Ace your upcoming board exams with the ultimate preparation tool. The Class XII Physics Sample Question Paper 2026 is now available to help you decode the latest exam pattern and marking scheme. Solving this sample paper is the most effective way to test your conceptual understanding, improve time management, and walk into the exam hall with complete confidence.
PHYSICS – Code No. 042
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
CLASS – XII (2025 – 26)
Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions
(1)There are 33 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
(2) This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section E.
(3) All the sections are compulsory.
(4) Section A contains sixteen questions, twelve MCQ and four assertion reasoning based of 1 mark each, Section B contains five questions of two marks each, Section C contains seven questions of three marks each, Section D contains two case study-based questions of four marks each and Section E contains three long answer questions of five marks each.
(5) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in two question in Section B, one question in Section C and all three questions in Section E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
(6) Use of calculators is not allowed.
SECTION A
- If a charged hollow sphere and a solid sphere of aluminum and copper of equal radii
are in electrostatic equilibrium, then which of the following statements is true?
(A) Both the spheres are having equal charges.
(B) The hollow sphere will have more charge than solid sphere at its surface.
(C) The aluminum sphere will have more charge on its surface than copper sphere.
(D) If hollow sphere is also made up of aluminum then it will have more charge.
- A coil contains N turns of insulated copper wire of diameter d and resistivity ρ
wound on a cylinder of diameter D. What is the total resistance between the two
ends of the coil of copper wire?(given: D>>d)
(A) 4𝜌𝑁𝐷/𝑑2
(B)8𝜌𝑁𝐷/𝑑2
(C) 2𝜌𝑁𝐷/𝑑2
(D) 12𝜌𝑁𝐷/𝑑2
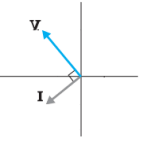
- If the phasor diagram for a device connected to AC supply is as shown in the fig,
then which of the following statements is true?
(A) When the frequency of the AC source is increased than the impedance of the
device decreases.
(B) This device behaves as conducting wire when connected across DC source.
(C) When the frequency of the AC source is decreased than the impedance of the device decreases. (D)This device stores energy in the form of magnetic potential energy.
- Which of the following statement is true for the radio waves and the gamma rays?
(A) The energy of gamma rays is lesser than that of the radio waves.
(B) The frequency of the radio waves is higher than that of gamma rays.
(C) The radio waves and the gamma rays have the same energy.
(D) The energy of radio waves is lesser than that of the gamma rays. - A glass prism has internal angles of 45°, 45° and 90°. The glass has a critical angle
of 45°. Which of the following ray diagrams depicts the possible path the of light
through the prism?
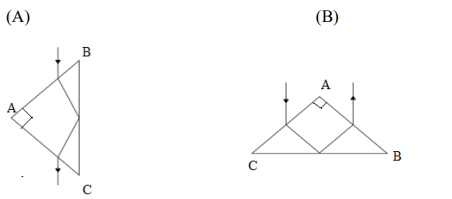

For VI-Candidates
Light passes from a certain medium into air. The critical angle of the given medium
is Ɵ, which of the following expressions gives the speed of light in the given
medium? Where c is the speed of light in air.
(A) 1/cSinƟ
(B) SinƟ/C
(C) C/SinƟ
(D) cSinƟ
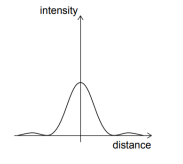
- The light from a monochromatic source is incident on a single slit and the resulting
diffraction pattern is viewed on a screen. The graph shows the variation of the
intensity with the distance on the screen.
The width of slit is increased keeping the intensity of the source the same. Which of
the following graphs is correct? (The original curve is shown with a dashed line.)

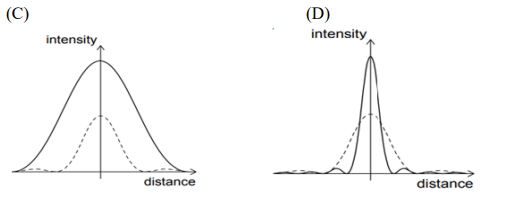
For VI-Candidates
The phenomenon of superposition of two waves, resulting in redistribution of
energy is known as……………
(A) diffraction (B) interference
(C) reflection (D) refraction
- Which of the following transitions corresponds to the emission of the radiation of
the maximum wavelength?

