The Solar System is one of the most fascinating topics in astronomy that helps us understand our place in the universe. In Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Solar System Oxford solution, students explore the origin, structure, and key features of the Sun, planets, moons, asteroids, and other celestial bodies. This chapter provides clear explanations and step-by-step Oxford textbook solutions to make learning simple and engaging for both Indian students following the CBSE or ICSE curriculum and international learners interested in basic astronomy concepts.
From Mercury’s speed to Neptune’s distance, this chapter takes you on an exciting journey through space, highlighting scientific facts, diagrams, and solved exercises. Whether you are studying for school exams in India or enhancing your general science knowledge abroad, these Oxford solutions will help you grasp every concept easily and improve your understanding of the Solar System.
🌞Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Solar System Oxford Textbook Solution
🌍 Introduction
The Solar System is a vast and fascinating family of the Sun, planets, moons, and several other celestial bodies. It helps us understand how Earth and other planets exist and move in space. This chapter introduces students to the structure, formation, and members of the Solar System in an easy and scientific way.
☀️ The Sun – The Center of the Solar System
The Sun is a huge ball of hot gases, mainly hydrogen and helium, and is the source of light and heat for all planets. It occupies almost 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System. The Sun’s gravity keeps all the planets and other objects in orbit. Without the Sun’s energy, life on Earth would not exist.
The average surface temperature of the Sun is about 5500°C.It produces energy through nuclear fusion reactions in its core.
🪐 The Eight Planets
There are eight planets in the Solar System. They revolve around the Sun in fixed paths called orbits and rotate on their own axes. The planets are divided into two groups:
1. Inner Planets (Terrestrial Planets)
These are small, rocky planets located closer to the Sun.
Mercury – The smallest and closest planet to the Sun. It has no atmosphere and experiences extreme temperatures.
Venus – Known as the “Earth’s twin” because of its similar size. It has a thick carbon dioxide atmosphere and is the hottest planet.
Earth – The only known planet with life. It has suitable air, water, and temperature.
Mars – Known as the “Red Planet” due to iron oxide on its surface. Scientists believe water once existed on Mars.
2. Outer Planets (Gas Giants)
These are large planets made mostly of gases like hydrogen and helium.
Jupiter – The largest planet in the Solar System with more than 75 moons.
Saturn – Famous for its beautiful rings made of ice and dust.
Uranus – Rotates on its side, and has a bluish-green color due to methane gas.
Neptune – The farthest planet from the Sun, cold and windy with a blue appearance.
🌕 Moons or Satellites
Moons are natural satellites that revolve around planets. Earth has one moon. Jupiter and Saturn have many moons. Moons reflect sunlight and do not have their own light.
☄️ Other Members of the Solar System
Asteroids – Small rocky bodies found mainly between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt.
Comets – Made of ice, dust, and rock; they have a bright glowing tail when they come near the Sun.
Meteoroids, Meteors, and Meteorites –
Meteoroids are small rocky pieces moving in space. When they enter Earth’s atmosphere, they burn up due to friction and form a meteor (shooting star).
If a part of it reaches the ground, it is called a meteorite.
🌌 The Earth as a Unique Planet
Earth is unique because it supports life. It has a moderate temperature, oxygen-rich atmosphere, liquid water, and protective ozone layer. It rotates from west to east and takes 24 hours to complete one rotation, causing day and night. It revolves around the Sun in 365¼ days, causing seasons.
🔭 The Solar System in the Milky Way Galaxy
The Solar System is a part of the Milky Way Galaxy, which contains billions of stars and planetary systems. Our galaxy looks like a spiral disc when viewed from above. The Sun is just one of the many stars in this vast galaxy.
Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Solar System Oxford Full Chapter
II. Very short answer type questions
A. Give one example for the following:
1. A galaxy
Answer: Milky Way
2. A solar system body that is not the Sun or a planet
Answer: Asteroid
3. A comet
Answer: Halley’s Comet
4. A natural satellite
Answer: Moon
5. An artificial satellite
Answer: INSAT-3C
6. A planet without a natural satellite
Answer: Mercury
7. A star bigger than the Sun
Answer: Betelgeuse
8. A constellation
Answer: Orion
9. A very light planet made up mostly of gases
Answer: Jupiter
10. An asterism
Answer: Big Dipper
III. Short answer type questions
1.What is a constellation?
Answer:
A constellation is a group of stars that form a recognizable pattern in the night sky. These patterns often resemble animals, mythological characters, or objects. For example, Orion and Ursa Major.
2. Name a star in the Orion constellation. Answer: Betelgeuse is a well-known star in the Orion constellation. It appears reddish in color and is one of the brightest stars in the night sky.
3.Name the Earth’s natural satellite.
Answer:
The Earth’s natural satellite is the Moon. It is the only natural satellite of Earth and is responsible for causing tides on our planet.
4. Where is the Asteroid Belt?
Answer:
The Asteroid Belt is located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It is a region filled with numerous rocky bodies known as asteroids.
