Every living organism, from the tiniest bacterium to the largest tree, is made up of small structural and functional units known as cells. The cell is the basic building block of life, just like bricks form a building. Whether it’s a single-celled organism like Amoeba or a multicellular organism like humans, the cell performs all the essential functions that sustain life.
🌿 Class 9 Science Ch 5 Fundamental unit of life-Cell (CONCEPT)
The discovery of the cell opened a new era in biological science. It helped scientists understand how living beings grow, repair, reproduce, and maintain themselves. The concept of the cell unites all living organisms under one common structure — showing that despite the diversity of life, all living things share a similar cellular foundation.
🔹 Discovery of the Cell
The first person to observe cells was Robert Hooke in 1665 when he examined thin slices of cork under a primitive microscope. He noticed small, box-like structures which he called “cells”, meaning “small rooms”. Later, Anton van Leeuwenhoek observed living cells for the first time using his handcrafted microscope.
The development of better microscopes over time allowed scientists to study cells in more detail, leading to the formation of the Cell Theory.
🔹 Cell Theory
The Cell Theory was proposed by Schleiden (a German botanist) and Schwann (a German zoologist) in 1838–1839. It was later modified by Rudolf Virchow in 1855. The main points of Cell Theory are:
- All living organisms are made up of one or more cells.
- The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life.
- All new cells arise from pre-existing cells.
This theory forms the foundation of modern biology and explains the continuity of life.
🔹 Structure of the Cell
A typical cell consists of three main parts:
- Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) – It is a thin, flexible boundary that separates the cell from its surroundings. It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, hence called selectively permeable.
- Cytoplasm – It is a jelly-like substance that fills the cell and contains various organelles. The cytoplasm provides space for chemical reactions to occur and keeps the cell components in place.
- Nucleus – It is the control center of the cell that contains genetic material (DNA). The nucleus directs all the activities of the cell such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
🔹 Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Each organelle within the cell performs a specific function necessary for the survival of the cell. Some important organelles are:
- Mitochondria – Known as the powerhouse of the cell, it releases energy from food during respiration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – It helps in the transport of materials; the rough ER is involved in protein synthesis, while the smooth ER synthesizes lipids.
- Golgi Apparatus – It modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion.
- Lysosomes – Known as the suicidal bags of the cell, they contain digestive enzymes that break down waste materials and dead cell parts.
- Plastids (in plant cells) – They contain pigments; chloroplasts perform photosynthesis.
- Vacuoles – These store water, food, and waste materials. Plant cells have large central vacuoles.
🔹 Types of Cells
- Prokaryotic Cells – These are simple, primitive cells without a well-defined nucleus or membrane-bound organelles (e.g., bacteria).
- Eukaryotic Cells – These have a well-organized nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (e.g., plant and animal cells).
🔹 Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Vacuole | Large and central | Small or absent |
| Plastids | Present (like chloroplasts) | Absent |
| Shape | Generally rectangular | Generally round or irregular |
| Centrioles | Absent | Present |
🔹 Concept Summary
The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of life that performs all vital activities like respiration, growth, and reproduction. Cells form tissues, tissues form organs, and organs form complete organisms. Understanding the cell helps us understand the functioning of the entire living system.
The study of cells is known as Cytology, and it continues to be one of the most fascinating and essential branches of biology.
✨ In Simple Words:
Every living thing begins its journey as a single cell.
From that one cell, life grows, multiplies, and evolves — proving that the cell truly is the fundamental unit of life.
Class 9 Science Ch 5 Fundamental unit of life-Cell (Textbook Answers)
Page 59
Question 1. Who discovered cells, and how?
Answer: Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665 while examining a thin slice of cork through a self-designed microscope. He saw that the cork resembled the structure of a honey comb consisting of many little compartments. These small boxes are called cells.
Question 2. Why the cell is called the structural and Junctional unit of life?
Answer: A cell is capable of independently carrying out all necessary activities of life. So, they are called basic or functional unit of life.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 61
Question 1. How do substances like C02 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer: Substances like CO₂ and water move in and out of the cell through a process called diffusion.
1.Diffusion: This is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
CO₂: During cellular respiration, CO₂ is produced inside the cell and needs to move out. Since there is a higher concentration of CO₂ inside the cell and a lower concentration outside, it moves out of the cell through the cell membrane by diffusion.
