Reproduction in Animals: Concept (Grade 10/NCERT/Oxford)
Reproduction in Animals is one of the most essential life processes in living organisms. It allows animals to produce offspring and continue their species from one generation to the next.
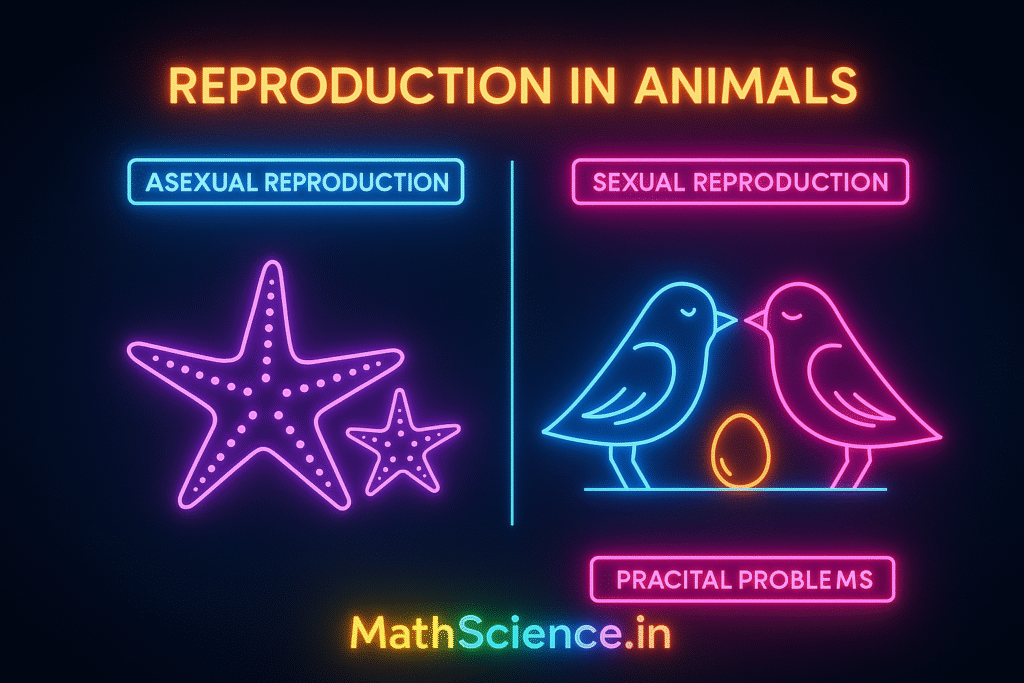
Reproduction in Animals 🧬
A Comprehensive Guide for Students
The Cycle of Life: A Fundamental Process
Reproduction is a fundamental biological process that ensures the continuation of a species. It is the process by which living organisms produce offspring, similar to themselves. The primary goal of reproduction is not just to create more individuals, but to pass on genetic information from one generation to the next. This guide will explore the two main modes of reproduction in the animal kingdom: **asexual** and **sexual**.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction that involves a **single parent** producing offspring. The key characteristic of this method is that the offspring are genetically identical to the parent. This happens because there is no fusion of gametes (sperm and egg) and no mixing of genetic material. Asexual reproduction is a rapid process, allowing organisms to multiply quickly in favorable conditions. It is most common in simpler, unicellular organisms.
1. Budding
In budding, a small, bulb-like projection, or “bud,” develops on the parent’s body. This bud is formed by the mitotic division of cells. As it grows, it eventually develops into a miniature version of the parent. Once the bud is fully mature, it detaches from the parent’s body and becomes a new, independent individual. The parent organism continues to live and can produce more buds.
Example: Hydra, Yeast
2. Binary Fission
Binary fission is a simple and direct form of asexual reproduction found primarily in unicellular organisms. The process begins with the replication of the organism’s genetic material (DNA). The parent cell then divides its cytoplasm and nucleus into two equal halves. This results in the formation of two new, genetically identical daughter cells. It’s essentially a form of cell division that results in new organisms.
