Welcome to the Science Practice Paper 2019-20 Questions and Answer for the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) Class 10 examination. This resource is designed to help students prepare for their exams by providing detailed solutions and explanations to a set of practice questions.

By reviewing these answers and diagrams, students can gain a better understanding of key concepts, improve their problem-solving skills, and feel more confident for their upcoming science board exam. Best of luck with your preparation! 📝
Science Practice Paper 2019-20 Questions and Answer
Class-X
Science-086
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2019-20
TIME: 3 Hrs. M.M.: 80
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises three sections – A, B and C. Attempt all the sections.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Internal choice is given in each section.
- All questions in Section A are one-mark questions comprising MCQ, VSA type and
assertion-reason type questions. They are to be answered in one word or in one sentence. - All questions in Section B are three-mark, short-answer type questions. These are to be
answered in about 50 – 60 words each. - All questions in Section C are five-mark, long-answer type questions. These are to be
answered in about 80 – 90 words each. - This question paper consists of a total of 30 questions.
SECTION A
1.Define catenation. 1
2.How does valency of an element vary across a period? 1
3.Answer question numbers 3(a) – 3(d) on the basis of your understanding of the following paragraph and the related studied concepts. Renewable energy sources such as wind energy are vital for the Indian economy, not only from the point of view of supply, but also from the perspective of environmental and social benefits. India is the world’s fifth largest wind-power producer and the largest windmill facilities in India are installed in Tamil Nadu. Muppandal is a small village of Tamil Nadu and one of the most important sites of wind-farm in the state. It uses wind from the Arabian Sea to produce renewable energy. The suitability of Muppandal as a site
for wind farms stems from its geographical location as it has access to the seasonal monsoon winds.

The electrical generators used on wind turbines in sites like Muppandal, produce an output AC of 240 V and a frequency of 50 Hz even when the wind speed is fluctuating. A transformer may be required to increase or decrease the voltage so it is compatible with
the end usage, distribution or transmission voltage, depending on the type of
interconnection.
3(a) State the principle behind electric generator. 1
3(b) The output frequency of wind turbine is 50 Hz. What is meant by this statement? 1
3(c) Why do you think Muppandal is at an advantageous position for this project? 1
3(d) Based on the data represented in the graph below, which of the two cities A or B would be an ideal location for establishing a wind-farm and why?
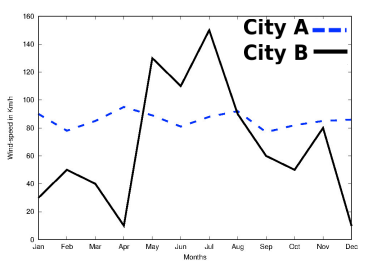
4.Question numbers 4(a) – 4(d) are based on the two tables given below. Study these tables related to blood sugar levels and answer the questions that follow.
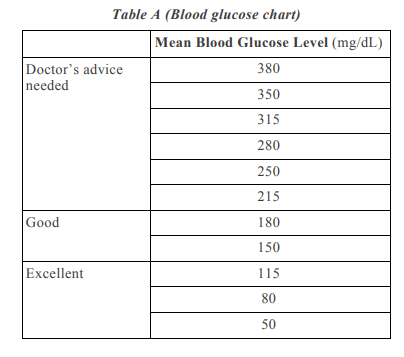
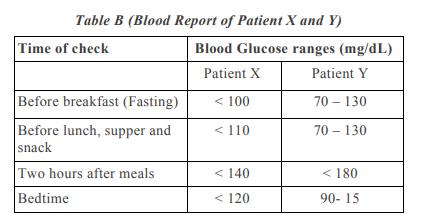
4(a) Refer to Table B showing the blood report of the levels of glucose of patients X and Y. Infer the disease which can be diagnosed from the given data. 1
4(b) Identify the hormone whose level in the blood is responsible for the above disease. 1
4(c) Which one of the following diets would you recommended to the affected patient?
i) High sugar and low fat diet.
ii) Low sugar and high protein diet.
iii) High Fat and low fiber diet.
iv) Low sugar and high fiber diet.