Water: Water moves in and out of the cell through osmosis, which is a type of diffusion specific to water. Water moves from an area of lower solute concentration (outside the cell) to an area of higher solute concentration (inside the cell), balancing the concentration on both sides.
Question 2. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer: It is called selectively permeable membrane because it allows the entry and exit of some substances, not all.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 63
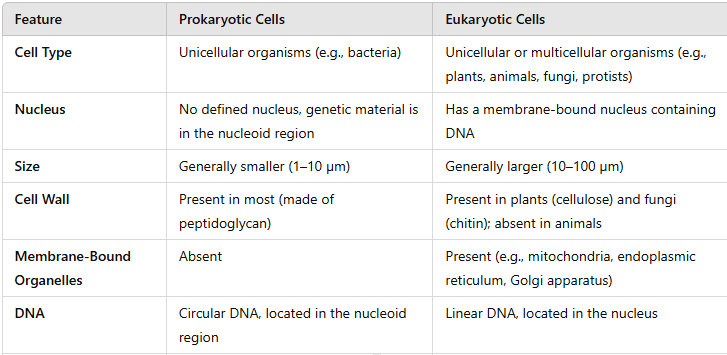
Question 1. Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 65
Question 1. Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer: The two organelles which have their own genetic material are:
1. Mitochondria 2. Plastids
Question 2. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer: If the organization of a cell is destroyed due to physical or chemical damage, the cell will not function properly. This can lead to the breakdown of its structures and processes. For example, the cell membrane might lose its ability to control what enters or leaves the cell, or the nucleus may not be able to manage cell activities like growth and division. In severe cases, the cell could die because it can no longer maintain its normal functions. The damage can also spread to nearby cells, affecting the overall health of the tissue or organ.
Question 3. Why are lysosomes known as suicide hags?
Answer: Lysosomes are called “suicide bags” because they contain strong enzymes that can break down the cell’s own parts. If the cell gets damaged or is no longer needed, the lysosomes release these enzymes, which destroy the cell. This helps remove unhealthy or old cells from the body. So, they are called “suicide bags” because they can cause the cell to destroy itself when necessary.
Question 4. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer: The proteins are synthesised in the ribosomes that are also known as protein factories.
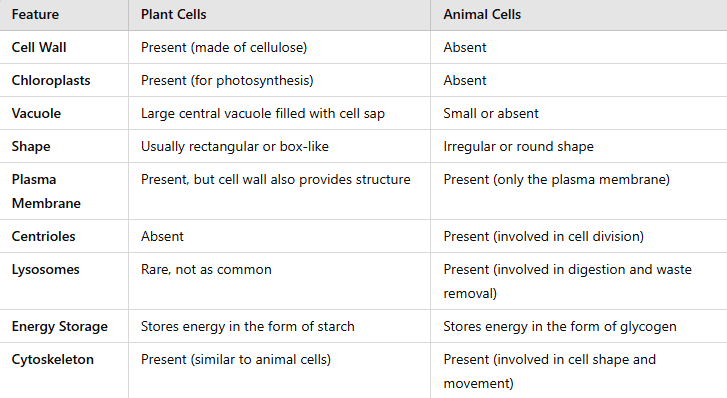
Question 1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are also different from animal cells.
Answer:
Question 2. How is prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer:
| Feature | Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | No true nucleus, DNA is free in the cytoplasm | Has a defined nucleus with a nuclear membrane |
| Size | Generally smaller (0.1–5 micrometers) | Larger (10–100 micrometers) |
| Organelles | No membrane-bound organelles | Contains membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, etc. |
| DNA | Single circular DNA strand | Multiple linear DNA strands (chromosomes) |
| Ribosomes | Smaller (70S) | Larger (80S) |
| Cell Division | Binary fission (simple division) | Mitosis and meiosis (complex division) |
| Examples | Bacteria, Archaea | Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists |
| Cell Wall | Present in most (made of peptidoglycan) | Present in plants (made of cellulose) or absent |
| Flagella | Simple, made of flagellin | Complex, made of tubulin |
Question 3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer: If plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down then molecules of some substances will freely move in and out.
Question 4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer: Golgi apparatus has the function of storage, modification and packaging of the products in vesicles. If there were no Golgi bodies, packaging and dispatching of materials synthesised by the cell will be stocked.
Question 5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer: Mitochondria is known as powerhouse of the cell because it releases the energy required for different activities of life.
