Chapter 15 of Class 8 Science (Oxford Book), titled “Light,” introduces students to the fundamental concepts of reflection, refraction, formation of images, and the behavior of light with different surfaces. Through simple activities and examples, this chapter helps learners understand how light travels and how mirrors and lenses affect the direction of light. The solutions provided here offer clear explanations and diagrams to support thorough understanding and effective exam preparation.
Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Light Oxford Book Answers
B. Circle the odd one out.
- Cornea, long sightedness, short-sightedness, cataract Moon, Stars, Earth, Trees
Odd one out: Trees
(Because Moon, Stars, and Earth are celestial objects, but Trees are living plants on Earth.) - Spectrum, Dispersion, Colours, Incident ray
Odd one out: Incident ray
(Because spectrum, dispersion, and colours are related to light splitting, while incident ray is the incoming ray of light.) - Leaf, Rough wall, Mirror, Skin
Odd one out: Mirror
(Because leaf, rough wall, and skin are natural surfaces, but mirror is a man-made reflective surface.) - Cornea, Long sightedness, Short-sightedness, Cataract
Odd one out: Cornea
(Because cornea is a part of the eye, others are eye problems.)
II. Very short answer type questions
A. Give one word/phrase for the following.
- Bodies that give out light of their own
Answer: Luminous bodies - The human eye retains an image produced for a short period of time.
Answer: Persistence of vision - An eye defect caused by cloudy or opaque eye-lens.
Answer: Cataract - A system which involves a pattern of raised dots used by the visually impaired to read.
Answer: Braille system
B. Define the following.
1. Diffused reflection:
When light falls on a rough surface, it reflects in many different directions. This is called diffused reflection. It helps us see objects clearly from any angle.
2. Multiple reflection:
When light bounces more than once between two or more surfaces, it is called multiple reflection. For example, light reflecting back and forth between two mirrors.
3. Lateral inversion:
When an image in a mirror appears reversed from left to right, it is called lateral inversion. This means the left side of the object looks like the right side in the mirror.
4. Dispersion:
When white light passes through a prism and splits into different colors, this splitting is called dispersion. It shows that white light is made up of many colors.
III. Short answer type questions
1. Why can we not see an image in an old and worn-out stainless-steel plate?
Answer:
We cannot see a clear image in an old and worn-out stainless-steel plate because its surface becomes uneven and scratched. This rough surface causes irregular reflection of light, which prevents the formation of a distinct image.
2. What is a spectrum?
Answer:
A spectrum is the band of different colours that is produced when white light is passed through a prism and splits into its constituent colours. The visible spectrum includes red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
3. On which part of the eye does the image (from the eye-lens) form?
Answer:
The image formed by the eye-lens is focused on the retina, which is a light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. The retina converts the image into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the optic nerve.
4. What kind of lens is used to correct myopia?
Answer:
A concave lens (also called a diverging lens) is used to correct myopia or short-sightedness. It helps by diverging the light rays before they reach the eye, so the image is formed correctly on the retina.
5. The deficiency of which vitamin can cause night blindness?
Answer:
Deficiency of Vitamin A can cause night blindness. This condition makes it difficult to see in dim light or at night because Vitamin A is essential for the proper functioning of the retina.
IV. Long answer type questions
1 Give a brief explanation of how we ‘see’ things around us.
Answer:
We see things because light from a source (like the Sun or a bulb) falls on objects and reflects off them. The reflected light enters our eyes through the pupil and is focused by the lens on the retina at the back of the eye. The retina converts the light into electrical signals, which travel to the brain through the optic nerve. The brain then processes these signals and forms an image, allowing us to see the object.
2. State the laws of reflection.
Answer:
The two main laws of reflection are:
- First law: The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal (a line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence) all lie in the same plane.
- Second law: The angle of incidence (the angle between the incident ray and the normal) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle between the reflected ray and the normal).
3. What are the characteristics of an image formed by a plane mirror?
Answer:
The image formed by a plane mirror has the following characteristics:
- It is virtual (cannot be projected on a screen).