4(d) Refer to the Table A and suggest the value of the mean blood glucose level beyond which doctor’s advice is necessary:
i) 180 mg/dL
ii) 115 mg/dL
iii) 50 mg/dL
iv) 80 mg/dL
5. When we enter a dark room coming from outside, immediately the things inside the room do not appear clear to our eyes. This is because
i) pupils do not open at all in the dark.
ii) pupils take time to adjust.
iii) light travels slower in a dark room.
iv) pupils open very quickly in the dark.
OR
The phenomena of light responsible for the working of the human eye is
i) reflection
ii) refraction
iii) power of accommodation
iv) persistence of vision
6. When a 4V battery is connected across an unknown resistor there is a current of 100 mA in the circuit. The value of the resistance of the resister is:
i) 4 Ω
ii) 40 Ω
iii) 400 Ω
iv) 0.4 Ω
7 Unit of electric power may also be expressed as:
i) volt-ampere
ii) kilowatt-hour
iii) watt-second
iv) joule-second
8. It was found that water from a river was contaminated with Coliform bacteria. Which one of the following pollutant might have got mixed with the water?
i) Fertilizer run off
ii) Industrial waste
iii) Pesticides
iv) Human faecal matter
OR
Which one of the following stakeholders of forests causes the maximum damage to forest?
i) People who live in or around the forest
ii) The forest department of the government
iii) The wildlife and native enthusiasts
iv) The industrialists
9.Which one of the following green house gases is a contributor due to incomplete combustion of coal and petroleum?
i) Oxides of nitrogen
ii) Methane
iii) Carbon monoxide
iv) Carbon dioxide
10. Which of the following reactions is an endothermic reaction?
i) Burning of coal.
ii) Decomposition of vegetable matter into compost.
iii) Process of respiration.
iv) Decomposition of calcium carbonate to form quick lime and carbon dioxide.
11. Identify the basic salt from the following salts:
i) Na2CO3 ii) NH4Cl
iii) NaNO3 iv) KCl
12 .The positions of four elements A, B, C and D in the modern periodic table are shown below. Which element is most likely to form an acidic oxide?
13 Assertion: Following are the structural isomers of butane.
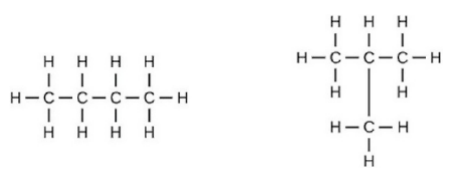
Reason: Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in their structures.
14 Assertion: A fuse wire is always connected in parallel with the mainline.
Reason: If a current larger than the specified value flows through the circuit, fuse wire melts. 1
SECTION B
15.(i) Write two observations when lead nitrate is heated in a test tube.
(ii) Name the type of reaction.
(iii) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above reaction. 3
16.A compound ‘X’ of sodium is used as an antacid and it decomposes on strong heating.
(i) Name the compound ‘X’ and give its chemical formula.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the decomposition of ‘X’.
(iii) Give one use of compound ‘X’ besides an antacid.
OR
You are provided with 90 mL of distilled water and 10 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid to prepare dilute sulphuric acid.
(i) What is the correct way of preparing dilute sulphuric acid? Give reason.
(ii) How will the concentration of H3O + ions change on dilution?
17.Two elements X and Y have atomic numbers 12 and 16 respectively. To which period of the modern periodic table do these two elements belong? What type of bond will be formed between them and why? Also give the chemical formula of the compound formed. 3
18 (i) Create a terrestrial food chain depicting four trophic levels.
(ii) Why do we not find food chains of more than four trophic levels in nature?
OR
How will you create an artificial aquatic ecosystem, which is self-sustainable?
19. Explain the processes of aerobic respiration in mitochondria of a cell and anaerobic respiration in yeast and muscle with the help of word equations. 3
20. In a pea plant, the trait of flowers bearing purple colour (PP) is dominant over white colour (pp). Explain the inheritance pattern of F1 and F2 generations with the help of a cross following the rules of inheritance of traits. State the visible characters of F1and F2
21.Explain giving reasons the bending of the shoot tip of a plant towards light source coming from one side of the plant. 3
22.It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
(i) What should be the range of the object distance in the above case?