5. Which celestial body has a head and a long tail?
Answer:
A comet is a celestial body that has a bright head and a long glowing tail. The tail always points away from the Sun due to solar wind.
IV. Long answer type questions
1. Describe the objects that one could see in the night sky.
Answer: When we look at the night sky, we can see many different objects. These include: Stars – They look like tiny shining dots but are actually huge balls of hot gases. The Sun is also a star.
The Moon – It is the Earth’s natural satellite. It appears in different shapes every night.
Planets – These look like stars but do not twinkle. Some planets we can see are Venus, Mars, and Jupiter.
Constellations – These are groups of stars that form patterns or shapes in the sky, like Orion or Ursa Major.
Comets – These are space objects with a glowing head and a long tail.
Artificial Satellites – Man-made machines like communication or weather satellites can also be seen moving slowly like stars.
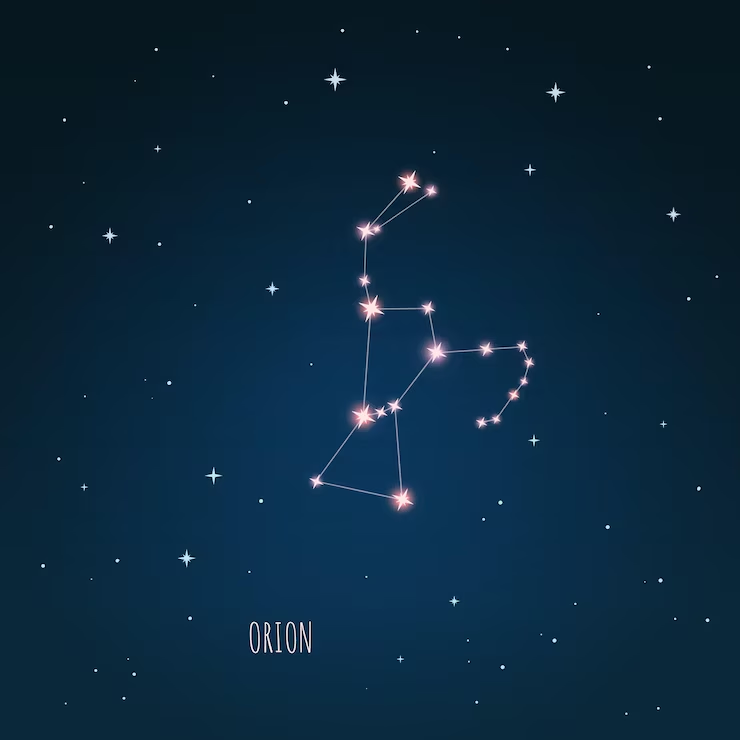
2. Draw a rough diagram and give a short description of any one constellation.
Answer:
Orion Constellation: Orion is one of the most famous constellations. It is also called “The Hunter”. It is clearly visible in the winter sky. It has a line of three bright stars in the center that form Orion’s Belt. Two bright stars in Orion are Betelgeuse (red) and Rigel (blue-white).
3. Name the planets of the Solar System. List them in the order of their distance from the Sun. Also, name the smallest and biggest planet.
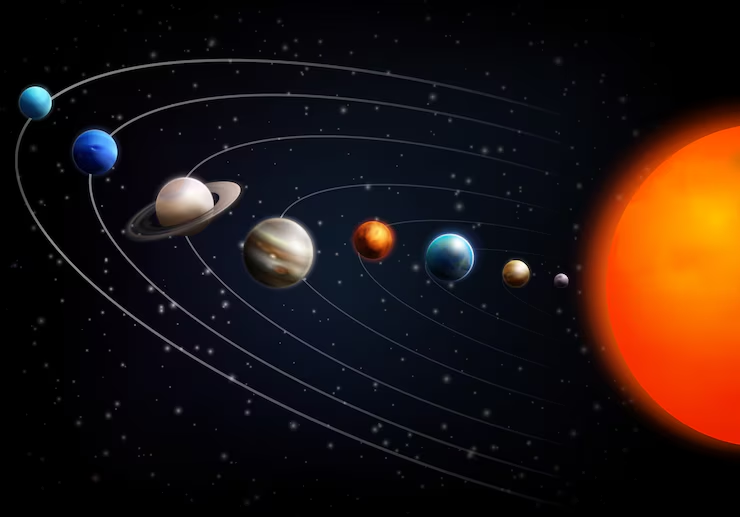
Answer:
The planets of our Solar System in order from the Sun are: Mercury ,Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune . The smallest planet is Mercury. The biggest planet is Jupiter.
4. Distinguish between meteoroids, meteors, and meteorites.
Answer:
| Term | Where it is found | What it does | Example/Note |
| Meteoroid | In space | A small rock or particle that moves through space. | May enter Earth’s atmosphere. |
| Meteor | In Earth’s atmosphere | A meteoroid that burns due to friction with air and appears as a streak of light (shooting star). | Does not usually reach the ground. |
| Meteorite | On Earth’s surface | A part of a meteor that survives the fall and lands on Earth. | Can form craters on impact. |
5. What are ‘Phases of the Moon’? Draw a rough diagram of any two phases and name them.
Answer:
The Phases of the Moon are the different ways the Moon looks from Earth over about a month. These changes in apparent shape occur because we see varying amounts of the Moon’s sunlit surface as the Moon orbits the Earth. The Moon itself doesn’t change shape; it’s always half-lit by the Sun, but our perspective on that illuminated half changes.
The complete cycle includes eight principal phases, but here’s a description and a diagram of two key phases:
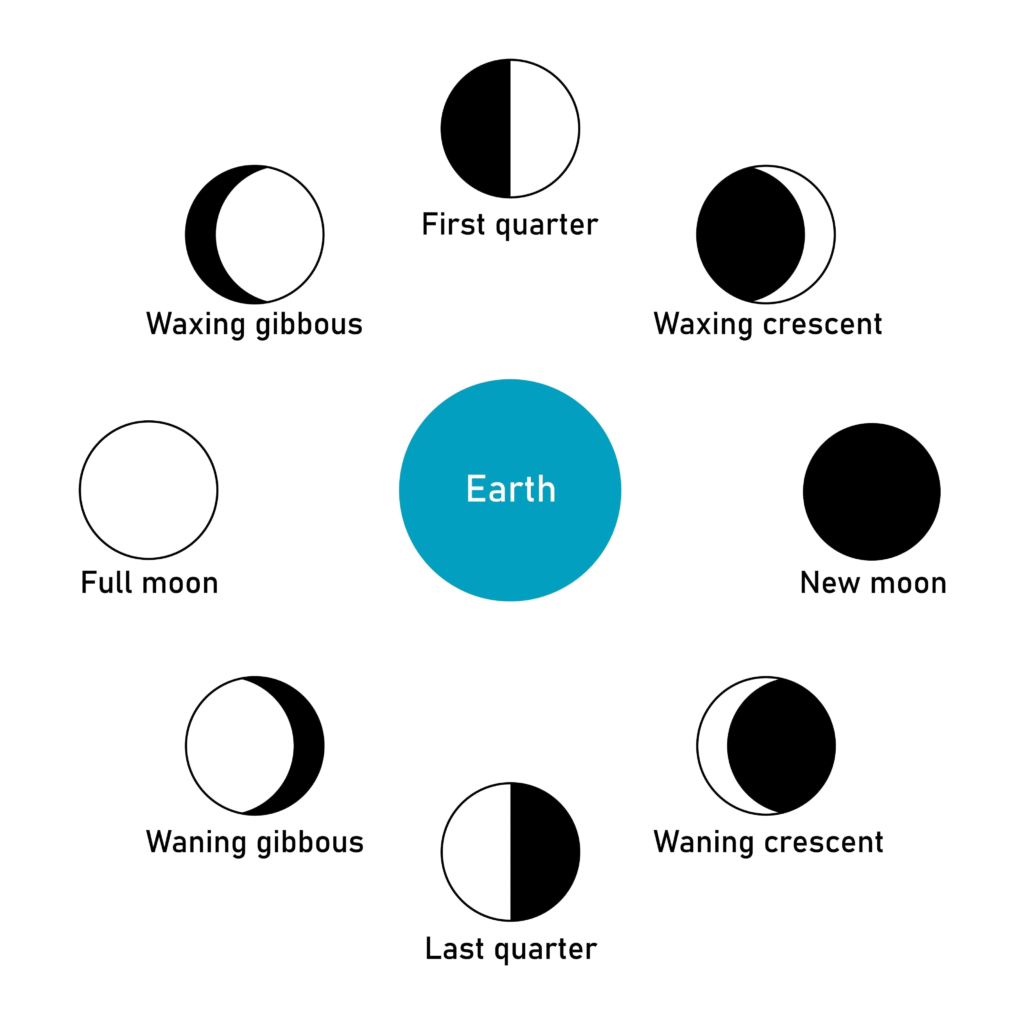
The eight main phases, in order, are:
Waning Crescent 🌘
New Moon 🌑 (Moon is not visible)
Waxing Crescent 🌒
First Quarter 🌓 (Half-moon, light increasing)
Waxing Gibbous 🌔
Full Moon 🌕 (Completely illuminated)
Waning Gibbous 🌖
Third Quarter 🌗 (Half-moon, light decreasing)
6. List five uses of artificial satellites.
Answer:
Artificial satellites are machines made by humans that orbit the Earth. They are useful in many ways: Television and Internet – Satellites help send TV and internet signals around the world. Weather Forecast – They take pictures of clouds and help predict weather. GPS and Navigation – They help us find directions and locations on maps. Space Research – Satellites are used to study planets, stars, and outer space. Military and Defense – Satellites help in spying and protecting a country.
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Science – CBSE SQP 2024
Class 9:
Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 8:
Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
Class 8 Science – NCERT Solutions
Class 7:
Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
Class 6:
Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
Subject-wise Solutions
Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Chemistry:
Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Biology:
Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
Math:
Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
For the official Class 8 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
NCERT Textbooks (for Class 8):