Example: Amoeba, Paramecium
3. Fragmentation and Regeneration
In fragmentation, the parent organism’s body breaks into multiple fragments, often due to physical damage or environmental factors. Each fragment is then capable of developing into a new, complete organism. This process is often linked with **regeneration**, which is the ability of an organism to regrow lost body parts.
Example: Starfish, Sponges, Planaria
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes (sperm and egg), a process known as **fertilization**. This fusion creates a new cell called a **zygote**, which develops into an offspring. Because the offspring receives genetic material from two different parents, it is genetically different from both, leading to **genetic variation**. This variation is the driving force behind evolution, as it helps species adapt to changing environments.
1. Fertilization
Fertilization is the pivotal event of sexual reproduction. It is the process of fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg). This fusion restores the diploid number of chromosomes and forms a new cell called a zygote.
- Internal Fertilization: The fusion of gametes occurs inside the body of the female parent. This method is common in terrestrial animals, as it protects the gametes and zygote from dehydration.
Example: Humans, dogs, cows, birds
- External Fertilization: The fusion of gametes occurs outside the female’s body, typically in a watery environment. This method is common in aquatic animals, which release their gametes into the water.
Example: Fish, frogs, starfish
2. Development of Zygote
After fertilization, the zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions to form an embryo. The location of this development and the method of birth classify animals into two distinct categories:
- Oviparous Animals (Egg-Laying): In these animals, the embryo develops inside a hard-shelled egg that is laid outside the female’s body. The embryo receives nourishment from the yolk within the egg. The parents may incubate the eggs to provide warmth and protection.
Example: Hens, frogs, lizards, most fish
- Viviparous Animals (Live-Bearing): In these animals, the embryo develops inside the female’s body and is nourished through a placenta. After a period of development, the female gives birth to live young. This method offers greater protection and a higher survival rate for the offspring.
Example: Humans, dogs, cats, whales
3. Metamorphosis (in some animals)
Some animals, particularly amphibians and insects, undergo a dramatic biological process called metamorphosis. This is a transformation from a juvenile form (like a larva or nymph) to an adult form. The body structure, diet, and habitat can change completely during this process.
Example: A tadpole (larva) develops into a frog (adult); a caterpillar (larva) transforms into a butterfly (adult).
Without reproduction, life would not sustain on Earth. In Class 10 Science, understanding the concept of reproduction in animals helps us explore how new individuals are formed, how traits are passed on, and why variation is important.

Introduction: Reproduction in Animals – A Complete Guide for Class 10
Score Full Marks in Class 10 Science by mastering Reproduction in Animals with concept clarity, real-life examples, and recommended study resources.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Reproduction
- Importance of Reproduction
- Modes of Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction in Animals
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Male Reproductive System
- Female Reproductive System
- Fertilisation and its Types
- Development of Embryo
- Viviparous vs Oviparous Animals
- Young Ones to Adults
- Metamorphosis in Animals
- Cloning
- Summary Points
- Practice Questions
- NCERT Back Exercises Solved
- Extra Reference Resources [Affiliate links]
- Final Tips to Score 100/100
1. Introduction to Reproduction
Reproduction is the biological process by which organisms produce offspring, ensuring the continuity of species. This is a crucial life process just like respiration and nutrition.
Every species, whether a unicellular amoeba or a complex human, reproduces to maintain its population.
2. Importance of Reproduction
- Prevents extinction of species
- Helps transfer genetic information
- Enables evolution through genetic variation
Without reproduction, no living being would survive beyond its lifespan.
3. Modes of Reproduction
There are two main types of reproduction in animals:
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
4. Asexual Reproduction in Animals
In asexual reproduction, a single parent is involved. No gametes are required.