(ii) Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
(iii) Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? 3
23.Suppose your parents have constructed a two room house and you want that in the livingroom there should be a provision of one electric bulb, one electric fan, a refrigerator and a plug point for appliances of power up to 2 kilowatt. Draw a circuit diagram showing electric fuse and earthing as safety devices. 3
24.In the figure given below, a narrow beam of white light is shown to pass through a
triangular glass prism. After passing through the prism, it produces a spectrum XY on the
screen.
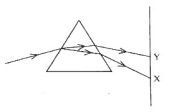
(i) Name the phenomenon.
(ii) State the colours seen at X and Y.
(iii)Why do different colours of white light bend at different angles through a prism?
OR
(i) What is visible spectrum?
(ii) Why is red used as the stopping light at traffic signals?
(iii)Two triangular glass prisms are kept together connected through their rectangular
side. A light beam is passed through one side of the combination. Will there be any dispersion? Justify your answer. 3
SECTION C
25 Metal X is found in nature as its sulphide XS. It is used in the galvanisation of iron articles. Identify the metal X. How will you convert this sulphide ore into the metal? Explain with equations. 5
OR
State the reason for the following:
(i) Aluminium oxide is called an amphoteric oxide.
(ii) An iron strip dipped in a blue copper sulphate solution turns the blue solution pale green.
(iii) Hydrogen gas is not evolved when most metals react with nitric acid.
(iv) Calcium does not occur in free state in nature.
(v) Sodium or potassium metals are kept immersed under kerosene.
26. The formulae of four organic compounds are given below:
A B C D
C2H4 CH3COOH C2H5OH C2H6
(i) Which one of these compounds A, B, C or D is a saturated hydrocarbon?
(ii) Identify the organic acid and give its structural formula.
(iii) Which of the above compounds when heated at 443K in the presence of
concentrated H2SO4 forms ethene as the major product? What is the role played by
concentrated H2SO4 in this reaction? Also write the chemical equation involved.
(iv) Give a chemical equation when B and C react with each other in presence of
concentrated H2SO4. Name the major product formed and mention one of its
important use
27.
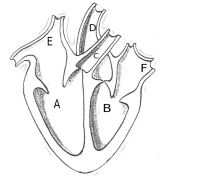
(i) Identify any two parts from the above diagram which carry oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
(ii) Explain the process of double circulation with the help of a flow chart. 5
28.(i) Describe the various steps involved in the process of binary fission with the help of a diagram.
(ii) Why do multicellular organisms use complex way of reproduction?
OR
(i) Describe the role of prostate gland, seminal vesicle and testes in the human male reproductive system.
(ii) How is the surgical removal of unwanted pregnancies misused?
(iii) Explain the role of oral contraceptive pills in preventing conception.
29 (i) Consider a conductor of resistance ‘R’, length ‘L’, thickness‘d’ and resistivity ‘ρ’.
Now this conductor is cut into four equal parts. What will be the new resistivity of
each of these parts? Why?
(ii) Find the resistance if all of these parts are connected in:
(a) Parallel
(b) Series
(iii) Out of the combinations of resistors mentioned above in the previous part, for a given voltage which combination will consume more power and why? 5
30 (i) A lens produces a magnification of -0.5. Is this a converging or diverging lens? If the focal length of the lens is 6 cm, draw a ray diagram showing the image formation in this case.
(ii) A girl was playing with a thin beam of light from a laser torch by directing it from different directions on a convex lens held vertically. She was surprised to see that in a particular direction, the beam of light continues to move along the same direction after passing through the lens. State the reason for her observation. Draw a
ray diagram to support your answer.
OR
(i) On entering in a medium from air, the speed of light becomes half of its value in air. Find the refractive index of that medium with respect to air?
(ii) A glass slab made of a material of refractive index n1 is kept in a medium of refractive index n2.
A light ray is incident on the slab. Draw the path of the rays of light emerging from the glass slab, if (i) n1> n2 (ii) n1 = n2 (iii) n1< n2
For the official Class 10 Mathematics Solutions, you can visit:
- NCERT Textbooks (for Class 10):
Class-wise Solutions
Class 12:
Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
Class 11:
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Class 10:
Class 9:
Class 8:
Class 7:
Class 6:
