Photosynthesis Process Equation and Importance
Plants are the foundation of all life on Earth, and at the heart of their survival lies a fascinating process called photosynthesis. Understanding the photosynthesis process equation and importance not only helps us appreciate how plants produce their own food but also reveals how this simple-looking process sustains all living beings.
Photosynthesis: The Engine of Life 🌿
A Comprehensive Guide for Students
Harnessing the Sun’s Energy
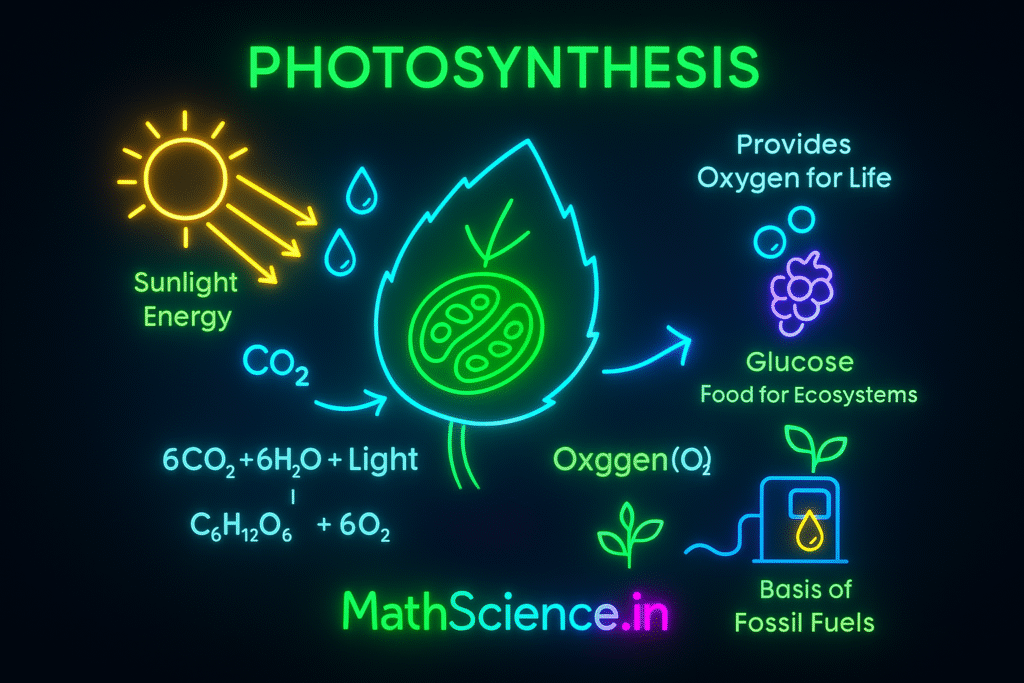
Photosynthesis is a remarkable process used by plants, algae, and some bacteria to convert light energy into chemical energy. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water. In essence, it’s how plants create their own food and, in the process, produce the oxygen that sustains most life on Earth.
The Photosynthesis Process: A Two-Step Journey
The process of photosynthesis is not a single reaction, but a complex series of steps divided into two main stages: the **Light-Dependent Reactions** and the **Light-Independent Reactions** (also known as the Calvin Cycle).
Stage 1: The Light-Dependent Reactions
This first stage occurs in the **thylakoid membranes** of the chloroplasts, the specialized organelles within plant cells. As the name suggests, this process requires direct sunlight.
- Light Absorption: **Chlorophyll**, the green pigment in plants, and other pigments absorb light energy from the sun. This light energy excites electrons within the chlorophyll molecule.
- Water Splitting (Photolysis): The absorbed light energy is used to split water molecules ($H_2O$) in a process called **photolysis**. This reaction breaks water into oxygen ($O_2$), protons ($H^+$), and electrons. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere, which is essential for aerobic respiration in animals.
- Energy Conversion: The energy from the excited electrons and protons is used to create two crucial energy-carrying molecules: **ATP** (Adenosine Triphosphate) and **NADPH** (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate). These molecules act as the temporary energy currency, which will power the next stage of photosynthesis.
Stage 2: The Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
This stage takes place in the **stroma**, the fluid-filled space within the chloroplasts, and does not directly require light. It uses the chemical energy from the ATP and NADPH created in the first stage.
- Carbon Fixation: The plant takes in carbon dioxide ($CO_2$) from the atmosphere. This $CO_2$ is “fixed” or incorporated into a five-carbon organic molecule, a crucial step that converts inorganic carbon into an organic form.
- Reduction: The energy from ATP and NADPH is used to convert the fixed carbon dioxide molecules into a simple sugar, typically glucose ($C_6H_{12}O_6$). This is the step where the plant actually produces its food.
- Regeneration: The cycle regenerates the initial five-carbon molecule, allowing the process to continue. The ATP and NADPH are converted back into ADP and NADP+, which are then recycled back to the light-dependent reactions to be re-energized.
The Overall Equation
While the process is complex and involves many intermediate steps, the overall chemical reaction can be summarized in this simple equation:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
(Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light Energy → Glucose + Oxygen)
Why is Photosynthesis So Important?
Photosynthesis is not just a process for plants; it is the fundamental force that drives and sustains most ecosystems on Earth. Its importance can be broken down into three critical points:
Food for All Life
Photosynthesis is the foundation of almost all food chains on our planet. Plants and other photosynthetic organisms are known as **producers** because they create their own food. Herbivores consume these producers, and carnivores, in turn, consume herbivores. Without photosynthesis, the entire food web would collapse, as the primary source of energy would disappear.
Oxygen Production
As a crucial byproduct, photosynthesis releases vast amounts of oxygen into the atmosphere. This oxygen is vital for the respiration of animals, including humans, and is essential for most aerobic life forms to survive. Our very ability to breathe depends on this process.
Carbon Cycle Regulation
Plants act as a major **carbon sink**, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This helps regulate the Earth’s climate by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases and mitigating the greenhouse effect, which is a major environmental concern.
Photosynthesis Process Equation and Importance Full Concept
1. What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a biological process in green plants where they use sunlight to make food from carbon dioxide and water. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants manufacture glucose (food) using carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight in the presence of chlorophyll.
2. Why is Photosynthesis Important?
- Produces oxygen necessary for human and animal life
- Maintains carbon dioxide-oxygen balance in the atmosphere
- Basis of the food chain
- Removes CO₂, reducing greenhouse effect
Without photosynthesis, there would be no life on Earth.
3. Where Does Photosynthesis Occur?
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts found in green parts of plants like:
- Leaves (main site)
- Green stems
- Sepals and sometimes in petioles
4. Raw Materials Needed
Plants require:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) – from air, through stomata
- Water (H₂O) – absorbed by roots from the soil
- Sunlight – source of energy
- Chlorophyll – the green pigment
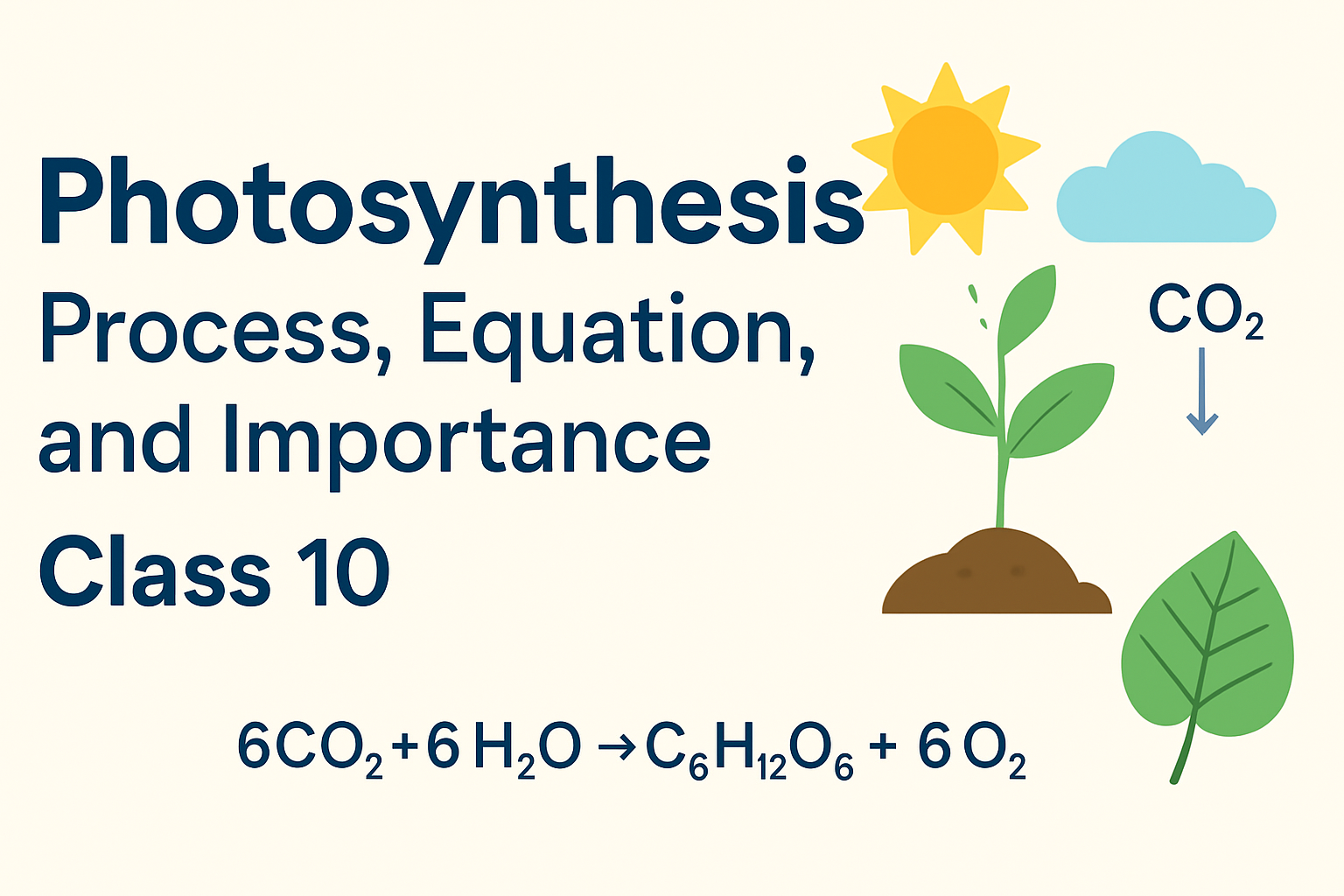
5. Photosynthesis Chemical Equation
Balanced chemical equation:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
(in presence of sunlight and chlorophyll)
6. Steps Involved in Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis happens in two main stages:
A. Light Reaction (Occurs in the grana)
- Requires light
- Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen (photolysis)
- ATP and NADPH are formed
B. Dark Reaction / Calvin Cycle (Occurs in stroma)
- Does not need direct light
- Uses ATP + NADPH + CO₂ to form glucose
7. Structure of Chloroplast – Photosynthesis Site
The chloroplast is the organelle where photosynthesis occurs.
Parts:
- Outer and inner membrane
- Thylakoid (contains chlorophyll)
- Grana (stacks of thylakoid)
- Stroma (fluid-filled)
8. Light vs Dark Reactions – In Detail
| Feature | Light Reaction | Dark Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Grana | Stroma |
| Requires Light? | Yes | No |
| Input | H₂O, sunlight | CO₂, ATP, NADPH |
| Output | O₂, ATP, NADPH | Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) |
| Process | Photolysis | Carbon Fixation |
9. Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Several external and internal factors affect photosynthesis rate:
- 🌞 Light intensity
- 🌡️ Temperature
- 🌫️ CO₂ concentration
- 🌊 Water availability
- 🌿 Chlorophyll concentration
10. Types of Photosynthesis
- C3 Photosynthesis
- Common in all plants like wheat and rice
- First stable compound is a 3-carbon molecule
- C4 Photosynthesis
- Found in maize, sugarcane
- Adapted for hot climates
- CAM Photosynthesis
- Found in desert plants like cactus
- Saves water by opening stomata at night
11. Photosynthesis vs Respiration
| Feature | Photosynthesis | Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Happens in | Green parts | All living cells |
| Gas Used | CO₂ | O₂ |
| Gas Released | O₂ | CO₂ |
| Energy | Consumes light energy | Releases ATP |
| Time | Day only | 24 hours |
12. Experiments to Show Photosynthesis
A. Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis
B. Light is essential
C. CO₂ is necessary
13. Photosynthesis Diagram (Labelled)
Include the standard Class 10 labelled diagram with:
- Leaf cross-section
- Sunlight, CO₂ arrows
- Water from root
- Oxygen released
- Glucose produced
14. Common Misconceptions
- Photosynthesis happens only in sunlight – ❌
- Only leaves do photosynthesis – ❌ (some stems can too)
- Plants don’t respire – ❌ (they do!)
15. Practice Questions for Class 10
- What is the balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis?
- Differentiate between light and dark reactions.
- Why is chlorophyll necessary for photosynthesis?
- How does carbon dioxide enter the leaves?
- What are the raw materials for photosynthesis?
16. NCERT Exercise Questions – Photosynthesis Answers
Q. What are the end products of photosynthesis?
Ans. Glucose and oxygen are the end products.
Q. How do plants obtain carbon dioxide?
Ans. From the air, through tiny pores called stomata.
Q. Explain the process of photosynthesis in detail.
Ans. In presence of sunlight and chlorophyll, plants take in carbon dioxide and water and convert them into glucose. Oxygen is released as a by-product.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is one of the most crucial life processes. It not only helps plants to survive but also supports life on Earth. From a Class 10 perspective, understanding photosynthesis helps you master 20–25% of the Life Processes chapter, which frequently appears in board exams.
Credit: Some scientific references in this post are inspired by trusted sources like Britannica – Photosynthesis Process Equation and Importance.