optical aids include visual aids, tactual aids, auditory aids and electronic aids
Question 19.
What are tactual aids ?
Answer:
Tactual aids include Braille writer, slate and stylus. They help the visually challenged persons in taking notes, reading and writing and in learning mathematics.
Question 20.
Fill in the blanks :
- The angle of reflection is ………… to the angle of incidence.
- The image formed by a plane mirror is ………….. inverted with respect to the object.
- The …………….. uses two plane mirror strips each of which is kept inclined at 45° to the axis of the tube.
Answer:
- equal
- laterally
- periscope.
Question 21.
Write one/two-word answer for each of the following :
- The ray of light that bounces back from a plane mirror.
- The nature of the image formed by a plane mirror.
- The number of images formed by a pair of parallel plane mirrors.
- A devices that is often used as “looking glass”.
Answer:
- Reflected ray
- Virtual image
- Multiple images
- Mirror.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 – 2 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which kind of spherical mirrors are used in vehicles ? Why ? [NCT 2007]
Answer:
A convex mirror is used in vehicles because it gives the driver a large field of view.
Question 2.
Why is it important to take care of our eyes ? Mention any two activities that may cause damage to our eyes. [KVS 2005]
Answer:
Eyes are the most wonderful gift of nature to us and they must serve us for whole life. Our eyes can be damaged by playing carelessly or by hurting them with sharp projections
Question 3.
Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see object in the room ? Can you see objects outside the room ? Explain. [NCERT]
Answer:
The objects cannot be seen inside the room because there is no light. The objects outside the room can only be seen if there is light outide.
Question 4.
State the laws of reflection. [NCT 2011, NCERT]
Answer:
Laws of reflection:
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
Question 5.
Distinguish between real and virtual image.
Answer:
Differences:
| Real image | Virtual image |
| (a) The rays actually meet at a point. (b) The image can be obtained on a screen. | (a) The rays donot meet at a point. (b) The image cannot bje obtained on a screen. |
Question 6.
What is the function of the eyelids ?
Answer:
- Eyelids prevents the objects from entering the eye.
- They also shut out light when not required.
Question 7.
Give some uses of plane mirror.
Answer:
Plane mirrors are used for dressing up, shaving beards, in scientific metres and for designing periscope.
Question 8.
How many plane mirror strips do we use in a kaleidoscope. At what angle are they inclined with respect to each other ?
Answer:
The kaleidoscope uses a set of three equal size plane mirror strips. The three strips are inclined to each other at angles of 60° each.
Question 9.
Why do we say that the image formed in a plane mirror is “virtual” ?
Answer:
The image formed in a plane mirror cannot be obtained on a screen. So we, say it is a ‘virtual’ image.
Question 10.
What would you do to see if the barber has cut your hair properly at the back ?
Answer:
I would keep another mirror parallel to the main mirror in a vertical position.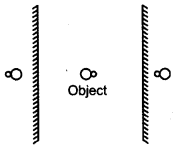
Question 11.
How many images are formed when two mirrors are placed edge to edge
- at right angles of each other.
- at an angle of 60° to each other ?
Answer:
- Three images will be formed.
- Five images will be formed.
Question 12.
- How are multiple iiriages formed ?
- Name a device based on this principle ?
Answer:
- When three rectangular strips of plane mirror are kept edge to edge at an angle of 60° to each other, multiple images are formed.
- Kaleidoscope is based on this principle.
Question 13.
What is colour blindness ? Give reason for this defect ?
Answer:
Some people cannot distinguish between the different colours. This is known as colour blindness. Colour blindness is due to the absence of cones on the nerve endings on the retina.
Question 14.
What is a nictating membrane ? In which animal is it found ?
Answer:
Nictating membrane is a transparent membrane over the eye to protect the eye from water. Fish and frogs have a nictating membrane.
Question 15.
What kind of eyes do the insects have ?
Answer:
Eye in insects is a compound eye with hundreds of small units, each with a lens of its own. The image seen by a insect is a blured picture.
Question 16.
Why should children take milk and eat carrots ?
Answer:
Milk, carrots and yellow fruits are rich in vitamin A, which is very essential for the eyes to maintain good vision.
Question 17.
How is night blindness caused ?
Answer:
Night blindness is caused by the deficiency of vitamin A and damage to the retina and the rods.
Question 18.
Distinguish between luminous and non-luminous bodies.
Answer:
Please refer to important points and definitions 21 and 22.
Question 19.
Is the moon a luminous body ? How are we able to see the moon ?
Answer:
The moon is non-luminous. We are able to see the moon because it reflects the sunlight falling on it.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 – 3 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° as shown in the figure. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror. [NCERT]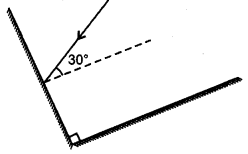
Answer: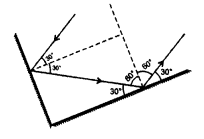
Question 2.