(A) I (B) III (C) IV (D) VI
(for V.I. Candidates)
Which of the following transitions corresponds to the emission of the radiation of
the maximum wavelength?

(A) I (B) III (C) IV (D) VI
- A charged particle is projected along the axis of a current carrying loop. Which of
the following statements is true?
(A) The acceleration of the charged particle will depend on the velocity with which
it is projected.
(B) The acceleration of the charged particle will depend on the magnitude of the
current passing through the coil.
(C) The acceleration of the charged particle will depend on the radius of the coil.
(D) The charged particle will move with constant velocity. - Two small identical magnets are allowed to fall freely one through a vertical
solenoid of 20 m made up of copper and another in air through the same vertical
distance. The time taken by the two magnets to fall will be
(A) same in both the cases.
(B) more for the magnet falling in air.
(C) more for the magnet falling through the solenoid.
(D) infinite. - The emf generated by an AC generator is given by V=Vo sin ωt, where ω is angular
frequency of armature of generator. What will be the emf if the angular frequency
is doubled
(A) V=Vo sin 2ωt ( B) V=2Vo sin ωt
(C) V=2Vo sin 2ωt (D) V=Vo sin ωt - The ratio of the nuclear densities of two nuclei having the mass numbers 8 and 27 is (A) 8:27 (B) 3:2 (C)2:3 (D) 1:1
- When we move magnetic compass from point P to Q then which of the following
statement is true
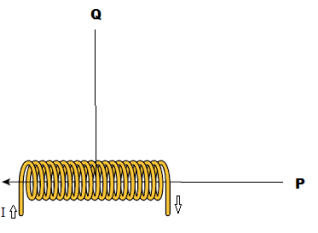
(A) The deflection of the magnetic needle at P and Q will be in the same direction.
(B) The deflection of the magnetic needle at P and Q will be in the opposite
directions.
(C) The deflection of the magnetic needle at P and Q will be perpendicular to each
other.
(D) The deflection of the magnetic needle at P and Q will be inclined at 45o with
respect to each other.
For Questions 13 to 16, two statements are given one labelled Assertion (A) and
other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from
the options as given below.
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of
Assertion.
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation
of Assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(D) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
- Assertion (A): Total energy of an electron in hydrogen atom is negative.
Reason (R): The centripetal force is provided by electrostatic force. - Assertion (A): The critical angle of light passing from glass to air is minimum for
violet colour.
Reason (R): The wavelength of blue light is greater than the light of other colours
- Assertion (A): Two light sources emitting waves of similar wavelengths are
coherent.
Reason (R): Two light sources emitting waves having zero or constant phase
difference are known as coherent sources. - Assertion (A): For three point charges to be in equilibrium, they must be collinear.
Reason(R): One of the three charges must have different polarity than rest of the
two.
SECTION B - The amplitude of the magnetic field of a plane electromagnetic wave propagating
along positive X axis in vacuum is 510 nT𝑘̂ and its angular frequency is 60 x 106
rad/sec. Write the expression for the electric field (𝐸→). - The following graph shows the potential difference across the terminals of a cell
against its load current.
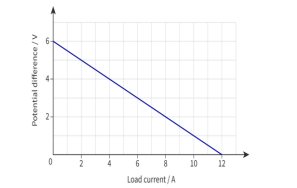
Find,
(I) the emf of the cell and
(II) the internal resistance of the cell.
For VI candidates
Find the relation between internal resistance, emf, external resistance and the total
current in the circuit ?
- A charge q is placed inside a sphere of radius ‘a’ filled with water and another
charge 2q is placed inside cube of side ‘2a’ which is vacuumed inside. Find the ratio
of the flux linked with the sphere to that linked with the cube. (Take relative
permittivity of water as 80)
20(I) Write an expression for the magnetic force per unit length between two parallel thin
current carrying wires. Hence define one ampere.
OR
20(II) Draw a diagram representing the behaviour of magnetic field lines for a
(A) diamagnetic &
(B) paramagnetic substance.
For VI-Candidates
Sate Gauss’s law of magnetism? Hence find the magnetic flux linked with the
sphere enclosing a current carrying solenoid?
21(I) How does the impact parameter affect the trajectory of a α – particles scattered by a heavy nucleus? What is the value of impact parameter for head on collision of α– particles with the nucleus?
OR
21(II) Plot a graph showing variation of de-Broglie wavelength λ versus
1/√𝑉 , where V is accelerating potential for a particle of mass m and charge q. Obtain the slope of this
graph.
SECTION C
- With the help of circuit diagram explain working of the full wave rectifier.
- (I) The current I1 in a wire is getting divided in two wires with currents I2 and I3 at a
junction in a circuit.The currents in the three wires are related by I1 = I2 + I3.
(A) State the fundamental law from which this relation is derived.
(B) Explain the validation of law of conservation of energy in Kirchhoff’s voltage
law?
(II) How the balancing condition gets affected if you are interchanging the
galvanometer and the cell in the Wheat stone bridge? - A fast-moving neutron collides with the nucleus of Plutonium (Pu), thereby
producing Xenon (Xe) and Zirconium (Zr) along with neutrons.
(I) Write the nuclear fission reaction.
(II) Find the energy released in the above nuclear reaction.
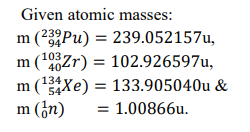
- A compound microscope consists of an objective lens of focal length 0.82 cm and
an eyepiece lens of focal length 2.9 cm. An object is placed 0.91 cm from the
objective lens. The image is formed at the near point (25 cm) from the eye.
(I) Calculate that the angular magnification of the microscope.
(II) Draw the ray diagram of compound microscope in normal adjustment. 3 - Draw the reflected wave front for a plane wave front incident on a plane reflecting
surface. Hence verify the laws of reflection using Huygen’s principle.
For VI Candidates
(I) Define wave front?
(II) Define wavelet?
(III) What will be the shape of the wave front intercepted by a large
reflecting type telescope on earth, due to a star far-away from our solar system
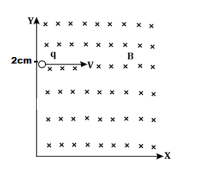
27(I) If a point sized object having charge 1C and mass 1g is projected with velocity of 2𝑖̂m/s from a point (0,2cm,0) in the region of magnetic field -0.1𝑘̂ T which spreads in the first quadrant.
(A) What will be the shape of the path followed by the given charged particle?
(B) At what point it will cross the X-axis?
(C) What will be the kinetic energy of particle when it will enter in the fourth quadrant?
A conducting coil of 50 turns and area 5/𝜋 cm2 is rotating along the axis of solenoid of length 50cm and 2000 turns, carrying current of 5 A. What will be the value of maximum emf generated?
SECTION – D
29 When an external voltage is applied across a semiconductor diode such that p-side is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and n-side to the negative terminal it is said to be forward biased. The applied voltage mostly drops across the depletion region and the voltage drop across the p-side and n-side of the junction is negligible. When an external voltage is applied across the diode such that n-side is positive and p-side is negative, it is said to be reverse biased. The applied voltage mostly drops across the depletion region.
(I) Ge and Si diodes start conducting at 0.3 V and 0.7 V respectively. In the following figure if Ge diode connection are reversed, the value of 0 V changes by (assume that the Ge diode has large breakdown voltage)


- Photoelectric effect is phenomenon of the ejection of electrons when the radiation of suitable frequency is made to fall on the surface of a metal. When light of suitable wavelength falls on the emitter C given in the diagram, the photoelectrons are emitted. These photoelectrons are drawn to the collector A. The photoelectric current of the order of a few microamperes can be normally obtained from the device given in figure. The device given converts a change in intensity of illumination into a change in photocurrent. This current can be used to operate control systems and in light measuring devices. The devices are made up of metals with low ionization enthalpies, for example platinum whose work function is 6.35 eV.
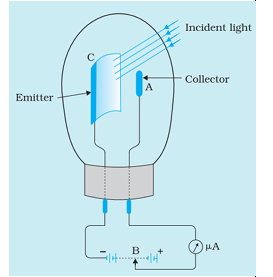
(I) If infrared radiation of 3 x 1011 Hz is used as incident radiation, determine the
reading of microammeter? Justify mathematically. 2
(II) In the given diagram, if terminal B is shifted towards the left then how will it
affect the reading of the microammeter?
(for V.I. candidates)
(II) If the supplied voltage is decreased, then what will be effect on the reading of
the microammeter?
(III) Plot a graph showing this variation in reading of micrometre on shifting the
terminal B towards the right.
(for V.I. candidates)
(III) If the intensity of incident radiation is doubled, by what factor will the kinetic
energy change?
SECTION E
31(I) (A) A dielectric slab of thickness t, is introduced between the plates of parallel plate capacitor of area A and separation d (where t<d). Find an expression for the capacitance with the dielectric slab.
(B) A copper sphere of capacitor C is dropped in ocean. Will the capacitance of the sphere increase, decrease or remain same? Justify.
(C) A capacitor is connected across a source of potential difference V and then the separation ‘d’ between the plates is increased using insulating stick. Plot ‘V’ vs ‘d’ graph for the given capacitor.
For VI Candidates
(C) A capacitor is connected across potential difference V and is then separation
between plates ‘d’ is increase using insulating stick. Will the energy stored in
capacitor increase or decrease? Justify
OR
31 (II)
(A) If a charge of 1µC is placed at the origin and another charge of 3 µC placed at
the point (20m,0m,0m) in an external uniform electric field of 40V/m 𝑖̂ with the
electric potential at origin to be zero. Find the electrical potential energy of
system.
(B) If one charge particle is moved from A to C To B and another charge particle of
equal magnitude is moved from A to D to B, In uniform external magnetic field.
Than for which charge particle more work will be needed? (use fig for reference)
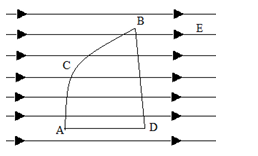
(C) Electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume of conductor has the same value on its surface why?
For VI candidates
(C) If A charge particle is taken from A to B from two different path one path has resistance of 10Ω and another has capacitance of 3µF. work done by which path will be more. 3+1+1
32(I) (A) Derive lens maker’s formula.
(B) Equi-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 10cm?
OR
32(II) (A) Define angle of deviation in a prism?
(B) Obtain the relation A+δ=i+e for a prism where A is the angle of prism, δ is the angle of deviation, i is the angle of incidence and e is the angle of emergence. Write this relation for the minimum deviation?
(C) Write the condition for minimum deviation. 1+3+1
- Please note that the assessment scheme of the Academic Session 2024-25 will continue in the current
session i.e. 2025-26.
33(I)
(A) State the working principle of a moving coil galvanometer? What modification is required in the galvanometer to make its scale linear?
(B) If a galvanometer of resistance 49.5Ω has range of 0.05A. What will be the value of resistance needed to convert it in ammeter of range 5A?
(C) How these two resistors should be connected to galvanometer in both cases?
OR
33(II) (A) An input potential Vin=200 Sin 100𝜋𝑡 V is provided to an ideal transformer having 1000 turns in primary coil and 100 turns in secondary coil as shown in figure. The load circuit has a resistance of 4Ω, a capacitive reactance of 2Ω and an inductive reactance of 6Ω.
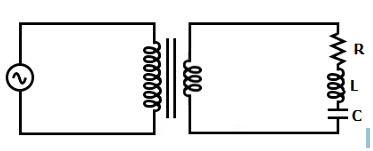
Find:
(i) the output voltage across the load circuit
(ii) the current flowing through the load circuit
(iii) the power supplied to the load circuit by the transformer
(B) State the working principle of a transformer and explain how it is a key
component in the transfer of electrical power over long distances.
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
Subject-wise Solutions
Physics:
Chemistry:
Biology:
Math:
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
Science:
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions
NEET BIOLOGY
- Evolution
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Human Health and Disease
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
Enhance Your Preparation!
Start practicing now by accessing chapter-wise solutions and boost your NEET or school exam scores. Download free PDFs directly from the links above.
Why Choose Our Resources?
- Comprehensive Solutions: Clear, step-by-step explanations for every chapter.
- Free Downloads: Access high-quality study material without any cost.
- Expert-Curated Content: Perfect for NEET, CBSE, and other exams.
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 10):