Examples:
- Binary Fission: Seen in Amoeba, Paramecium
- Budding: Hydra reproduces by developing buds on its body
- Fragmentation: Planaria
No variation is seen here; offspring are genetically identical.
5. Sexual Reproduction in Animals
Sexual reproduction involves:
- Male and female gametes (sperm and ovum)
- Fusion of gametes to form a zygote
- Development of embryo → baby
This method ensures genetic variation, which is important for evolution and adaptability.
6. Male Reproductive System (Class 10 Focus)
Main parts include:
- Testes – Produce sperm
- Sperm duct/vas deferens
- Penis – Delivers sperm
Each sperm has a head (nucleus), midpiece (energy), and tail (movement).
7. Female Reproductive System
Key organs:
- Ovaries – Produce ova (eggs)
- Oviduct (Fallopian Tube) – Fertilisation site
- Uterus – Embryo develops here
- Vagina – Birth canal
Every month, one ovum is released by the ovary (ovulation).
8. Fertilisation and Its Types
Fertilisation: The fusion of male and female gametes.
Types:
- Internal fertilisation – Inside female’s body (e.g., humans, dogs)
- External fertilisation – Outside body (e.g., frogs, fish)
🧪 Use this Fertilisation Simulation Chart –
9. Zygote Formation & Embryo Development
- After fertilisation, zygote forms
- Zygote divides → Embryo
- Embryo attaches to uterus and grows into foetus
🍼 9 months later, birth takes place in viviparous animals.
10. Viviparous vs Oviparous Animals
| Category | Viviparous | Oviparous |
|---|---|---|
| Egg presence | No (internal dev.) | Yes (external) |
| Example | Human, Cat | Frog, Hen |
| Survival rate | Higher | Lower |
11. From Young Ones to Adults
- In mammals, young ones resemble adults
- In insects/frogs, major transformation (metamorphosis) takes place
12. Metamorphosis in Animals
Definition: A drastic change in body form during development.
Examples:
- Frog: Egg → Tadpole → Frog
- Butterfly: Egg → Caterpillar → Pupa → Butterfly
13. What is Cloning?
Cloning is the process of creating genetically identical organisms.
Example: Dolly the Sheep – The first cloned animal
Recommended: “Cloning Explained for Students” booklet or model
14. Summary Points to Remember
- Reproduction ensures continuity of life
- Two types: asexual and sexual
- Internal and external fertilisation
- Human beings reproduce sexually
- Zygote → Embryo → Foetus → Baby
- Metamorphosis is seen in frogs/insects
- Cloning is artificial reproduction
15. Practice Questions (Class 10 Style)
- What is reproduction? Explain its significance.
- Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction.
- Draw the male and female reproductive systems.
- What is fertilisation? List its types.
- Define metamorphosis with examples.
18. Final Tips to Score 100/100 in Reproduction in Animals
- Revise all diagrams multiple times
- Practice both label-based and reasoning questions
- Use models and charts for visual learning
- Solve previous year CBSE papers
- Don’t skip the NCERT in-text questions
Smart Techniques to Boost Science Study Habits include:
- Daily revision
- Using visual aids
- Practice through MCQs and worksheets
- Mock tests
- Time-bound practice
✅ Try these Smart Techniques to Boost Science Study Habits and get full marks!
Also Visit:
- Class 10 Science Chapter List
- Life Processes Class 10
- Smart Study Plan for Class 10 Science
- Heredity and Evolution Q&A
📘 Math & Science Solutions by Class
🔹 Class 9
🔹 Class 8
🔹 Class 7
🔹 Class 6
🔹 Class 12
🔹 Class 11
- Class 11 Math Solutions
- Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Class 11 Biology Solutions
Class-wise Solutions
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
Subject-wise Solutions
- Class 11 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 12 Physics – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 12 Chemistry – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Biology – NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Math – NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 Science – NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 7 Science – Oxford Solutions
- Class 6 Science – Oxford Solutions