What are cones and rods ? What are their functions ?
Answer:
Cones are the nerve endings which are sensitive to colour light. They help us to distinguish between colours.
Rods are the nerve endings which are sensitive to bright light.
Question 3.
- In a periscope two mirrors are arranged parallel to each other but they do not form multiple images. Why ?
- What is the use of periscope ?
Answer:
- In a periscope two mirrors are placed parallel and facing each other but are in an inclined position at an angle of 45°. So they do not form multiple images.
- Uses of periscope
- in submarines to view the happening on the surface of water.
- to view objects behind the wall.
Question 4.
Draw a diagram to show dispersion of light.
Answer: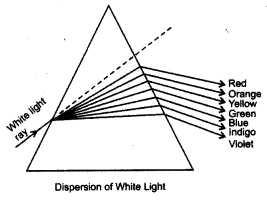
Question 5.
- What is spectrum ?
- What is the meaning of VIBGYOR ?
Answer:
- Spectrum is the band of seven colours obtained on the screen when white light splits on passing through a prism.
- VIBGYOR represents the seven colours of the spectrum, i.e. violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red.
Question 6.
How is a rainbow formed ?
Answer:
The water droplets suspended in the air after the rain act as prisms. When the sun is towards the horizon the inclined rays pass through the water drops to disperse into the seven colours of the specturm.
Question 7.
Why does white light disperse when it passes through a glass prism ?
Answer:
White light is a combination of seven colours of light. The speed of each colour is different. So, while passing through the glass prism each colour deviates by different amounts. Therefore, despersion of light into a spectrum takes place.
Question 8.
- Which part of the human eye makes a person ‘blue eyed’ ?
- What role is played by ciliary muscles ?
- What is the importance of retina in the eye ?
Answer:
- Iris is responsible for making the person blue eyed.
- Ciliary muslces help to adjust the focal length of the lens to view all objects clearly.
- The image of the object is formed on the retina of the eye.
Question 9.
What is the difference between the eyes of the night birds and day birds ?
Answer:
The day birds can see clearly during the day but not at night. The day birds have more cones and less rods. The cones are sensitive to bright light and can sense colours. Night birds can see clearly at night but not cjuring the day. Their eyes have a large cornea and pupil to allow more lighted pass. Also their retina has mostly rods and few cones. Rods are more sensitive to dim light. –
Question 10.
What is cataract of the eye ?
Answer:
Cataract is a condition in which the lens becomes milky. Light does not pass through such a lens to reach the retina. It can be corrected by replacing the lens with a synthetic lens.
Question 11.
What are the causes of blindness ?
Answer:
Blindness may be caused due to damage to :
- the lens
- the cornea
- the complete eye
Question 12.
How do visually impaired people communicate ?
Answer:
Visually impaired people can communicate by following methods :
- By using the Braille system which employs groups of dots to represent printed letters and numbers.
- in 1980, Braille computer software was developed. It can input, output and translate documents to and from Braille.
- by speech technology that can convert ordinary text into speech.
Question 13.
How is Braille system used ?
Answer:
Every character in the Braille code is based on the arrangement of one to six raised dots. Each dot has a numbered position in the Braille cell. These characters make up the letters of the alphabet, punctuation marks, numbers and everything else that can be printed does not have a separate alphabet of capital letters as there is in a print.
Question 14.
Explain how a screen reader can help visually impaired people ?
Answer:
A screen reader is a software programme that provides access to computer software applications and the internet by using a speech synthesizer to read the information on the monitor loudly.
Question 15.
- For how long does the image remain on the retina ?
- How are we able to see a moving picture ?
Answer:
- The imperssion of an image is retained on the retina for about l/16th of a second.
- If still images are projected on the retina at the rate more than 16 pictures per second, – then the eye will see the pictures moving.
Question 16.
Draw a ray diagram to show incident ray, reflected ray, normal, angle of incidence,, angle of reflection; if the angle of incidence is 45°
Answer: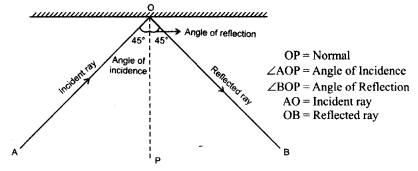
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 – 5 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How can you compare human eye with a photographic camera ? [MSE (Chandigarh) 2008]
Answer:
| Human Eye | Photographic Camera |
| (a) Real, inverted image is formed on retina. (b) The image cannot be stored as a photograph. (c) The focal length of convex lens can be adjusted by ciliary muscles. (d) Eyes uses line cell to detect light. | (a) Real, inverted image is formed on a film. (b) The image can be stored as a photograph. (c) The focal length of the lens cannot be adjusted. (d) Camera uses diaphragm to detect light and capture image. |
Question 2.