Question 6. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer: Lipids and proteins are synthesised in ER [Endoplasmic Reticulum].
Question 7. How does Amoeba obtain it’s food?
Answer: Amoeba obtains food through phagocytosis. It extends its pseudopodia to surround and engulf food, forming a food vacuole. Inside the vacuole, digestive enzymes break down the food into nutrients, which are absorbed by the cell. Any waste is then expelled from the cell.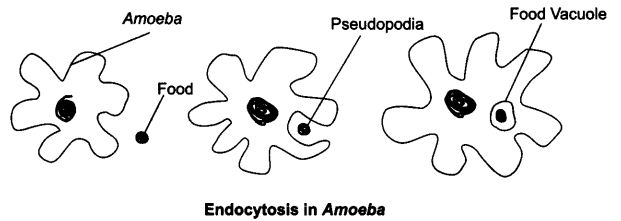
Question 8. What is osmosis?
Answer: Osmosis is the process of movement of water molecule from a region of higher water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane to a region of lower water concentration.
Question 9. Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups, one of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water.
Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C ‘
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D.
Answer: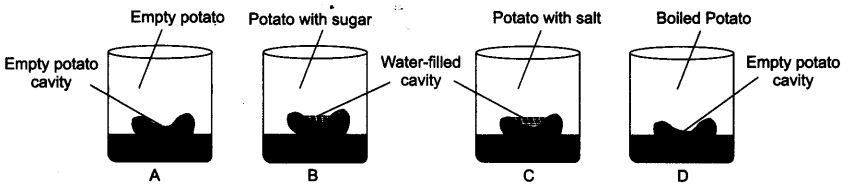
(i) Water gathers in B and C because in both the situations there is difference in the concentration of water in the trough and water in the cup of Potato. Hence, osmosis takes place as the potato cells act as a semi-permeable membrane.
(ii) Potato A is necessary for this experiment for comparison, it acts as a control.
(iii) Water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D. As cup of A does not have change in the concentration for water to flow. For osmosis to occur one of the concentration should be higher than the other.
In cup D, the cells are dead and hence the semi-permeable membrane does not exists for the flow of water and no osmosis takes place.
Class 9 Science Ch 5: Fundamental unit of life-Cell-Extra questions
1.What is the basic structural and functional unit of life?
Answer: The basic structural and functional unit of life is the cell. It is the smallest unit of an organism that performs all the vital functions of life, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
2. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Answer: Prokaryotic cells do not have a defined nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Examples include bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Examples include plant, animal, and fungi cells.
3. What are the main components of the cell membrane?
Answer: The cell membrane is mainly composed of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. This structure allows the cell membrane to be selectively permeable, controlling the entry and exit of substances.
4. What is the function of mitochondria?
Answer: Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell. They generate energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration, which is essential for the cell’s functions.
5. What is the function of the nucleus?
Answer: The nucleus controls the activities of the cell and contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA). It is responsible for growth, reproduction, and the functioning of the cell.
6. Explain the structure and function of chloroplasts.
Answer: Chloroplasts are found in plant cells and contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. They are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy to make food.
7. What is the role of ribosomes in a cell?
Answer: Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis. They help assemble amino acids into proteins based on the instructions carried by mRNA from the nucleus.
8. What is osmosis?
Answer: Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration, until equilibrium is reached.
9. What are vacuoles and what is their function?
Answer: Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles in cells, mainly found in plant cells. They store water, nutrients, and waste products. In plant cells, the large central vacuole also helps maintain turgidity.
10. What is the role of lysosomes in the cell?
Answer: Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They help break down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign substances. They also play a role in autophagy and apoptosis (programmed cell death).
11.What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
Answer: The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes found in the cytoplasm. There are two types of ER:
Smooth ER: Lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and storage of calcium ions.
Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes and helps in the synthesis and transport of proteins.
12.Explain the role of the vacuole in plant cells.
Answer: The vacuole in plant cells is a large, membrane-bound organelle filled with water, nutrients, and waste products. It helps maintain turgidity (rigidity) of the cell, stores essential substances, and plays a role in maintaining the cell’s shape. The vacuole also helps in the breakdown of waste materials and toxins.
You can access the official NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics on the NCERT website at the following link:
NCERT Class 10 Mathematics Solutions
This page will guide you to the textbook and solutions, as provided by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT).