- It is of the same size as the object.
- It is laterally inverted (left and right sides are reversed).
- The image is formed at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
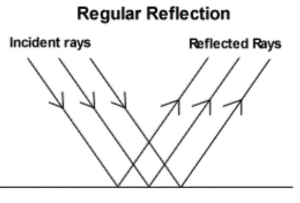
4. With the help of simple diagrams, show how light is reflected from a rough surface and a smooth surface.
Answer:
Light behaves differently when it reflects from smooth and rough surfaces:
- A smooth surface (like a mirror or polished metal) reflects all the incident light rays in a single direction. This type of reflection is called regular reflection. It produces a clear and sharp image.
- A rough surface (like paper, cloth, or wall) reflects the incident light rays in different directions. This is called diffused or irregular reflection. It does not form a clear image.
Key Points:
- Regular reflection results in image formation.
- Irregular reflection causes scattered light and no image is formed.
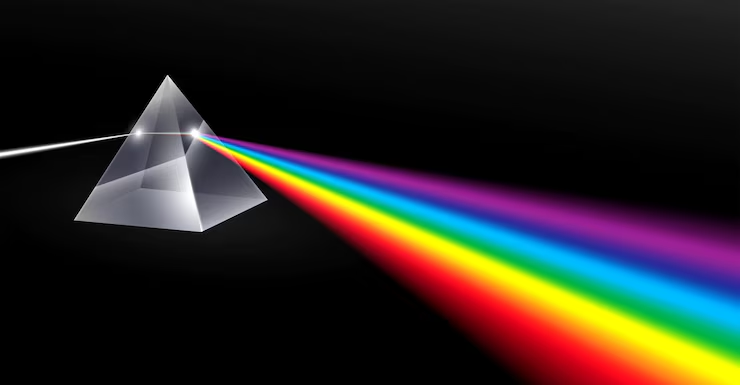
5. What is dispersion? Explain with the help of a simple diagram of a prism.
Answer:
Dispersion is the phenomenon of splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours (Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red — VIBGYOR) when it passes through a transparent medium like a glass prism.
This happens because different colours of light bend by different amounts when they pass through the prism. Violet bends the most, and red bends the least. As a result, the white light separates into a spectrum of colours.
Diagram description:
6. Write a short note on the following:
a. Defects of the eye:
Some common defects of the eye are:
- Myopia (Short-sightedness): Difficulty seeing distant objects clearly.
- Hypermetropia (Long-sightedness): Difficulty seeing nearby objects clearly.
- Cataract: Clouding of the eye lens, causing blurry vision.
- Astigmatism: Unequal curvature of the cornea causing blurred vision.
These defects can be corrected by using glasses, contact lenses, or surgery.
b. Alternative technology available to visually challenged people:
Visually impaired people use special technologies such as:
- Braille system: A tactile writing system using raised dots that helps them read by touch.
- Audio books and screen readers: These convert text into speech.
- White cane: Helps in navigation and avoiding obstacles.
- Assistive apps and devices: Like magnifiers or smart glasses that enhance vision.
c. Nutrition and eye health:
Good nutrition is important to keep our eyes healthy. Foods rich in vitamins A, C, and E help protect eyesight. Vitamin A is especially important because it helps in the formation of a pigment called rhodopsin, which allows us to see in low light. Carrots, spinach, eggs, and citrus fruits are good for eye health. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding excessive screen time also help prevent eye strain and dryness.
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8: Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Light Oxford & NCERT Solution- Explore
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
NEET BIOLOGY
- Evolution
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Human Health and Disease
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
For the official Class 8 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 8):
The concepts covered in Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Light Oxford are fundamental to understanding how light behaves in our daily lives. This chapter explains important topics like reflection, refraction, and image formation in a simple way.
By studying Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Light Oxford, students gain a clear grasp of how mirrors and lenses work. The examples and exercises in Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Light Oxford help reinforce these ideas effectively. Overall, mastering the topics in Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Light Oxford builds a strong foundation in optics for future science learning.