Draw a labelled sketch of human eye. [NCT2011]
Answer: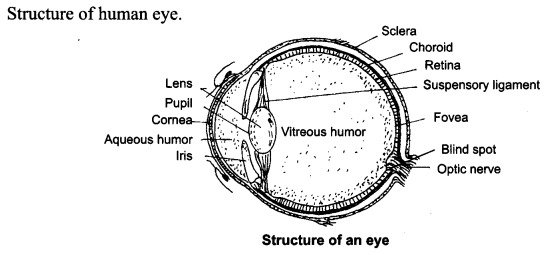
Question 3.
Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection ? [NCERT]
Answer:
When the reflected rays are parallel to each other, it is known as regular reflection. When the reflected rays are not parallel, the reflection is known as diffused or irregular reflection. Diffused reflection is not due to the failure of the laws of reflection. It is caused by irregularities in the reflecting surface.
Question 4.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case. [NCERT]
- Polished wooden table
- Chalk powder
- Cardboard surface
- Marble floor with water spread over it
- Mirror
- Piece of paper
Answer:
- polished wooden table
- chalk powder
- cardboard surface and
- marble floor with water spread over it and
- mirror will show regular reflection. This happens because the surface is plane without any defects.
- piece of paper show irregular reflection because the reflecting surface is not smooth. There are irregularities in the reflecting surface.
Question 5.
Fill in the blanks in the following : [NCERT]
- A person 1 m inffont of a plane mirror seems to be ………… m away from his image.
- If you touch your …………. ear with right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with .
- The size of the pupil becomes ………….. when you see in dim light.
- Night birds have ………….. cones than rods in their eyes.
Answer:
- 2 m
- left, left hand
- bigger
- few
Question 6.
Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope. [NCERT]
Answer:
To make a kaleidoscope, get three rectangular strips of glass 15 cm long and 4 cm wide each. Join them together to form a prism. Fix them with a few thick chart papers in a slightly long circular tube. Close one end of the tube by a cardboard disc having a hole in centre. At the other end touching the mirrors fix a circular plane glass sheet. Invert the tube and place some broken small pieces of coloured bangles on the glass plate. Close this end of the tube by a ground glass plate.
Question 7.
Explain how you can take care of your eyes. [NCERT]
Answer:
We can take care of our eyes in the following ways-
- have a regular check up.
- if advised, use suitable spectacles.
- avoid too much or too little light,
- wash your eyes frequently with clean water.
- always read at the normal distance for vision.
Question 8.
Give four properties of the image of an object formed by a plane mirror.
Answer:
The properties of the image formed by a plane mirror
- The image is formed as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
- The image formed is a virtual image.
- The image formed is an erect image and of same size of the object.
- The image formed is laterally inverted with respect to the object.
Question 9.
Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror as shown in figure. Can he see himself in the mirror ? Also can he see the image of objects situated at P, Q and R ? [NCERT]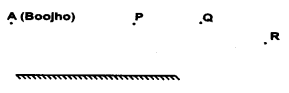
Answer:
Yes, Boojho can see his image. Yes, he can see the objects situated at P, Q and R.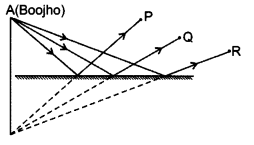
Question 10.
- Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror (figure). [NCERT]
- Can Paheli at B see this image ?
- Can Boojho at C see this image ?
- When Paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move ?

Answer:

- Yes Paheli can see the image of A.
- Yes, Boojho can see this image.
- When Paheli moves from B to C, the image of A will move from B to C.
Question 11.
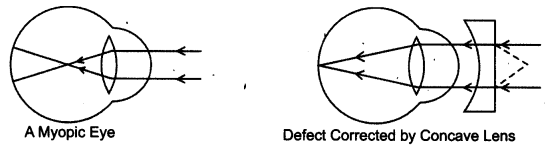
- What is myopia ?
- How is it caused ?
- How can it be corrected ?
- Draw diagrams to show myopic eye and its correction.
Answer:
- When a person can see nearby object clearly, but not far away objects, he is suffering from myopia.
- It is caused by the flattening of the eyeball and the lens becomes thick and rigid.
- It can be corrected by using spectacles with concave lenses.
Question 12.
- What is hypermetropia ?
- How is it caused ?
- How can it be corrected ?
- Draw diagram to show defective eye and its correction.
Answer:
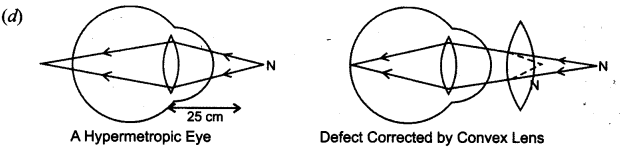
A person suffering from hypermetropia can clearly see distant objects but finds difficulty in reading, writing and viewing different objects.
It is caused by the elongation of the eyeball and the lens becomes flat.
It can be corrected by using a convex lens.
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 10
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 10):
https://ncert.nic.in/textbook.php?class=10